PPT_Module 3) Type of Companies_Part I.pdf
0 likes4 views
A company is a legal entity created by law that allows a group of people to come together to achieve common goals and share risks. It has a separate legal identity from its owners and can exist indefinitely over time. Some key characteristics of companies include limited liability for owners, transferable shares, and a common seal. There are several types of companies including private companies which are subject to restrictions on shareholding and transfers, public companies which can raise capital from the public, government companies which are majority owned by the government, foreign companies operating in India, and holding companies which have controlling ownership of other subsidiary companies.
1 of 13
Download to read offline









Ad
Recommended
Companies Act 2013 presentation of it .pdf
Companies Act 2013 presentation of it .pdfvallamdas007
?
This document provides an overview of companies under the Companies Act 2013 in India. It defines a company and outlines key features such as being an incorporated association, having separate legal identity, limited liability for members, transferable shares, perpetual existence, and use of a common seal. It also classifies companies based on liability, access to capital, shareholding, control, and number of members. The important stages in company formation are outlined as promotion, registration, obtaining a certificate of incorporation, and commencing business.Company formation accounts -xi-Utsab Shrestha
Company formation accounts -xi-Utsab ShresthaUtsab Shrestha
?
The document outlines the formation and characteristics of companies, emphasizing their legal status as artificial persons with distinct rights and responsibilities. It defines various types of companies based on incorporation, liability, and number of members, detailing the differences between private and public companies. Additionally, it explains essential documents such as the Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA), along with the role of company promoters.Business Ideas, project identification, project formulation.pptx
Business Ideas, project identification, project formulation.pptxMegharajSagar1
?
Business Ideas, Project Identification and Formulation: Forms of Business
Ownership, Issues in Selecting Forms of Ownership, Environmental Analysis,
Identifying Problems and Opportunities, Defining Business Idea, Planning
Business Process; Project Management: Concept, Features, Classification of
Projects, Issues in Project Management; Project Identification; Project
Formulation; Project Design and Network Analysis; Project Evaluation; Project
Appraisal; Project Report Preparation; Specimen of a Project Report. (Recent
Developments) indian Company law
indian Company lawPANKAJ PANDEY
?
The document discusses Indian company law and defines key terms related to companies. It describes a company as a voluntary association formed for a common purpose with capital divided into shares. Key features of a registered company include being a separate legal entity, having perpetual succession, and members having limited liability. The document outlines the different types of companies based on incorporation, member liability, ownership, and more. It also summarizes the process of company formation including promotion, incorporation, capital raising, and business commencement.Company Law.pptx
Company Law.pptxKrishi49
?
This document defines a company and outlines its key characteristics. A company is a separate legal entity created by law that has perpetual succession, a common seal, and exists separately from its members. It has limited liability for its members and transferable shares. The document then discusses the different types of companies based on incorporation, liability, number of members, control, ownership, and other factors. It provides examples and compares private and public companies.Chapter_2. Structure of organization and its explanation
Chapter_2. Structure of organization and its explanationalishazaibmaham
?
The document outlines key concepts related to the structure and legal forms of organizations, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs), and emphasizes the importance of legal existence and organizational governance. It discusses the roles of directors, the structure of companies, functional units of organizations, and different management roles such as project management and production management. Additionally, it highlights motivation factors, performance appraisal processes, and the potential risks of sub-optimization within organizations.Company law
Company lawsugirdhanelson
?
This document provides an overview of company law and secretarial practice in India. It defines a company and outlines its key characteristics such as separate legal identity, limited liability, transferable shares, and perpetual existence. It then classifies companies based on liability, members, control/holding, and other categories. The document also discusses company promotion, registration procedures, memorandum and articles of association, and the differences between private and public limited companies.Unit 1.pdf
Unit 1.pdfMohitSoni99772
?
The document provides an introduction to companies under Indian law. It defines a company and outlines its key features such as being an artificial legal person, having perpetual succession, and members having limited liability. It also classifies companies by mode of incorporation (chartered, statutory, registered) and by number of members (public, private, one person). The memorandum of association and articles of association are discussed as the primary legal documents that establish a company. The memorandum includes clauses about the company's name, objectives, capital, and liability, while the articles govern its internal rules and regulations.Lecture-2.pptx Free Preparation for professional practice of CS
Lecture-2.pptx Free Preparation for professional practice of CSshahxadrai92
?
The document discusses various legal forms of organizations including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies, each with distinct characteristics and implications for ownership and liability. It also outlines the structure and governance of organizations, emphasizing centralization versus decentralization, the importance of quality management, and motivation strategies. Additionally, it highlights performance appraisal methods and the necessity of setting clear objectives between managers and subordinates.The Structure of Organization and the omplete
The Structure of Organization and the ompleteg3za9rma6
?
The document outlines the structures and legal forms of organizations, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. It explains the essential characteristics of each entity type, such as ownership, liability, and governance, highlighting the importance of constitutions and the roles of directors and company secretaries. Furthermore, it emphasizes corporate governance as the relationship between stakeholders and management within companies.Companies Act, 2013
Companies Act, 2013Nishant Kumar
?
The document discusses the concept of a company. It defines a company as a legal entity formed by individuals to operate a business. It then discusses key characteristics of companies like separate legal entity status, limited liability, perpetual succession, and common seals. It also discusses the concept of lifting the corporate veil in situations where a company's legal personality is misused. Finally, it briefly outlines different types of companies based on mode of incorporation, ownership, control, nationality, and number of members.LBE 4.1.pptx
LBE 4.1.pptxnirajchaudhari27
?
The document discusses companies under Indian law. It defines a company as an incorporated entity distinct from its members. It describes key characteristics of companies like separate legal personality, limited liability, transferable shares, and perpetual existence. It outlines different types of companies based on incorporation, liability, members, control, and listing status. Finally, it compares public and private companies on aspects like minimum members, directors, share transfer rules, financial disclosure requirements, and more.Introduction-to-Companies in company law
Introduction-to-Companies in company lawDR.DHIVYA S
?
The document provides an overview of companies, outlining their definitions, characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as the process for formation and incorporation. It emphasizes the legal entity status of companies, limited liability for owners, and the continuity of existence regardless of ownership changes. Additionally, it discusses the types of companies, such as private and public, and the procedures for converting a private company into a public one through an initial public offering (IPO).the structure of organization to make your growth
the structure of organization to make your growthwahabbaloch1
?
The document outlines the structures and legal forms of organizations, distinguishing between sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations, along with their individual characteristics and responsibilities. It emphasizes the significance of a company's constitution, including the memorandum and articles of association, which govern its operations and internal affairs. Additionally, it discusses the roles of directors and company secretaries, disclosure requirements, and the concept of corporate governance.Professional Practices Week2.pptx
Professional Practices Week2.pptxTechBasti
?
This document discusses different types of organizations and their legal structures. It covers sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and different types of companies. It describes key aspects of companies including their constitution, directors, disclosure requirements, and corporate governance. Specifically, it notes that companies have a memorandum of association that controls external relations and articles of association that govern internal affairs. It also outlines the roles and responsibilities of directors and company secretaries.Business Law
Business LawCochin University
?
The document provides an overview of types of companies and their classifications according to the Companies Act of 1956 in India. It defines a company, outlines its main features, and explains different categories such as statutory, registered, private, and public companies, along with their respective characteristics and requirements for incorporation. Additionally, it covers aspects like limited liability partnerships and the necessary steps for registering a private limited company.Company act,2013
Company act,2013HARSHIT GARG
?
The document provides definitions and key information about companies under Indian law. It defines a company as an association of persons united for a common objective and an artificial person created by law. It then outlines some key features of companies including that they are artificial legal persons, have separate legal entities, use a common seal, have perpetual succession, provide limited liability, and allow transferability of shares. The document also discusses different types of companies based on liabilities, members, control, and other characteristics. It provides details on the incorporation process for a company including required documents like the memorandum and articles of association.Unit 4 indian_companies_act_2013
Unit 4 indian_companies_act_2013Ashish Awasthi
?
The Indian Companies Act 2013 establishes the legal framework for companies in India, introducing concepts such as one-person companies and mandatory corporate social responsibility. It defines a company as a legal entity with limited liability, and outlines various types and classifications of companies, along with requirements for incorporation and documentation. Additionally, it details the roles and responsibilities of company directors, the processes for meetings, and winding up procedures.Unit 4 corporations
Unit 4 corporationskimguy
?
A corporation is a business owned by shareholders and authorized by the state to act as a single entity. It has a board of directors elected by shareholders to oversee officers who manage daily operations. Shareholders can trade shares, vote on matters, receive dividends, and claim assets if the company dissolves. Corporations can be publicly traded on stock exchanges or privately held. Other business structures include limited liability companies, joint ventures, nonprofits, cooperatives, and government-supported quasi-public corporations.Unit 4 corporations
Unit 4 corporationskimguy
?
A corporation is a business owned by shareholders and authorized by the state to act as a single entity. It has a board of directors elected by shareholders to oversee officers who manage daily operations. Shareholders can trade shares, vote on matters, receive dividends, and claim assets if the company dissolves. Corporations can be publicly traded or closely held. Other business structures include limited liability companies, joint ventures, nonprofits, cooperatives, and quasi-public corporations.Company law
Company lawJithin Zcs
?
This document provides an overview of company law in India based on the Companies Act of 1956. It defines a company as a voluntary association formed for business purposes that has a distinct name and limited liability. It discusses the types of companies (public, private, unlimited), classifications based on ownership (government, non-government, foreign), and key concepts like corporate personality, perpetual succession, and holding/subsidiary relationships. The document also summarizes the formation process for companies and objectives of the Companies Act.Company's Act 1956
Company's Act 1956Vipul Jain
?
The document provides an overview of company law in India according to the Companies Act of 1956. It defines a company and outlines its key characteristics such as separate legal entity status, transferable shares, and limited liability. It also categorizes companies based on their incorporation (chartered, statutory, registered), liability (unlimited, limited by guarantee, limited), nationality (national, multinational), and public interest (private, public, government). The types of companies are further described and distinguished. The document also discusses holding companies, subsidiary companies, one-man companies, and illegal associations.P.Pratices week 4.pptx
P.Pratices week 4.pptxIshratFatima288747
?
This document outlines different types of business organizations and their legal structures. It discusses sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and different types of companies. It describes key aspects of companies like their constitution, directors, disclosure requirements, and corporate governance. The legal forms of organization each have different ownership structures and liabilities. Companies must have memorandums and articles of association, and are governed by boards of directors.Introduction to Indian Companies Act-2013
Introduction to Indian Companies Act-2013Rama Krishna Angirekula
?
The document outlines the different types of companies under the Companies Act of 2013, including classifications based on membership (e.g., one-person, private, and public companies), size (micro, small, medium), liability (limited by shares, guarantee, and unlimited), and control (holding and subsidiary companies). It also details the process for company formation, including promotion, registration, and incorporation stages, as well as important documents such as the Memorandum of Association and types of meetings like annual general and extraordinary meetings. Additionally, the document explains the doctrines of ultra vires and constructive notice, emphasizing their legal implications for companies.Company Law: Defination , Types , Incorporation, Chages from Pvt to Public.pptx
Company Law: Defination , Types , Incorporation, Chages from Pvt to Public.pptxDipankar Dutta
?
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Indian Companies Act, outlining the evolution and significance of companies, characteristics such as limited liability, separate legal entity, and perpetual succession. It details various types of companies, including private, public, and government companies, along with the processes of promotion, incorporation, and the roles and responsibilities of promoters. Additionally, it discusses the legal implications and liabilities associated with company formation and operation, emphasizing the regulatory framework established under the Companies Act 2013.Lecture-3--of professional practice.pptx
Lecture-3--of professional practice.pptxhaaamin01
?
This document provides an overview of organizational structure and types of organizations. It discusses the key legal forms of organizations including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and companies. It also describes functional units within organizations, options for geographical and centralized/decentralized structure, and management roles. The lecture covers topics like the memorandum and articles of association that govern companies.Unit 3 for business management law.pptx
Unit 3 for business management law.pptxrameshnirej
?
This document provides an overview of company law as per the Companies Act of 1956, detailing the definition, characteristics, types, and formation of companies. Key features include the separate legal entity status, perpetual succession, limited liability of members, and the process of incorporation. It classifies companies based on incorporation, liability, ownership, and membership, also explaining the memorandum of association and the requirements for commencing business.最新版美国犹他大学毕业证(U of U毕业证书)原版定制
最新版美国犹他大学毕业证(U of U毕业证书)原版定制Taqyea
?
2025原版犹他大学毕业证书pdf电子版【q薇1954292140】美国毕业证办理U of U犹他大学毕业证书多少钱?【q薇1954292140】海外各大学Diploma版本,因为疫情学校推迟发放证书、证书原件丢失补办、没有正常毕业未能认证学历面临就业提供解决办法。当遭遇挂科、旷课导致无法修满学分,或者直接被学校退学,最后无法毕业拿不到毕业证。此时的你一定手足无措,因为留学一场,没有获得毕业证以及学历证明肯定是无法给自己和父母一个交代的。
【复刻犹他大学成绩单信封,Buy The University of Utah Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
犹他大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括犹他大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(原版纸质、底色、纹路)我们工厂拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有成品以及工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】犹他大学学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理美国成绩单犹他大学毕业证【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证最新版意大利卡梅里诺大学毕业证(鲍狈滨颁础惭毕业证书)原版定制
最新版意大利卡梅里诺大学毕业证(鲍狈滨颁础惭毕业证书)原版定制taqyea
?
2025原版卡梅里诺大学毕业证书pdf电子版【q薇1954292140】意大利毕业证办理UNICAM卡梅里诺大学毕业证书多少钱?【q薇1954292140】海外各大学Diploma版本,因为疫情学校推迟发放证书、证书原件丢失补办、没有正常毕业未能认证学历面临就业提供解决办法。当遭遇挂科、旷课导致无法修满学分,或者直接被学校退学,最后无法毕业拿不到毕业证。此时的你一定手足无措,因为留学一场,没有获得毕业证以及学历证明肯定是无法给自己和父母一个交代的。
【复刻卡梅里诺大学成绩单信封,Buy Università degli Studi di CAMERINO Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
卡梅里诺大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括卡梅里诺大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(原版纸质、底色、纹路)我们工厂拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有成品以及工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】卡梅里诺大学学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理意大利成绩单卡梅里诺大学毕业证【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证More Related Content
Similar to PPT_Module 3) Type of Companies_Part I.pdf (20)
Unit 1.pdf
Unit 1.pdfMohitSoni99772
?
The document provides an introduction to companies under Indian law. It defines a company and outlines its key features such as being an artificial legal person, having perpetual succession, and members having limited liability. It also classifies companies by mode of incorporation (chartered, statutory, registered) and by number of members (public, private, one person). The memorandum of association and articles of association are discussed as the primary legal documents that establish a company. The memorandum includes clauses about the company's name, objectives, capital, and liability, while the articles govern its internal rules and regulations.Lecture-2.pptx Free Preparation for professional practice of CS
Lecture-2.pptx Free Preparation for professional practice of CSshahxadrai92
?
The document discusses various legal forms of organizations including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies, each with distinct characteristics and implications for ownership and liability. It also outlines the structure and governance of organizations, emphasizing centralization versus decentralization, the importance of quality management, and motivation strategies. Additionally, it highlights performance appraisal methods and the necessity of setting clear objectives between managers and subordinates.The Structure of Organization and the omplete
The Structure of Organization and the ompleteg3za9rma6
?
The document outlines the structures and legal forms of organizations, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. It explains the essential characteristics of each entity type, such as ownership, liability, and governance, highlighting the importance of constitutions and the roles of directors and company secretaries. Furthermore, it emphasizes corporate governance as the relationship between stakeholders and management within companies.Companies Act, 2013
Companies Act, 2013Nishant Kumar
?
The document discusses the concept of a company. It defines a company as a legal entity formed by individuals to operate a business. It then discusses key characteristics of companies like separate legal entity status, limited liability, perpetual succession, and common seals. It also discusses the concept of lifting the corporate veil in situations where a company's legal personality is misused. Finally, it briefly outlines different types of companies based on mode of incorporation, ownership, control, nationality, and number of members.LBE 4.1.pptx
LBE 4.1.pptxnirajchaudhari27
?
The document discusses companies under Indian law. It defines a company as an incorporated entity distinct from its members. It describes key characteristics of companies like separate legal personality, limited liability, transferable shares, and perpetual existence. It outlines different types of companies based on incorporation, liability, members, control, and listing status. Finally, it compares public and private companies on aspects like minimum members, directors, share transfer rules, financial disclosure requirements, and more.Introduction-to-Companies in company law
Introduction-to-Companies in company lawDR.DHIVYA S
?
The document provides an overview of companies, outlining their definitions, characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as the process for formation and incorporation. It emphasizes the legal entity status of companies, limited liability for owners, and the continuity of existence regardless of ownership changes. Additionally, it discusses the types of companies, such as private and public, and the procedures for converting a private company into a public one through an initial public offering (IPO).the structure of organization to make your growth
the structure of organization to make your growthwahabbaloch1
?
The document outlines the structures and legal forms of organizations, distinguishing between sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations, along with their individual characteristics and responsibilities. It emphasizes the significance of a company's constitution, including the memorandum and articles of association, which govern its operations and internal affairs. Additionally, it discusses the roles of directors and company secretaries, disclosure requirements, and the concept of corporate governance.Professional Practices Week2.pptx
Professional Practices Week2.pptxTechBasti
?
This document discusses different types of organizations and their legal structures. It covers sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and different types of companies. It describes key aspects of companies including their constitution, directors, disclosure requirements, and corporate governance. Specifically, it notes that companies have a memorandum of association that controls external relations and articles of association that govern internal affairs. It also outlines the roles and responsibilities of directors and company secretaries.Business Law
Business LawCochin University
?
The document provides an overview of types of companies and their classifications according to the Companies Act of 1956 in India. It defines a company, outlines its main features, and explains different categories such as statutory, registered, private, and public companies, along with their respective characteristics and requirements for incorporation. Additionally, it covers aspects like limited liability partnerships and the necessary steps for registering a private limited company.Company act,2013
Company act,2013HARSHIT GARG
?
The document provides definitions and key information about companies under Indian law. It defines a company as an association of persons united for a common objective and an artificial person created by law. It then outlines some key features of companies including that they are artificial legal persons, have separate legal entities, use a common seal, have perpetual succession, provide limited liability, and allow transferability of shares. The document also discusses different types of companies based on liabilities, members, control, and other characteristics. It provides details on the incorporation process for a company including required documents like the memorandum and articles of association.Unit 4 indian_companies_act_2013
Unit 4 indian_companies_act_2013Ashish Awasthi
?
The Indian Companies Act 2013 establishes the legal framework for companies in India, introducing concepts such as one-person companies and mandatory corporate social responsibility. It defines a company as a legal entity with limited liability, and outlines various types and classifications of companies, along with requirements for incorporation and documentation. Additionally, it details the roles and responsibilities of company directors, the processes for meetings, and winding up procedures.Unit 4 corporations
Unit 4 corporationskimguy
?
A corporation is a business owned by shareholders and authorized by the state to act as a single entity. It has a board of directors elected by shareholders to oversee officers who manage daily operations. Shareholders can trade shares, vote on matters, receive dividends, and claim assets if the company dissolves. Corporations can be publicly traded on stock exchanges or privately held. Other business structures include limited liability companies, joint ventures, nonprofits, cooperatives, and government-supported quasi-public corporations.Unit 4 corporations
Unit 4 corporationskimguy
?
A corporation is a business owned by shareholders and authorized by the state to act as a single entity. It has a board of directors elected by shareholders to oversee officers who manage daily operations. Shareholders can trade shares, vote on matters, receive dividends, and claim assets if the company dissolves. Corporations can be publicly traded or closely held. Other business structures include limited liability companies, joint ventures, nonprofits, cooperatives, and quasi-public corporations.Company law
Company lawJithin Zcs
?
This document provides an overview of company law in India based on the Companies Act of 1956. It defines a company as a voluntary association formed for business purposes that has a distinct name and limited liability. It discusses the types of companies (public, private, unlimited), classifications based on ownership (government, non-government, foreign), and key concepts like corporate personality, perpetual succession, and holding/subsidiary relationships. The document also summarizes the formation process for companies and objectives of the Companies Act.Company's Act 1956
Company's Act 1956Vipul Jain
?
The document provides an overview of company law in India according to the Companies Act of 1956. It defines a company and outlines its key characteristics such as separate legal entity status, transferable shares, and limited liability. It also categorizes companies based on their incorporation (chartered, statutory, registered), liability (unlimited, limited by guarantee, limited), nationality (national, multinational), and public interest (private, public, government). The types of companies are further described and distinguished. The document also discusses holding companies, subsidiary companies, one-man companies, and illegal associations.P.Pratices week 4.pptx
P.Pratices week 4.pptxIshratFatima288747
?
This document outlines different types of business organizations and their legal structures. It discusses sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and different types of companies. It describes key aspects of companies like their constitution, directors, disclosure requirements, and corporate governance. The legal forms of organization each have different ownership structures and liabilities. Companies must have memorandums and articles of association, and are governed by boards of directors.Introduction to Indian Companies Act-2013
Introduction to Indian Companies Act-2013Rama Krishna Angirekula
?
The document outlines the different types of companies under the Companies Act of 2013, including classifications based on membership (e.g., one-person, private, and public companies), size (micro, small, medium), liability (limited by shares, guarantee, and unlimited), and control (holding and subsidiary companies). It also details the process for company formation, including promotion, registration, and incorporation stages, as well as important documents such as the Memorandum of Association and types of meetings like annual general and extraordinary meetings. Additionally, the document explains the doctrines of ultra vires and constructive notice, emphasizing their legal implications for companies.Company Law: Defination , Types , Incorporation, Chages from Pvt to Public.pptx
Company Law: Defination , Types , Incorporation, Chages from Pvt to Public.pptxDipankar Dutta
?
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Indian Companies Act, outlining the evolution and significance of companies, characteristics such as limited liability, separate legal entity, and perpetual succession. It details various types of companies, including private, public, and government companies, along with the processes of promotion, incorporation, and the roles and responsibilities of promoters. Additionally, it discusses the legal implications and liabilities associated with company formation and operation, emphasizing the regulatory framework established under the Companies Act 2013.Lecture-3--of professional practice.pptx
Lecture-3--of professional practice.pptxhaaamin01
?
This document provides an overview of organizational structure and types of organizations. It discusses the key legal forms of organizations including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and companies. It also describes functional units within organizations, options for geographical and centralized/decentralized structure, and management roles. The lecture covers topics like the memorandum and articles of association that govern companies.Unit 3 for business management law.pptx
Unit 3 for business management law.pptxrameshnirej
?
This document provides an overview of company law as per the Companies Act of 1956, detailing the definition, characteristics, types, and formation of companies. Key features include the separate legal entity status, perpetual succession, limited liability of members, and the process of incorporation. It classifies companies based on incorporation, liability, ownership, and membership, also explaining the memorandum of association and the requirements for commencing business.Recently uploaded (20)
最新版美国犹他大学毕业证(U of U毕业证书)原版定制
最新版美国犹他大学毕业证(U of U毕业证书)原版定制Taqyea
?
2025原版犹他大学毕业证书pdf电子版【q薇1954292140】美国毕业证办理U of U犹他大学毕业证书多少钱?【q薇1954292140】海外各大学Diploma版本,因为疫情学校推迟发放证书、证书原件丢失补办、没有正常毕业未能认证学历面临就业提供解决办法。当遭遇挂科、旷课导致无法修满学分,或者直接被学校退学,最后无法毕业拿不到毕业证。此时的你一定手足无措,因为留学一场,没有获得毕业证以及学历证明肯定是无法给自己和父母一个交代的。
【复刻犹他大学成绩单信封,Buy The University of Utah Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
犹他大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括犹他大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(原版纸质、底色、纹路)我们工厂拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有成品以及工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】犹他大学学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理美国成绩单犹他大学毕业证【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证最新版意大利卡梅里诺大学毕业证(鲍狈滨颁础惭毕业证书)原版定制
最新版意大利卡梅里诺大学毕业证(鲍狈滨颁础惭毕业证书)原版定制taqyea
?
2025原版卡梅里诺大学毕业证书pdf电子版【q薇1954292140】意大利毕业证办理UNICAM卡梅里诺大学毕业证书多少钱?【q薇1954292140】海外各大学Diploma版本,因为疫情学校推迟发放证书、证书原件丢失补办、没有正常毕业未能认证学历面临就业提供解决办法。当遭遇挂科、旷课导致无法修满学分,或者直接被学校退学,最后无法毕业拿不到毕业证。此时的你一定手足无措,因为留学一场,没有获得毕业证以及学历证明肯定是无法给自己和父母一个交代的。
【复刻卡梅里诺大学成绩单信封,Buy Università degli Studi di CAMERINO Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
卡梅里诺大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括卡梅里诺大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(原版纸质、底色、纹路)我们工厂拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有成品以及工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】卡梅里诺大学学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理意大利成绩单卡梅里诺大学毕业证【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证How Business Debt Collection Agencies Can Improve Cash Flow
How Business Debt Collection Agencies Can Improve Cash FlowWilliams Rush & Associates
?
Williams Rush & Associates is a trusted business debt collection agency, delivering professional, results-driven solutions. With a focus on ethical recovery, they help companies regain control of their finances while preserving valuable client relationships and improving overall cash flow.美国学位证(狈闯毕业证书)普林斯顿大学毕业证书如何办理
美国学位证(狈闯毕业证书)普林斯顿大学毕业证书如何办理 taqyed
?
NJ普林斯顿大学毕业证书多少钱【q薇1954292140】1:1原版普林斯顿大学毕业证+NJ成绩单【q薇1954292140】完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理普林斯顿大学毕业证|NJ成绩单【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证
三.材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问【微信:1954292140】毕业证购买指大学文凭购买,毕业证办理和文凭办理。学院文凭定制,学校原版文凭补办,扫描件文凭定做,100%文凭复刻。Mens Rea & Actus Reus in Criminal Law.pptx
Mens Rea & Actus Reus in Criminal Law.pptxBarrister Amna (A Levels Academy Islamabad)
?
The Concept of Mens Rea and Actus Reus in Criminal Law:
In criminal law, two basic elements must be present for a person to be found guilty of a crime: Mens Rea and Actus Reus. These are Latin terms where Actus Reus means “guilty act” and Mens Rea means “guilty mind.” Both are essential for most criminal offences. A crime is generally not complete unless a person commits a wrongful act (Actus Reus) with a wrongful intention (Mens Rea).
Actus Reus refers to the physical act of the crime. It is the external action or conduct that is prohibited by law, such as killing, stealing, or hurting someone. For example, if a person hits another person with a stick, the physical act of hitting is the Actus Reus. This act must be voluntary; if the person was forced or acted unconsciously, then it may not be considered a crime. Actus Reus can also include omissions. In some cases, not doing something can be considered a criminal act if the law says there was a duty to act. For example, a parent not feeding their child could be an omission that causes harm, and thus a criminal act.
Mens Rea, on the other hand, is about the mental state of the accused. It refers to the intention or knowledge of wrongdoing. In simple words, it asks the question: Did the person mean to do wrong? If yes, they had Mens Rea. There are different levels of Mens Rea. The most serious is intention, where the person wanted the outcome to happen. Then comes knowledge, where they knew their actions were illegal or harmful. Recklessness involves knowing a risk but choosing to ignore it, and negligence means failing to take reasonable care, which results in harm.
For a crime to be legally proven, the accused must have both Actus Reus and Mens Rea at the same time. For example, if someone plans to kill another person and then actually kills them, both the guilty mind and guilty act are present. But if a person accidentally harms someone without bad intention, the Mens Rea may be missing, and the case may not qualify as a serious crime like murder.
There are some exceptions. In certain minor offences called strict liability offences, Mens Rea is not required. Just doing the act is enough for punishment. These usually relate to traffic rules, public safety, or health regulations.
In conclusion, Mens Rea and Actus Reus are two key elements in criminal law. One is the action, and the other is the intention. Both are usually required to establish criminal responsibility. Without proving both, the accused cannot be fairly punished under the law. This combination ensures that people are only held guilty when they have both done something wrong and meant to do it.Hearing Court Kurchinski VS Kouskoutis.pdf
Hearing Court Kurchinski VS Kouskoutis.pdfalekurchinski
?
Highlight the transcript probate court system in Pinellas county. My experience as widow and mother of two young girls. I feel that Special Master has not been impartial. Agent attorney and successor trustee from the trust negotiation excessive compensation fees from the Trust Estate.
It feels like the Estate and Trust are being used to pay for ongoing court fights, and the people in charge Agent Attoney, Successor Trustee, Personal Representative, Special Master, Mediation and Guardian Ad Litem - they are making money while the case keeps going.
With respect and hope for justice,
Alessandra Kurchinski
Widow of Franklin Kurchinski
Mother of Jacqueline and Caroline.
Services Consultation FAQ Sheet for Kairos
Services Consultation FAQ Sheet for KairosKairos Capital Legal Advisors,LLC
?
The document outlines the services offered by Kairos, including an advance payment option for legal services through a third-party provider and a limited-time affordable subscription program. It addresses common FAQs regarding service charges, attorney availability, document review turnaround time, and payment plans. Clients are informed about the steps to initiate services, the necessity of upfront payments, and the conditions for payment plans.SILENT EMERGENCY OF CHILD LABOUR WORLD WIDE
SILENT EMERGENCY OF CHILD LABOUR WORLD WIDEaaphazratbal
?
“STOLEN CHILDHOODS":
Every pair of tiny hands that holds a tool instead of a toy… Holds the weight of a failed society.
Childhood is meant to be a garden of dreams—Filled with laughter, play, and innocent schemes.
Yet, across dusty roads and behind dim factory walls,Little hands tremble not with joy, but with burdened calls.Elliot Dear Attorney – Trusted Legal Advocate in Monsey, NY
Elliot Dear Attorney – Trusted Legal Advocate in Monsey, NYElliotDearAttorney
?
Elliot Dear is a respected attorney based in Monsey, New York, with over a decade of experience in civil litigation, family law, personal injury, and real estate matters. Known for his client-first approach, Elliot offers personalized case handling, clear legal strategies, and responsive support. He holds a strong presence in the community through pro bono work and legal outreach. Clients value his integrity, professionalism, and consistent results. Whether it's courtroom advocacy or consultation, Elliot delivers trusted legal representation with honesty, compassion, and skill—making him a reliable choice for individuals and businesses across New York.Court Hearing Kurchinski vs Kouskoutis.pdf
Court Hearing Kurchinski vs Kouskoutis.pdfVOLUNT?RIA CAUSA SOCIAL
?
I am Alessandra Kurchinski, the surviving spouse of Franklin Kurchinski and one of the beneficiaries of his Estate and Trust, along with my daughters, Jacqueline and Caroline. On October 26, 2023, I participated in a court hearing before Special Master Robert Persante regarding the trust and estate litigation involving attorney Michael Kouskoutis and my sister-in-law, Nancy Gorby, who was appointed as the Personal Representative and Successor Trustee.
This hearing, and everything leading up to it, has been one of the most emotionally and legally painful experiences of my life. I was simply trying to understand what happened to my husband's estate and make sure that our rights were respected. Instead, I was met with silence, avoidance, high legal bills, and a legal system that felt stacked against me.
I tried many times to communicate directly with Nancy. I even invited her to the bank with me to resolve things in person. She refused to come. I was told by Mr. Kouskoutis not to contact her directly, which meant every communication had to go through lawyers—raising legal costs unnecessarily. That was never what Franklin wanted.
Before we got married, Franklin and I signed a prenuptial agreement saying each of us would own 50% of everything. I never filed a lawsuit to undo the trust—I respected his estate plan—but I wanted the prenup to be followed. Instead, the court treated me like I was trying to invalidate the trust, which was not true. I just wanted the assets fairly divided according to our contract.
I asked for a reimbursement of family expenses. Instead of honoring that request, they filed a legal petition for a "family allowance" without my approval—just to bill more fees.
The legal team filed important documents like fee motions and billing logs the day before the hearing. I had no time to read or respond. I was representing myself and had no attorney. This has happened more than once. It felt like a tactic to keep me confused and unprepared.
Summary of What I Faced (2022–2025)
Nancy and her lawyer took my husband’s original wills from me and never returned them.
I filed multiple police reports about missing documents and financial mismanagement.
I was trespassed from the lawyer’s office after asking for my husband’s documents.
I was Baker Acted and humiliated in front of my daughters and neighbors.
While I was hospitalized, my home was entered without consent.
They filed civil litigation against me and my daughters using trust funds.
They filed excessive and unexplained legal fees and charged for every step.
They ignored the prenup, cut me off from information, and tried to isolate me.
I am a grieving widow, a mother, and a woman trying to protect what’s rightfully mine and my daughters’.
I only want justice, transparency, and for the Trust and Estate to follow what Franklin and I agreed on. I want this to end, so we can heal and move forward.Sanidul-sheikh-for-abdul-sheikh-June-4-1.pdf
Sanidul-sheikh-for-abdul-sheikh-June-4-1.pdfsabranghindi
?
Assam Government Gauhati High Court Detained PeopleFlat Fee vs. Hourly Billing: Comparison Tool for Law Firms
Flat Fee vs. Hourly Billing: Comparison Tool for Law FirmsAccurate Legal Billing
?
Flat Fee vs. Hourly Billing: Compare legal billing models to boost revenue, client trust & efficiency. Ideal guide for modern law firms.89th Legislative Session Debrief: Panel Discussion
89th Legislative Session Debrief: Panel Discussiontagdpa
?
This document provides an overview of the 89th Legislative Session, highlighting key outcomes and their implications for the water sector.Kathleen Campbell Davis - The Stages of Civil Litigation
Kathleen Campbell Davis - The Stages of Civil LitigationKathleen Campbell Davis
?
Civil litigation refers to a series of legal processes that seek to resolve disputes between individuals, organizations, and businesses. Unlike criminal litigation, which often involves the state and a private entity, civil litigation primarily involves private entities seeking redress or remedies for specific performance or financial compensation. It consists of stages, such as pre-filing and evidence gathering.Law Office of John A. Bloom - Law Center
Law Office of John A. Bloom - Law CenterLaw Office of John A. Bloom
?
The Law Office of John A. Bloom in Santa Rosa, CA, is headed by a Certified Specialist with over 40 years of experience in California Workers' Compensation Law. We provide reliable advocacy for injured workers, managing work injury claims and settlements with bilingual support in English and Spanish. If you're looking for an experienced work injury lawyer nearby, we are ready to defend your rights.Understanding Section 1061: Carried Interest Rules
Understanding Section 1061: Carried Interest RulesAlexander Apostolopoulos
?
Section 1061 of the Internal Revenue Code reshapes how investment profits are taxed, particularly for fund managers receiving carried interest.K Royal, JD, PhD for Top Cyber News MAGAZINE May 2025
K Royal, JD, PhD for Top Cyber News MAGAZINE May 2025Dr. Ludmila Morozova-Buss
?
The Lex Lumina of Privacy Law
Who claimed beauty, brains, and heart don't belong together with cybersecurity and law?
The Grace and the Law. The Charisma and the Leadership. The Privacy and the Influence. Meet the pageant queen who masters the world stage in law, cybersecurity, and pageants - currently holding the title of South Carolina Classic Universe Woman... Not just a title of beauty, but a symbol of brilliance.
In a world awash with data - where surveillance shadows every click and compliance guides every move - a new light has risen: the Lex Lumina, the luminous spirit of privacy law. She knows no borders yet shapes global governance. She is passionate, authentic and vibrant in the boardroom and the battlefields of public trust.
Her name? …K Royal, JD, PhD
She moves with the grace of justice - not cloaked in robes, but in clarity. Her presence is found in firm governance and the gentle nudge of ethical innovation. Her charisma is not loud – it is magnetic, drawing the best minds in law, policy, and purpose into her orbit.
In the May edition, we invite you to step into her presence and witness her story. Privacy is not a checkbox. It is a force. A protector of dignity. A strategic compass in an uncertain digital age. This month, you are not a spectator. You are the voice she defends. The future she empowers. The decision-maker she enlightens.
Step into the radiance of Lex Lumina. Experience the fusion of privacy, leadership, and law - like never before!
'Privacy is the Right. Data Privacy Law is how we Protect that Right in the Digital Age.’ ~ K Royal, JD, PhD
英国成绩单范本利物浦大学成绩单复刻鲍翱尝尝别迟迟别谤2025年新版
英国成绩单范本利物浦大学成绩单复刻鲍翱尝尝别迟迟别谤2025年新版taqyed
?
鉴于此,办理UOL大学毕业证利物浦大学毕业证书【q薇1954292140】留学一站式办理学历文凭直通车(利物浦大学毕业证UOL成绩单原版利物浦大学学位证假文凭)未能正常毕业?【q薇1954292140】办理利物浦大学毕业证成绩单/留信学历认证/学历文凭/使馆认证/留学回国人员证明/录取通知书/Offer/在读证明/成绩单/网上存档永久可查!
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
【办理利物浦大学成绩单Buy University of Liverpool Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
利物浦大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括利物浦大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!INDUSTRIAL DISPUTE AND LEGISLATION CONCERNING SETTLEMENT OF INDUSTRIAL DISPUT...
INDUSTRIAL DISPUTE AND LEGISLATION CONCERNING SETTLEMENT OF INDUSTRIAL DISPUT...apoorvexe
?
INDUSTRIAL DISPUTE AND LEGISLATION CONCERNING SETTLEMENT OF INDUSTRIAL DISPUTESAd
PPT_Module 3) Type of Companies_Part I.pdf
- 1. Amity Business School TOPIC: Type of Companies
- 2. Amity Business School Company ? A company is like a group of people who come together because they want to achieve something together. They put their money into it, and this money is divided into parts called "shares." The best part is that they are not responsible for all the company's debts; their responsibility is limited to the money they put in. ? Now, here's the interesting part: A company is not a real person like you or me. It's a kind of "imaginary person" created by the law. The law treats it like a person, even though it doesn't exist in the way we do. It's a legal concept. ? According to a law called the Companies Act from 1956, a company is defined as "a company formed and registered under this Act or an existing company as defined in section 3 (1) (ii)." In simple words, it's a company that's been created and registered according to this law or one that already existed when this law was made.
- 3. Amity Business School Main characteristics of a company ? Separate Legal Entity: A company is like a separate person in the eyes of the law. Imagine you have a favorite toy, and you give it a name. That toy is now a separate thing from you. Similarly, a company is its own thing, separate from the people who own it. If something goes wrong with the company, the owners aren't personally responsible. ? Perpetual Succession: A company can live forever, even if the people who started it pass away. Think of it like a school that never closes. It keeps running year after year, no matter what happens to the teachers or students.
- 4. Amity Business School ? Limited Liability: This means that if the company gets into financial trouble and owes money, the owners (shareholders) are only responsible for the amount they invested in the company. Let's say you buy a ticket for a movie. If the movie turns out to be bad, you're not responsible for the whole movie; you're only out the cost of the ticket. ? Separate Property: Just like you have your things (toys, books, etc.), a company has its own stuff, like money, buildings, and equipment. Even though people own the company, these things belong to the company itself.
- 5. Amity Business School ? Transferability of Shares: Shares in a company are like pieces of a big cake. If you have a piece of the cake (a share), you can sell it to someone else. It's like sharing your candy with a friend. ? Common Seal: A common seal is like a special stamp that a company uses to make important documents official. Imagine you have a stamp that says, "Approved." When you stamp a paper with it, it shows that the company agrees with what's written on the paper.
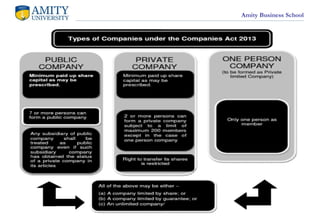
- 6. Amity Business School Types of Company ? A private company is a kind of company that has some special rules. To be a private company: ? It needs to have at least 2 people who own and run it. So, you can't start a private company all by yourself; you need at least one more person. ? It can't have more than 50 people who own it. But, there's a catch: if some of those people work for the company or used to work for it and still want to be part of it, they don't count toward this 50-people limit. ? It has to keep its shares within the company. This means that if you have shares in a private company, you can't just sell them to anyone you want. You need permission from the company to do that. ?
- 7. Amity Business School ? It can't ask the public for money. Unlike some big companies that ask lots of people to buy their shares or lend them money, a private company can only get money from its own members (the people who own it), the directors, or their relatives. ? It needs to put "private limited" in its name. When you see a company name with "private limited" at the end, you know it's a private company. ? So, to sum it up, a private company is a bit like a small, close-knit group of people running a business together, and it has some special rules to follow.
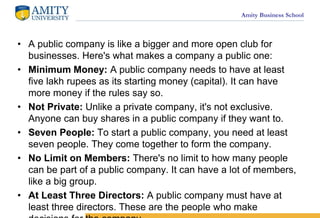
- 8. Amity Business School ? A public company is like a bigger and more open club for businesses. Here's what makes a company a public one: ? Minimum Money: A public company needs to have at least five lakh rupees as its starting money (capital). It can have more money if the rules say so. ? Not Private: Unlike a private company, it's not exclusive. Anyone can buy shares in a public company if they want to. ? Seven People: To start a public company, you need at least seven people. They come together to form the company. ? No Limit on Members: There's no limit to how many people can be part of a public company. It can have a lot of members, like a big group. ? At Least Three Directors: A public company must have at least three directors. These are the people who make
- 9. Amity Business School ? A "Government company" is a special type of company that's mostly owned by the government. Here's how it works: ? Ownership: To be a Government company, more than half (at least 51%) of the company's shares (or ownership) should belong to either: a) The Central Government (like the big national government). b) Any state government (like the government of a particular state). c) It can also be a mix, where some shares belong to the Central Government, and some to one or more state governments. ? Special Audit: Government companies are a bit different because they're owned by the government. So, the law has special rules for checking their financial records, which is called an "audit." ? Auditor Appointment: The person who checks the financial records of a Government company (the auditor) is chosen by a special government official called the "Comptroller and Auditor General of India."
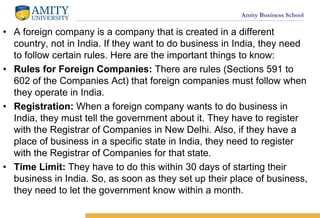
- 10. Amity Business School ? A foreign company is a company that is created in a different country, not in India. If they want to do business in India, they need to follow certain rules. Here are the important things to know: ? Rules for Foreign Companies: There are rules (Sections 591 to 602 of the Companies Act) that foreign companies must follow when they operate in India. ? Registration: When a foreign company wants to do business in India, they must tell the government about it. They have to register with the Registrar of Companies in New Delhi. Also, if they have a place of business in a specific state in India, they need to register with the Registrar of Companies for that state. ? Time Limit: They have to do this within 30 days of starting their business in India. So, as soon as they set up their place of business, they need to let the government know within a month.
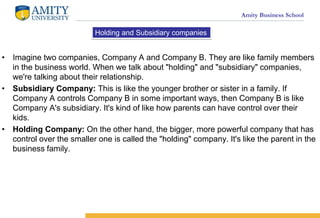
- 11. Amity Business School ? Imagine two companies, Company A and Company B. They are like family members in the business world. When we talk about "holding" and "subsidiary" companies, we're talking about their relationship. ? Subsidiary Company: This is like the younger brother or sister in a family. If Company A controls Company B in some important ways, then Company B is like Company A's subsidiary. It's kind of like how parents can have control over their kids. ? Holding Company: On the other hand, the bigger, more powerful company that has control over the smaller one is called the "holding" company. It's like the parent in the business family. Holding and Subsidiary companies
- 12. Amity Business School ? Now, let's see how the law defines this relationship: ? Control of Directors: If Company A (the holding company) gets to decide who sits on Company B's (the subsidiary company) board of directors, it's like Company A is the boss, and Company B follows its orders. ? Holding More Than Half the Money: If Company A (the holding company) owns more than half of the money that Company B (the subsidiary company) has in its shares, it's like Company A has a big say in how Company B runs its business. ? Family Tree: If Company A is a subsidiary of another company, let's call it Company C, then Company B (if it's controlled by Company A) is like a grandchild of Company C.
