Practical micro
- 1. Sterilization Fig. 1.1: Simple laboratory autoclave(moist heat) Temp. 121┬░C (due to double atmospheric pressure) Time : required: 20 min. Used for: surgical inst ,gauze,cotton,&culture media that are destroyed by heat. It is an efficient method of sterilization due to penetration power of steam &high temp. How to test efficacy of autoclave? By 1. chemical method :by cultivation of bacillus sterothermophilus( that can survive up to 120 c and beyond that it die) then it is cultivated to test efficacy. 2. biological method :by chemical indicator on a tape that changes its colour into black or dark purple if the autoclave is efficient.
- 2. Fig. 1.2: Hot air oven(dry heat). Temp. 160┬░C Time required: 1 hour Used for: metal & glass ŌĆō ware equipment &powder and oil.
- 3. With discs have varying diameter & varying pore size ŌĆó Suitable for large volume of fluid. ŌĆó and any biological fluids contain proteins that would coagulate if sterilized by autoclave as serum, vaccines and media used for cultivation of viruses
- 4. N.B. Bacterial loop : ( enoculating needle ) Sterilized by red heat PLASTIC SYRINGE: By ethylene oxide gas or gamma rays.
- 5. Fig. 2.1: Blood agar opaque red in color Type: Enriched & indicator medium Differentiate bet bact. By their hemolytic action on red cells (complete , partial, no hemolysis) .it is not sterilized by autoclave The sterile blood is added to sterile agar at temp. of 55 and poured in sterile plates Fig. 2.2: Blood agar showing: -Alpha heaemolysis (partial & greenish) -Beta haemolysis (complete ) Media
- 6. Fig. 2.3: MacConkeyŌĆÖs medium Reddish transparent medium Fig. 2.4: MacConkeyŌĆÖs medium showing: -Lactose fermenter ŌåÆ rose pink colonies -Non Lactose fermenter ŌåÆ pale yellow colonies Type: indicator (differential media) indicator: neutral red sugar content : lactose Use: to differ. Between lactose , non lactose frementers and for isolation of enteric media Sterilized by autoclave
- 7. Suitable for: growth of Nesisseria meningitides &haemophilus sterilize by : autoclave type: enriched media Sterilize by: heating in inspissator (oven) at 80c for 2h for 3 successive days to kill bacterial spores
- 8. Fig. 2.8: TCBS media -Green, Transparent medium - It is used for isolation of Vibrio cholera Growh after 6-8 weeks Type: selective media inhibitory substance by: malachite green that inhibit all bacterial flora exept mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sterilize by: heating in inspissator (oven) at 80c for2 hours for 3 successive days
- 9. Used for: cultivation of anerobic bact. Suitable for growth of clostridia & other anaerobes. sterilize by : autoclave Used for: cultivation of anaerobic bact. Indicator: methylene blue
- 10. Bacterial Identification Fig. 3.1: Gram-positive bacilli (violet in colour) Fig. 3.2: Gram ŌĆō negative bacilli (Red in colour)
- 11. Fig. 3.8: Catalase test -Positive test shows gas production -Give positive: with staphylococci Fig. 3.11: Oxidase test Positive test gives deep purple color Give positive: with Neisseria , vibrio &pseudomonas Fig. 3.10: Urease test Positve test gives Pink color Give positive: with proteus Indicator: phenol red
- 12. Fig. 3.14: Antibiotic sensitivity test Use: To choose the most effective drug used for ttt. Type: Disc diffusion method The drug show the largest zone of inhibition is the most effective ┘枬┘Ŗž¼┘ē ┘ü ž¦┘䞦┘ģž¬žŁž¦┘å ┘ģž▒┘é┘ģ┘ć ┘ł┘ģ┘Ŗ┘å ž¦┘āž¬ž▒ ž»┘łž¦žĪ ┘Ŗž│ž¬ž«ž»┘ģ ┘āž╣┘䞦ž¼ SENSITIVE (LARGEST ZONE OF INHIBITION) Non sensitive (resistant)
- 13. Fig. 1.1: Staph. Aureus on blood agar it produce Beta haemolysis Fig. 1.2: Staph aureus on nutrient agar it produce golden yellow endopigment Staphylococci Systemic bacteriology Or bunches or gape like
- 14. Fig. 1.6: Coagulase test Staph. Aureus gives positive coagulase test Fig. 1.5: Catalase test all Staphylococci are catalase positive
- 15. strepcoocci Fig. 2.2: Growth of Strept viridians on blood agar showing partial or alpha heaemolysis Fig. 2.1: Growth of Strept pyogenes on blood agar showing complete or Beta haemolysis Fig. 2.3: Strept. In culture gram stain. (Gram positve cocci arranged in chain)
- 16. Fig. 2.8: Optochin sensitivity test strept. Pneum is sensitive strept. Viridance is resistant Fig. 2.9: Bacitracin sensitivty test strept. Pyogens is sensitive strept. Agalactiae is resistant Fig. 2.4: Sterpt. In pus Gram positive cocci
- 17. pneumococci Fig. 2.7:Pneumococci , Quelling reaction (capsule swelling with specific anti-sera) Fig. 2.6: Pneumococci in tissue, gram stain gram positive capsulated diplococci
- 18. Blood culture Added to 50 ŌĆō 100 ml fluid medium 5 ŌĆō 10 ml blood Use of Blood culture for diagnosis of acute bacterial endocarditis Disease diagnosed by bl. Culture:subacute bacterial endocarditis (streptococcus viridans) ŌĆ£ sanguis, salivariusŌĆØ + post streptococcal disease , brucellosis ,typhoid fever and puerperal sepsis.
- 19. 3. Toxin-Antitoxin Neutralization Test Antistreptolysin test O (ASO) Use: 1. For diagnosis of rheumatic fever 2. detection of post streptococcal infection. 3. Acute glomerulonephiritis Type of test: Neutralization (in vitro) The presence of antitoxin in sera neutralizes the hemolytic effect of toxin on addition of red blood cells. Diagnostic test: >200 todd unit 1/25 1/50 1/100 1/200 1/400 1/800 control Titer 1/400 Fig. 2. 11: Antistreptolysin O Titer (ASO)
- 20. Neisseria menngitides Fig. 3.2: Neisseria in cluture Gram negative cocci Fig. 3.3: Pathogenic neisseria in pus, gram stain. (Intra & exteracellular Gram negative diplococci) Fig. 3.4: Oxidase test All neisseria is oxidase positive
- 21. Neisseria gonorrhea ŌĆó The media used for cultivation is Thayer martin media which is chocolate blood agar + antibiotics (vancomycin for gm positve bacteria +nystatin for fungi +cholesyin for gm negative bacteria ) ŌĆó Antibiotics are put because it is separated from vagina or urethera.
- 22. CORYNEBACTERIUM GROUP Fig. 4.3: Coryn. Diphtheria in culture methylen blue stain Fig. 4.4: Coryn. Diphtheria (Gram positive bacilli have Chinese letter arrangement) Media: lofflerŌĆÖs serum agar. Stain: gram & methylene blue Test: ElekŌĆÖs test
- 23. Type of reaction: precipitation test (Ag- Ab reaction) use: Detection of toxiogenic strain of C . Diphtheriae it is a double immunodiffusion test diffusion of the organism toxin with the antitoxin forming precipitation band or line Positive test Fig. 4.6: ElekŌĆÖs test Test strain Precipitation band Negative test Artiserum in the strip.
- 24. Mycobacterium Fig. 5.3: Myc. TB in Sputum, Z.N stain (few thin pink bacilli with blue background) Fig. 5.1: Selective media for Myc. T.B. Fig. 5.2: Culture of Myc. TB on L.J. media - Grow after 6-8 week
- 25. Fig. 5.5: Tuberculin test It involves intradermal injection of Purified Protein Derivative (PPD) type of test: Delayed type hypersenstivity used for Diagnosis of T.B. Type of reaction: antigen-anibody reaction +ve: give area of induration about 9 mm Time: 48 ŌĆō 72 hours after injection Media: lowensten jensen media stain: ziehl neelsen stain
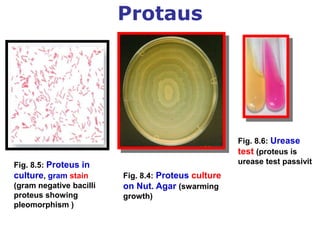
- 26. Protaus Fig. 8.4: Proteus culture on Nut. Agar (swarming growth) Fig. 8.5: Proteus in culture, gram stain (gram negative bacilli proteus showing pleomorphism ) Fig. 8.6: Urease test (proteus is urease test passivit
- 27. +ve -ve Fig. 8.9: Oxidase test (pseudomonas & Vibrio are ) oxidase psoitve Fig. 8.8: Pseudomonas culture on Nut. Agar (produce greenish blue exopigment Fig. 8.7: Pseudomonas in culture, gram stain (gram negative bacilli) Pseudomanas
- 28. Spore forming gram-positive bacilli(Bacillus & clostridium group) Fig. 9.4 Gram stained film of clost. Tetani in culture - Gram-positive long bacillus with terminal plugging spore (dram-stick) appearance Fig. 9.6 RobertsonŌĆÖs cooked-meat broth medium glutathione is released after boiling (reducing agent)
- 29. Fig. 11.2 Fontana stained film showing commensally spirochetes Type of stain: Special stain Spirochaetes Fig. 11.3 Dark ground illumination microscopy of Treponema pallidum. ┘垦ž»ž▒ž¦ ž¦┘ģž¦ ž¬┘åž▓┘ä Fig. 11.4:Indirect Immunofluorescence for spirochetes. It is called indirect as we put antibody then we put antiantibody with fluorescent die. To identify treponema pallidum
- 30. Reading of the results: - No hemolysis means a positive reaction i.e the complement is bound to the antigen-antibody complex. - Hemolysis means a negative reaction Fig. C-2: Complement fixation test wasserman test wasserman test
- 31. MYCOLOGY Fig. 12.3 Germ tube test for pathogenic strain of C. albicans Fig. 12.1 GramŌĆÖs stained films of Candida albicans Fig. 12.2 Candida albicans culture on sabouraudŌĆÖs dextrose agar Mention type of test to identify the candida organism : Germ tube Mention 2 type for commensals of candida: vagina & alimentary tract & mouth
- 32. VIROLOGY Fig. 1.4: CPE (cytopathic effect of Herpes virus) Showing: Enlarged, aggregated and ballooned cells causing multi- nucleated giant cells Cell culture for vesicular lesion : herpes giant cell virus
- 33. immunology E. Immunofluorecence Fig. E-1: Direct immunofluorecence for detection of specific antigen Direct immunofluorecence - A specific antibody labeled with a fluorescent molecule (fluorescein or rhodamine) is added to the unknown antigen in the specimen. - It is used to detect the presence of an antigen on a cell or tissue.
- 34. F. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) -It is used for detection of antigen, antibodies. -ELISA is based on the measurement of an enzymatic reaction associated with immune complexes as detected by color development. Fig. F-1: Plate of ELISA test
- 35. Immunologic reactions 1. Antistreptolysin o titer 2. ElekŌĆÖs test 3. Direct immunoflourescence test 4. Elisa plate test 5. Tuberculin skin test