preconception_care_presentation_slides.ppt
- 1. World Health Organization Preconception care: Maximizing the gains for maternal and child health
- 2. Facts ŌĆó 4 out of 10 women report that their pregnancies are unplanned ŌĆó Perinatal deaths are 50% higher among babies born to adolescent mothers ŌĆó Up to 10% of pregnancies among women with untreated gonococcal infections result in perinatal death
- 3. Facts ŌĆó Maternal undernutrition and iron-deficiency anemia account for at least 20% of maternal mortality ŌĆó Female genital mutilation increases the risk of neonatal death by 15% - 55% ŌĆó In the absence of interventions, rates of HIV transmission from mother to child are between 15 and 45%
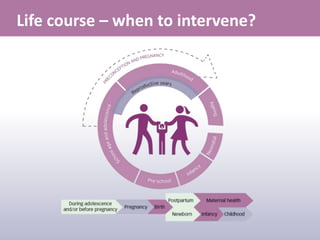
- 4. Life course ŌĆō when to intervene?
- 5. What is preconception care? What is its aim? Preconception care is the provision of biomedical, behavioral and social health interventions to women and couples before conception occurs. ŌĆó Aims at improving health status and reducing behaviors and individual and environmental factors that could contribute to poor maternal and child health outcomes. ŌĆó Its ultimate aim is improved maternal and child health outcomes, in both the short and long term.
- 6. Preconception care has a positive effect on a range of health outcomes: hypothyroidism childhood cancers vertical transmission of HIV/STIs underweight and stunting reduced breastfeeding type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in later life child mortality maternal mortality preterm birth macrosomia neonatal hypoglycemia birth defects low birth weight goitre cretinism diarrhoea mental retardation congenital and neonatal infections
- 7. WHO has developed a package of preconception care interventions
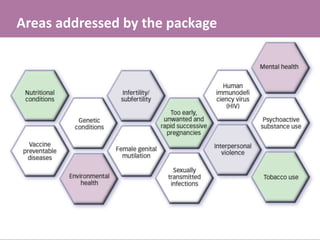
- 8. Areas addressed by the package
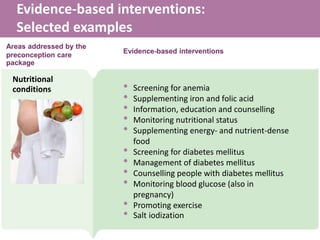
- 9. Evidence-based interventions: Selected examples Areas addressed by the preconception care package Evidence-based interventions ŌĆó Screening for anemia ŌĆó Supplementing iron and folic acid ŌĆó Information, education and counselling ŌĆó Monitoring nutritional status ŌĆó Supplementing energy- and nutrient-dense food ŌĆó Screening for diabetes mellitus ŌĆó Management of diabetes mellitus ŌĆó Counselling people with diabetes mellitus ŌĆó Monitoring blood glucose (also in pregnancy) ŌĆó Promoting exercise ŌĆó Salt iodization Nutritional conditions
- 10. Evidence-based interventions: Selected examples ŌĆó Screening for anemia ŌĆó Taking a thorough family history ŌĆó Family planning ŌĆó Genetic counselling ŌĆó Carrier screening and testing ŌĆó Appropriate treatment ŌĆó Providing community-based education ŌĆó Community-wide or national screening among populations at high risk ŌĆó Population-wide screening Genetic conditions Areas addressed by the preconception care package Evidence-based interventions
- 11. Evidence-based interventions: Selected examples ŌĆó Keeping girls in school ŌĆó Influencing cultural norms that support early marriage and coerced sex ŌĆó Creating visible, high-level support for pregnancy prevention programmes ŌĆó Educating girls and boys about sexuality, reproductive health and contraceptive use ŌĆó Building community support for preventing early pregnancy and for contraceptive provision to adolescents ŌĆó Enabling adolescents to obtain contraceptive services ŌĆó Empowering girls to resist coerced sex ŌĆó Engaging men and boys to critically assess norms and practices regarding gender-based violence and coerced sex ŌĆó Educating women and couples about the dangers to the baby and mother of short birth intervals ŌĆó Providing contraceptives Too-early, unwanted and rapid successive pregnancy Areas addressed by the preconception care package Evidence-based interventions
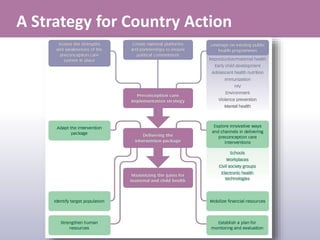
- 12. A Strategy for Country Action
- 13. Successful preconception care initiatives ŌĆó There is growing experience in implementing preconception care initiatives: ŌĆó in high-income countries, such as Italy, the Netherlands and the United States ŌĆó in low- and middle-income countries, such as Bangladesh, the Philippines and Sri Lanka
- 14. WHO support to countries Introduce professionals in countries to international experience, research, evidence and good practices. Provide a methodology to analyze and understand the strengths and weaknesses of the preconception care system in place, and opportunities for improvement. Adapt the package of preconception care interventions to regional and country priorities, and health systems contexts. Explore various delivery strategies for preconception care interventions, and their comparative advantages in terms of coverage, feasibility, acceptability and cost. Explore and document innovative ways to deliver preconception care outside the traditional maternal and child health programmes, while recognizing the importance of integrated delivery mechanisms. Monitor, evaluate and document progress. Create regional/national platforms and partnerships to advance preconception care interventions. Develop a roadmap to make changes over time. WHO supports regions and countries in implementing a step-by-step processes to improve availability of and access to preconception care interventions
- 15. Examples of successful preconception care initiatives are available to inform policy makers There is growing experience in implementing preconception care initiatives both in high-income countries, such as Italy, the Netherlands and the United States, and in low- and middle-income countries, such as Bangladesh, the Philippines and Sri Lanka www.who.int
Editor's Notes
- #3: Four out of ten women report that their pregnancies are unplanned. As a result, essential health interventions provided once a woman and her partner decide to have a child will be too late in 40% of pregnancies. Perinatal deaths are 50% higher among children born to mothers under 20 years of age compared to mothers aged 20ŌĆō29 years Up to 35% of pregnancies among women with untreated gonococcal infections result in low birth weight infants and premature deliveries, and up to 10% result in perinatal death
- #4: Maternal undernutrition and iron-deficiency anaemia increase the risk of maternal death, accounting for at least 20% of maternal mortality worldwide Female genital mutilation increases the risk of neonatal death (including stillbirths) by 15% - 55% In the absence of interventions, rates of HIV transmission from mother to child are between 15 and 45%
- #5: For women and men to be healthy physically, psychologically and socially - strong public health programmes that use a life-course perspective from infancy through childhood and adolescence are needed There is growing evidence that extending the maternal, newborn and child health continuum with one step before prenatal care (ie before pregnancy occurs) can increase the well-being of women and couples and improve subsequent pregnancy and child health outcomes In both couples contemplating a pregnancy and in couples not currently contemplating a pregnancy ŌĆō both women and men should be targeted Groups that should be specially targeted: Individuals, couples, families and communities who are socially and economically marginalized Adolescent girls Couples with previous adverse reproductive outcomes
- #6: Preconception care is the provision of biomedical, behavioral and social health interventions to women and couples before conception occurs. It aims at improving their health status, and reducing behaviours and individual and environmental factors that contribute to poor maternal and child health outcomes. Its ultimate aim is to improve maternal and child health, in both the short and the long term Even if preconception care aims primarily at improving maternal and child health, it brings health benefits to the adolescents, women and men as individuals in their own right (not just as╠² potential parents). For example, many ╠²nutritional, environmental, mental health interventions as well as interventions aiming to reduce psychoactive substance use and interpersonal violence improve health and well-being of girls and boys, women and couples irrespective of their plans to become parents. ╠²
- #7: Preconception care has a positive effect on a range of health outcomes. Among others, preconception care can: Reduce maternal and child mortality Prevent unintended pregnancies Prevent complications during pregnancy and delivery Prevent stillbirths, preterm birth and low birth weight Prevent birth defects Prevent neonatal infections Prevent underweight and stunting Prevent vertical transmission of HIV/STIs Lower the risk of some forms of childhood cancers Lower the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease later in life
- #8: In 2012, WHO organized a meeting to develop global consensus on preconception care to reduce maternal and childhood mortality and morbidity The meeting report provides information and perspectives on alternative definitions, sensitive issues, target groups, delivery mechanisms and specific regional considerations
- #9: However, the report most importantly provides the evidence based 'package of interventions' addressing 13 various areas: Nutritional conditions; vaccine preventable diseases; genetic conditions; environmental health; infertility/subfertility; female genital mutilation; too early, unwanted and rapid successive pregnancies; sexually transmitted infections; HIV; interpersonal violence; mental health; psychoactive substance abuse; and tobacco use
- #10: I will go through three examples of areas; that is nutritional conditions; genetic conditions; and too early, unwanted and rapid successive pregnancies "Read the evidence-based interventions"
- #11: "Read the evidence-based interventions"
- #12: "Read the evidence-based interventions"
- #13: This slide shows in a pictorial way main elements of a Strategy for Country Action Such Strategy would need to be informed by an assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of the preconception care system in place, it will need to be supported by key stakeholders and partnerships to ensure political commitment, and it will need to leverage on existing public health program In order to ensure effective delivery of the preconception care package, it will need to be adapted to country priorities and target population, service delivery mechanisms will need to be identified within existing programmes but also innovative ways will need to be explored. It is equally important that adequate financial resources are mobilized to support the implementation, and a plan for monitoring and evaluation is established.
- #14: There is growing experience in implementing preconception care initiatives both in high, middle and low income countries. Countries with particular experience are Italy, the Netherlands, United States, Bangladesh, the Philippines and Sri Lanka
- #15: This slide explains what are the specific areas in which WHO can support countries to implement universal access to preconception care.
- #16: For more information, please visit our website: www.who.int. The report, this slide set, and a policy brief for advocacy can be found when searching for 'Preconception care'