PPT-Ore-reserve-resource.pptx
- 1. Ore Geology and Fuel Geology
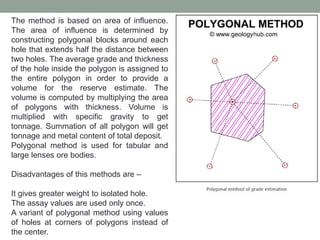
- 8. The method is based on area of influence. The area of influence is determined by constructing polygonal blocks around each hole that extends half the distance between two holes. The average grade and thickness of the hole inside the polygon is assigned to the entire polygon in order to provide a volume for the reserve estimate. The volume is computed by multiplying the area of polygons with thickness. Volume is multiplied with specific gravity to get tonnage. Summation of all polygon will get tonnage and metal content of total deposit. Polygonal method is used for tabular and large lenses ore bodies. Disadvantages of this methods are – It gives greater weight to isolated hole. The assay values are used only once. A variant of polygonal method using values of holes at corners of polygons instead of the center.
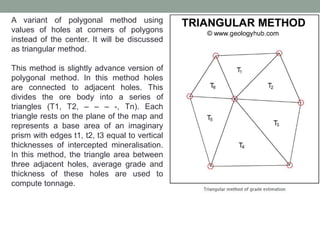
- 9. A variant of polygonal method using values of holes at corners of polygons instead of the center. It will be discussed as triangular method. This method is slightly advance version of polygonal method. In this method holes are connected to adjacent holes. This divides the ore body into a series of triangles (T1, T2, – – – -, Tn). Each triangle rests on the plane of the map and represents a base area of an imaginary prism with edges t1, t2, t3 equal to vertical thicknesses of intercepted mineralisation. In this method, the triangle area between three adjacent holes, average grade and thickness of these holes are used to compute tonnage.
- 13. Cross Section Method In this method ore body is interpreted on cross-section. The ore body is divided into different segments with the help of transverse section lines. The section line can be spaces at equal or unequal intervals based on grid interval and hole locations