Ppt on monsoon
- 2. What is monsoon âĒ Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea.
- 3. Typeof monsoon ïSummer monsoon âĒ Summer Monsoon. The summer monsoon is associated with heavy rainfall. It usually happens between April and September. As winter ends, warm, moist air from the southwest Indian Ocean blows toward countries like India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and Myanmar.
- 4. ïWinter monsoon âĒ Winter monsoons have a dominant easterly component and a strong tendency to diverge, subside, and cause drought. Both are the result of differences in annual temperature trends over land and sea.
- 5. ïDry monsoon âĒ a seasonal prevailing wind in the region of South and SE Asia, blowing from the south-west between May and September and bringing rain (the wet monsoon ), or from the north-east between October and April (the dry monsoon ).
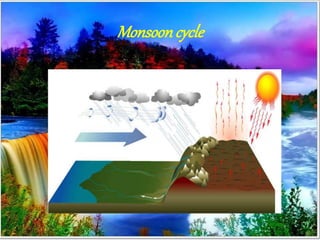
- 6. Monsooncycle
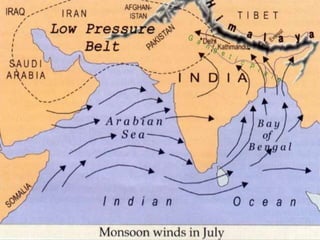
- 7. south west monsoon âĒ South West monsoon is the rain bearing seasonal winds that flow from Arabian Sea to the main land of India from the South-West direction. They start to cross India around May, and as per Indian Meteorological Department, the official monsoon season is between June to September.
- 8. Different heatingand cooling of landand water