Pre natal development
- 1. What are some early signs of pregnancy?
- 2. 2 of 30 Stages of Prenatal Development ’éŚZygotic (or Germinal) Stage 0-2 weeks ’éŚEmbryonic Stage 2-8 weeks ’éŚFetal Stage 9-40 weeks
- 3. Conception ’éŚConception occurs when a sperm cell penetrates and fertilizes an egg cell ’éŚSuccessful conception depends on ’üČovaries releasing one healthy egg cell ’üČegg cell migrates most of the way down the fallopian tube ’üČOne sperm must penetrate the ovum to form a zygote.
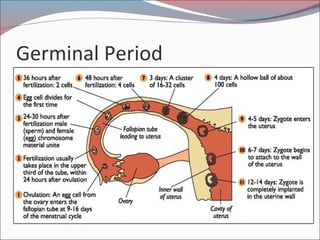
- 4. Germinal Period ’éŚBegins when egg is fertilized in the fallopian tube. ’éŚPeriod of rapid cell division ’éŚEnds 2 weeks later when the zygote is implanted in the wall of the uterus
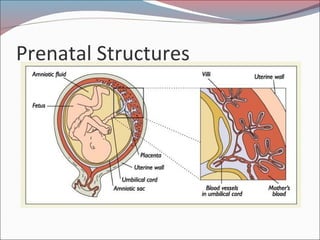
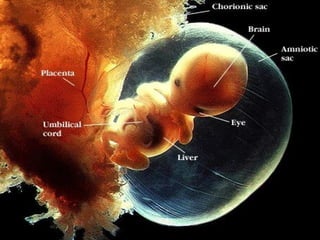
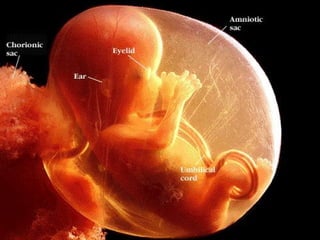
- 6. Embryonic Period ’éŚFrom 2 to 8 weeks after conception ’éŚCell differentiation intensifies ’éŚLife support systems for the embryo develop ’éŚOrgans Appear
- 8. 8 of 30 At 2 weeks, the embryonic disk as 3 layers: ’éŚEntoderm: from which develops pharynx, tonsils, thyroid, trachea, lungs, digestive system, bladder, urethra ’éŚMesoderm: from which develops muscles, bones, circulatory system, lymph system, kidneys, gonads ’éŚEctoderm: from which develops skin, hair, nails, sense organs, nervous tissue
- 9. Fetal Period ’éŚFrom 9 weeks after conception to birth ’éŚIncrease in size and systems begin to function ’éŚAge of viability: 22 to 28 weeks
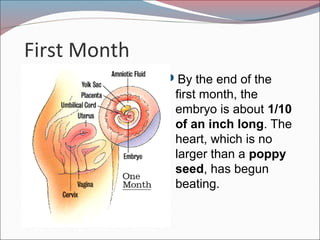
- 10. First Month ’éŚBy the end of the first month, the embryo is about 1/10 of an inch long. The heart, which is no larger than a poppy seed, has begun beating.
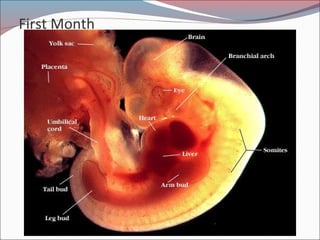
- 11. First Month
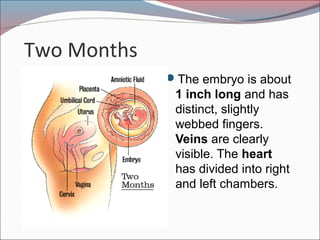
- 12. Two Months ’éŚThe embryo is about 1 inch long and has distinct, slightly webbed fingers. Veins are clearly visible. The heart has divided into right and left chambers.
- 13. Two Months
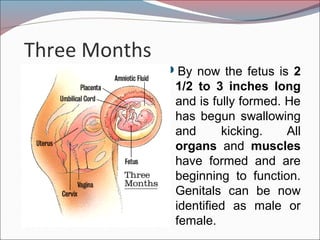
- 14. Three Months ’éŚBy now the fetus is 2 1/2 to 3 inches long and is fully formed. He has begun swallowing and kicking. All organs and muscles have formed and are beginning to function. Genitals can be now identified as male or female.
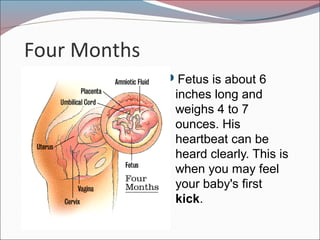
- 15. Four Months ’éŚFetus is about 6 inches long and weighs 4 to 7 ounces. His heartbeat can be heard clearly. This is when you may feel your baby's first kick.
- 16. 4 months
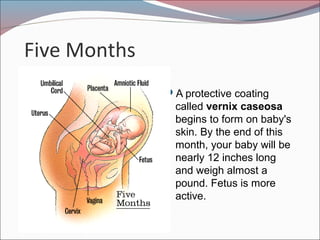
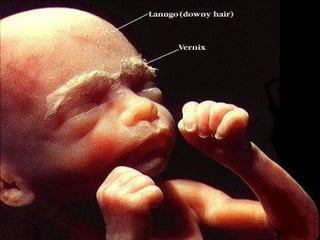
- 17. Five Months ’éŚA protective coating called vernix caseosa begins to form on baby's skin. By the end of this month, your baby will be nearly 12 inches long and weigh almost a pound. Fetus is more active.
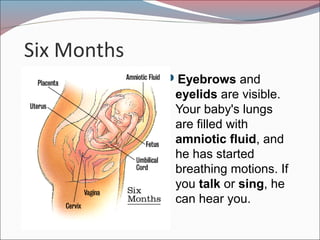
- 18. Six Months ’éŚEyebrows and eyelids are visible. Your baby's lungs are filled with amniotic fluid, and he has started breathing motions. If you talk or sing, he can hear you.
- 19. 6 Months
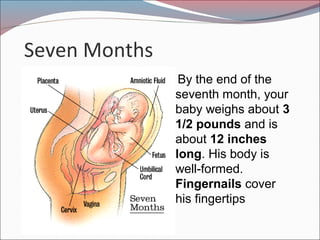
- 20. Seven Months ’éŚBy the end of the seventh month, your baby weighs about 3 1/2 pounds and is about 12 inches long. His body is well-formed. Fingernails cover his fingertips
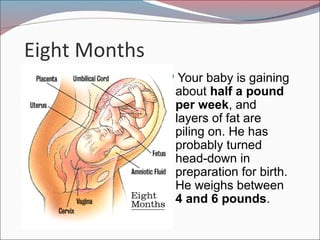
- 22. Eight Months ’éŚYour baby is gaining about half a pound per week, and layers of fat are piling on. He has probably turned head-down in preparation for birth. He weighs between 4 and 6 pounds.
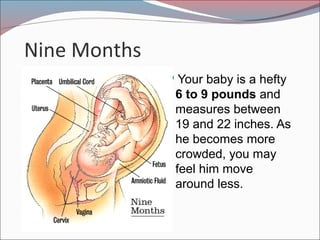
- 24. Nine Months ’éŚYour baby is a hefty 6 to 9 pounds and measures between 19 and 22 inches. As he becomes more crowded, you may feel him move around less.
- 26. Factors Affecting to Prenatal Development ’éŚGeneral Risk Factors ’éŚTeratogens: Diseases, Drugs, and Environmental Hazards ’éŚHow Teratogens Influence Prenatal Development ’éŚPrenatal Diagnosis and Treatment
- 27. General Risk Factors ’éŚNutrition: adequate amount of food, protein, vitamins, & minerals ’éŚStress: decreases oxygen to fetus and weakens motherŌĆÖs immune system ’éŚMotherŌĆÖs Age: neither too young, nor too old
- 28. Prescription and Nonprescription Drugs ŌĆō Several drugs used by the mother that have negative effects on the embryos and fetuses. Psychoactive drugs are used to alter states of consciousness, modify perceptions, and change moods. The effects of alcohol, nicotine, and illegal drugs on the fetus are well-documented. Incompatibility of blood types where the fetusŌĆÖs blood is RH positive ad the motherŌĆÖs is RH negative cause antibodies to attack the fetus, resulting in serious, often life-threatening damage.
- 29. Environmental hazards of the modern world can cause chromosomal abnormalities. Exposure to toxins, radiation, pollutants, and excess heat can all contribute to a negative impact on the fetus. Other maternal factors such as infectious diseases (Rubella, Syphilis, AIDS), all have varying degrees of impact on the fetus. Also considered are emotional stress, age, and nutrition of the mother. Paternal factors can impact fetal growth such as pesticides at the workplace, smoking and diet.
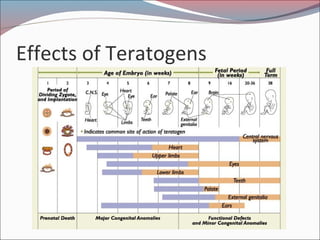
- 30. Teratogens: Diseases, Drugs, and Environmental Hazards ŌĆó Many diseases pass through the placenta directly and attack the fetus ŌĆó Potentially dangerous drugs not limited to cocaine but include alcohol and caffeine ŌĆó Environmental hazards are treacherous because weŌĆÖre often unaware of their presence
- 31. How Teratogens Influence Prenatal Development ’éŚNot universally harmful ’éŚHarm particular structures at a particular point in development in particular animals
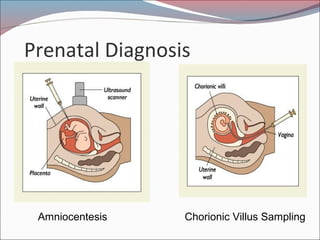
- 33. Prenatal Diagnosis and Treatment ’éŚDiagnosis: ultrasound, amniocentesis, and chorionic villus sampling can detect physical deformities and genetic disorders ’éŚTreatment: fetal medicine and genetic engineering are experimental
- 34. Prenatal Diagnosis Amniocentesis Chorionic Villus Sampling
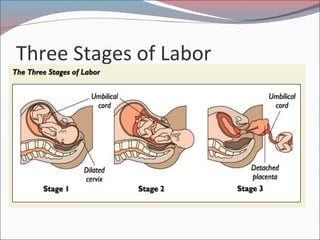
- 35. Labor and Delivery ’éŚStage 1: starts when the muscles of the uterus contract and ends when the cervix is fully enlarged (about 10 cm) ’éŚStage 2: baby is pushed down the birth canal ’éŚStage 3: placenta is expelled
- 36. Three Stages of Labor