Presentation 2
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes344 views
This document discusses hypothesis testing, which is a method used in scientific research to either accept or reject hypotheses. It outlines the key steps: 1) Formulating a research question and hypothesis. The null hypothesis states there is no effect or relationship, while the alternative suggests there is. 2) Collecting and analyzing data. 3) Using a p-value and significance level (typically 0.05) to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis, based on the probability the results occurred by chance. 4) Drawing inferences and presenting the findings. Type 1 and 2 errors in hypothesis testing are also discussed.
1 of 18
Download to read offline












![Significance - Definition The significance level of a test is the probability that the test statistic will reject the null hypothesis when the [hypothesis] is true .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-2-101013000634-phpapp02/85/Presentation-2-15-320.jpg)


Ad
Recommended
hypothesis testing
hypothesis testingmsrpt
Ěý
This document discusses hypothesis testing, which is a method used in scientific research to either accept or reject hypotheses. It outlines the key steps:
1) Formulating a research question and hypothesis, which is either the null hypothesis or alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the statement being tested.
2) Collecting and analyzing data and using a statistical test to calculate the p-value, which represents the probability of obtaining results as extreme as the actual outcome by chance alone.
3) Comparing the p-value to a predetermined significance level (usually 5%) to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, with lower p-values leading to rejection. This determines whether the results support the alternative hypothesis.Hypothesis testing and p values 06
Hypothesis testing and p values 06DrZahid Khan
Ěý
This document discusses hypothesis testing and p-values. It defines a hypothesis as a proposition or prediction about the outcome of an experiment. Hypotheses are tested to evaluate their credibility against observed data. There are two main types of hypotheses: the null hypothesis, which corresponds to a default or general position, and the alternative hypothesis, which asserts a relationship different from the null. Errors in hypothesis testing can occur if the decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis is wrong. The p-value indicates how likely the observed or more extreme results would be if the null hypothesis were true. A lower p-value provides stronger evidence against the null hypothesis.Lesson p values
Lesson p valuesCrystal Delosa
Ěý
This document discusses statistical significance and p-values. It explains that statistical significance determines whether differences in experimental and control groups are real or due to chance. Tests of significance are used to measure the influence of chance, and results are considered statistically significant if p < 0.05, meaning there is less than a 5% probability the results are due to chance. The document provides examples of interpreting p-values in experiments.Null hypothesis AND ALTERNAT HYPOTHESIS
Null hypothesis AND ALTERNAT HYPOTHESISADESH MEDICAL COLLEGE
Ěý
The document explains the null hypothesis, which posits no difference or effect, and details the process for testing it using statistical significance, including the role of p-values. It also describes normal distribution and skewed distributions, elaborating on the calculation of probabilities using addition and multiplication rules, especially in the context of independent and mutually exclusive events. Additionally, examples are provided to illustrate the calculation of probabilities in various scenarios.Presentation 2
Presentation 2msrpt
Ěý
This document discusses hypothesis testing, which is a method used in scientific research to either accept or reject hypotheses. It outlines the key steps:
1) Formulating a research question and hypothesis, which is either the null hypothesis or alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the statement being tested.
2) Collecting and analyzing data and using a statistical test to calculate the p-value, which represents the probability of obtaining results as extreme as the actual outcome by chance alone.
3) Comparing the p-value to the significance level (usually 0.05) to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, with type 1 and type 2 errors representing incorrect decisions.Positioning And Mobilization
Positioning And Mobilizationmsrpt
Ěý
Positioning can improve oxygen transport and lung function in patients with cardiopulmonary dysfunction. Different positions like supine, side lying, and prone affect lung volumes and ventilation in different areas of the lungs. The supine position decreases lung capacity but improves ventilation distribution, while side lying improves ventilation in the dependent lung. Prone positioning increases lung capacity and decreases airway closure. Head down and forward leaning positions can relieve dyspnea. Upright positioning augments drug effects and improves ventilation-perfusion matching. Mobilization provides both acute benefits like increased ventilation and oxygen transport, as well as chronic benefits including increased exercise capacity and decreased cardiac workload.Presentation1
Presentation1msrpt
Ěý
The document summarizes various primary manifestations of cerebellar symptoms including hypotonia, ataxia, dysarthria, and ocular dysfunctions. It provides details on testing for each symptom such as using the Ashworth scale to test for hypotonia in adults and observing pronator drift. For ataxia, it lists tests like finger-to-nose coordination and heel-to-shin rubbing. Kinetic tremors are also discussed as well as non-motor manifestations like spatial dysgraphia and cognitive issues.Hypothesis testing, error and bias
Hypothesis testing, error and biasDr.Jatin Chhaya
Ěý
This document discusses hypotheses, hypothesis testing, and research bias. It defines a hypothesis as a tentative assumption about a population parameter that is statistically tested. The main types of hypotheses covered are the null hypothesis (H0), which is attempted to be disproven, and the alternative hypothesis (H1). The four steps of hypothesis testing are outlined as stating the hypotheses, collecting sample data, calculating sample statistics, and analyzing results to accept or reject H0. Key concepts discussed include p-values, levels of significance, type I and type II errors, and bias. Common biases explained are selection, memory/recall, confounding, and interviewer bias.hypothesis testing overview
hypothesis testing overviewi i
Ěý
Hypothesis testing involves stating a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (H1). H0 assumes there is no effect or relationship in the population. H1 states there is an effect. A study is conducted and statistics are used to determine if the data supports rejecting H0 in favor of H1. The p-value indicates the probability of obtaining results as extreme as the observed data or more extreme if H0 is true. If p ≤ the predetermined significance level (α = 0.05), H0 is rejected in favor of H1. Otherwise, H0 is retained but not proven true. Type I and II errors can occur when the true hypothesis is incorrectly rejected or retained.Hypothesis
HypothesisDr. Priyanka Jain
Ěý
The document discusses hypothesis testing, which involves testing a hypothesis about a population using a sample of data. It explains that a hypothesis test has four main steps: 1) stating the null and alternative hypotheses, where the null hypothesis asserts there is no difference between the sample and population, 2) setting the significance level, 3) determining the test statistic and critical region for rejecting the null hypothesis, and 4) making a decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on whether the test statistic falls in the critical region. Type I and type II errors are also defined. The document provides examples of null and alternative hypotheses using mathematical symbols and discusses how to determine if a p-value is statistically significant.Reporting Results of Statistical Analysis
Reporting Results of Statistical Analysis Centre for Social Initiative and Management
Ěý
The document discusses the limitations and criticisms of p-values in statistical significance testing, emphasizing the need for effect size and confidence intervals to better represent study findings. It highlights the difference between null and alternative hypotheses, the implications of type I and type II errors, and how sample size and multiple comparisons can affect the reliability of p-values. Ultimately, the document argues for a more nuanced understanding of statistical significance beyond conventional threshold values like p < .05.Hypothesis testing
Hypothesis testingSohail Patel
Ěý
This document discusses hypothesis testing and interpretation of data. It provides an example of two lecturers, Sandy and Mandy, who want to test whether providing seminar classes in addition to lectures improves student performance compared to lectures alone. The document outlines the steps in hypothesis testing: 1) Identify the research problem and variables, 2) Specify the null and alternative hypotheses, 3) Choose a significance level, 4) Identify the test statistic, 5) Determine the rejection region, and 6) Select the appropriate statistical test. It defines type 1 and type 2 errors and explains key concepts like the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, and significance level.Hypothesis Testing.pptx
Hypothesis Testing.pptxheencomm
Ěý
A hypothesis test examines two opposing hypotheses: the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the statement being tested, usually stating "no effect". The alternative hypothesis is what the researcher hopes to prove true. A hypothesis test uses a sample to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis based on a p-value and significance level. There are 5 steps: specify null and alternative hypotheses, set significance level, calculate test statistic and p-value, and draw a conclusion. Type I and II errors are possible - type I rejects a true null hypothesis, type II fails to reject a false null hypothesis.Basic Conecepts of Inferential Statistics _ şÝşÝߣshare.pptx
Basic Conecepts of Inferential Statistics _ şÝşÝߣshare.pptxElementary & Secondary Education Department, KP, Pakistan
Ěý
The document covers the foundational concepts of inferential statistics, including hypothesis testing, significance levels, and types of errors. It explains the principles of hypothesis formation, types of hypotheses, and the statistical methods used to analyze data, such as p-values and standard errors. Additionally, it discusses the risks of type I and type II errors in hypothesis testing and emphasizes the importance of carefully planning study designs.Hypothesis testing 1.0
Hypothesis testing 1.0Dr. C.V. Suresh Babu
Ěý
The document covers the fundamentals of hypothesis testing in research, explaining concepts such as significance levels, p-values, sampling errors, and types of errors in statistical tests. Hypothesis tests assess two conflicting theories regarding population properties, striving to provide evidence against the null hypothesis that assumes no effect. It emphasizes the importance of setting appropriate significance levels to reduce the risk of type I and type II errors in data interpretation.lecture no.7 computation.pptx
lecture no.7 computation.pptxssuser378d7c
Ěý
This document discusses hypothesis testing. It defines a hypothesis as a tentative statement about the relationship between variables. The null hypothesis proposes no relationship, while the alternative hypothesis proposes a relationship. There are two types of errors in hypothesis testing - type I errors occur when a true null hypothesis is rejected, and type II errors occur when a false null hypothesis is not rejected. Key concepts discussed include critical regions, critical values, significance levels, and one-tailed versus two-tailed tests.Hypothesis
HypothesisMmedsc Hahm
Ěý
The document discusses hypothesis testing, including defining the null and alternative hypotheses, types of errors, test statistics, and the process of hypothesis testing. Some key points:
- The null hypothesis states that a population parameter is equal to a specific value. The alternative hypothesis is paired with the null and states inequality.
- Type I errors occur when the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true. Type II errors occur when the null is not rejected when it is false.
- A test statistic is calculated based on sample data and compared to critical values to determine if the null hypothesis can be rejected.
- Hypothesis testing follows steps of stating hypotheses, choosing a significance level, collecting/analyzing data,Rm 3 Hypothesis
Rm 3 Hypothesisitsvineeth209
Ěý
Hypothesis testing is an important tool in research. A hypothesis is a statement or proposition that can be tested through scientific investigation. The null hypothesis represents the default position that there is no relationship between variables or no difference among groups. The alternative hypothesis is what the researcher aims to prove. Through hypothesis testing, researchers aim to reject the null hypothesis by collecting data and calculating the probability of the results if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is then compared to the pre-determined significance level, often 5%, to determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Proper hypothesis testing involves clearly stating the hypotheses, selecting a random sample, determining the appropriate statistical test based on the data, and interpreting the results.Definition of Hypothesis jynyyetbxhzwtrb xb
Definition of Hypothesis jynyyetbxhzwtrb xbgarefed500
Ěý
A hypothesis is a testable statement formulated to explain phenomena, serving as the basis for scientific inquiry. Hypothesis testing involves evaluating data to accept or reject a null hypothesis, with a focus on significance levels and p-values. It also discusses type I and type II errors, highlighting their inverse relationship and the trade-off researchers face when balancing the two.HypothesisT I think I will be in there for the
HypothesisT I think I will be in there for themarialuisarada
Ěý
The document discusses the principles and procedures of hypothesis testing in statistics, detailing how to formulate null and alternative hypotheses, and the significance of p-values. It outlines the six steps of hypothesis testing, including generating hypotheses, checking assumptions, and determining the significance level, while also addressing type I and type II errors. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between statistical significance and clinical importance in research findings.Basis of statistical inference
Basis of statistical inferencezahidacademy
Ěý
Statistical inference involves using probability concepts to draw conclusions about populations based on samples. It includes point and range estimation to estimate population values, as well as hypothesis testing to test hypotheses about populations. Hypothesis testing involves making a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis before collecting sample data. Common hypotheses include claims of no difference or significant differences. Statistical tests like z-tests, t-tests, and chi-square tests are used to either accept or reject the null hypothesis based on the sample data and a significance level, typically 5%. P-values indicate the probability of observing the sample results by chance. Type 1 and type 2 errors can occur when making inferences about hypotheses.Hypothesis Testing.pptx
Hypothesis Testing.pptxMelba Shaya Sweety
Ěý
Hypothesis testing involves making tentative assumptions about population parameters or distributions, called null hypotheses (H0). Alternative hypotheses (Ha) are also defined. Sample data is used to determine if H0 can be rejected. If rejected, the conclusion is that Ha is true. There are two types of errors that can occur - type I errors when a true H0 is rejected, and type II errors when a false H0 is not rejected. The significance level and power aim to control these errors. One-tailed and two-tailed tests look at relationships between variables in different ways.Chapter 20 and 21 combined testing hypotheses about proportions 2013
Chapter 20 and 21 combined testing hypotheses about proportions 2013calculistictt
Ěý
This document discusses hypotheses testing and the reasoning behind it. It explains that hypotheses testing involves proposing a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis based on a parameter of interest. Data is then analyzed to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Specifically:
1) The null hypothesis proposes a baseline model or value for a parameter.
2) Statistics are calculated based on the data and compared to what we would expect if the null hypothesis is true.
3) If the results are inconsistent enough with the null hypothesis, we can reject it in favor of the alternative hypothesis. Otherwise we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
The goal is to quantify how unlikely the results would be if the null hypothesis is true, hypothesis test
hypothesis testUnsa Shakir
Ěý
This document provides an overview of estimation and hypothesis testing. It defines key statistical concepts like population and sample, parameters and estimates, and introduces the two main methods in inferential statistics - estimation and hypothesis testing.
It explains that hypothesis testing involves setting a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (Ha), calculating a test statistic, determining a p-value, and making a decision to accept or reject the null hypothesis based on the p-value and significance level. The four main steps of hypothesis testing are outlined as setting hypotheses, calculating a test statistic, determining the p-value, and making a conclusion.
Examples are provided to demonstrate left-tailed, right-tailed, and two-tailed hypothesis testsTesting Of Hypothesis
Testing Of HypothesisSWATI SINGH
Ěý
The document explains hypothesis testing as a statistical method for evaluating claims about a population parameter, involving a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (H1). It outlines the significance level, types of errors (Type I and Type II), and provides procedures for conducting hypothesis tests using either the rejection region method or p-value estimation method. Additionally, it discusses one-tailed and two-tailed tests, emphasizing the importance of clear hypotheses in guiding research outcomes.Test of hypothesis
Test of hypothesisvikramlawand
Ěý
The document discusses hypothesis testing in research. It defines a hypothesis as a proposition that can be tested scientifically. The key points are:
- A hypothesis aims to explain a phenomenon and can be tested objectively. Common hypotheses compare two groups or variables.
- Statistical hypothesis testing involves a null hypothesis (H0) and alternative hypothesis (Ha). H0 is the initial assumption being tested, while Ha is what would be accepted if H0 is rejected.
- Type I errors incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis. Type II errors fail to reject a false null hypothesis. Hypothesis tests aim to control the probability of type I errors.
- The significance level is the probability of a type I error,More Related Content
Similar to Presentation 2 (20)
Hypothesis testing, error and bias
Hypothesis testing, error and biasDr.Jatin Chhaya
Ěý
This document discusses hypotheses, hypothesis testing, and research bias. It defines a hypothesis as a tentative assumption about a population parameter that is statistically tested. The main types of hypotheses covered are the null hypothesis (H0), which is attempted to be disproven, and the alternative hypothesis (H1). The four steps of hypothesis testing are outlined as stating the hypotheses, collecting sample data, calculating sample statistics, and analyzing results to accept or reject H0. Key concepts discussed include p-values, levels of significance, type I and type II errors, and bias. Common biases explained are selection, memory/recall, confounding, and interviewer bias.hypothesis testing overview
hypothesis testing overviewi i
Ěý
Hypothesis testing involves stating a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (H1). H0 assumes there is no effect or relationship in the population. H1 states there is an effect. A study is conducted and statistics are used to determine if the data supports rejecting H0 in favor of H1. The p-value indicates the probability of obtaining results as extreme as the observed data or more extreme if H0 is true. If p ≤ the predetermined significance level (α = 0.05), H0 is rejected in favor of H1. Otherwise, H0 is retained but not proven true. Type I and II errors can occur when the true hypothesis is incorrectly rejected or retained.Hypothesis
HypothesisDr. Priyanka Jain
Ěý
The document discusses hypothesis testing, which involves testing a hypothesis about a population using a sample of data. It explains that a hypothesis test has four main steps: 1) stating the null and alternative hypotheses, where the null hypothesis asserts there is no difference between the sample and population, 2) setting the significance level, 3) determining the test statistic and critical region for rejecting the null hypothesis, and 4) making a decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on whether the test statistic falls in the critical region. Type I and type II errors are also defined. The document provides examples of null and alternative hypotheses using mathematical symbols and discusses how to determine if a p-value is statistically significant.Reporting Results of Statistical Analysis
Reporting Results of Statistical Analysis Centre for Social Initiative and Management
Ěý
The document discusses the limitations and criticisms of p-values in statistical significance testing, emphasizing the need for effect size and confidence intervals to better represent study findings. It highlights the difference between null and alternative hypotheses, the implications of type I and type II errors, and how sample size and multiple comparisons can affect the reliability of p-values. Ultimately, the document argues for a more nuanced understanding of statistical significance beyond conventional threshold values like p < .05.Hypothesis testing
Hypothesis testingSohail Patel
Ěý
This document discusses hypothesis testing and interpretation of data. It provides an example of two lecturers, Sandy and Mandy, who want to test whether providing seminar classes in addition to lectures improves student performance compared to lectures alone. The document outlines the steps in hypothesis testing: 1) Identify the research problem and variables, 2) Specify the null and alternative hypotheses, 3) Choose a significance level, 4) Identify the test statistic, 5) Determine the rejection region, and 6) Select the appropriate statistical test. It defines type 1 and type 2 errors and explains key concepts like the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, and significance level.Hypothesis Testing.pptx
Hypothesis Testing.pptxheencomm
Ěý
A hypothesis test examines two opposing hypotheses: the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the statement being tested, usually stating "no effect". The alternative hypothesis is what the researcher hopes to prove true. A hypothesis test uses a sample to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis based on a p-value and significance level. There are 5 steps: specify null and alternative hypotheses, set significance level, calculate test statistic and p-value, and draw a conclusion. Type I and II errors are possible - type I rejects a true null hypothesis, type II fails to reject a false null hypothesis.Basic Conecepts of Inferential Statistics _ şÝşÝߣshare.pptx
Basic Conecepts of Inferential Statistics _ şÝşÝߣshare.pptxElementary & Secondary Education Department, KP, Pakistan
Ěý
The document covers the foundational concepts of inferential statistics, including hypothesis testing, significance levels, and types of errors. It explains the principles of hypothesis formation, types of hypotheses, and the statistical methods used to analyze data, such as p-values and standard errors. Additionally, it discusses the risks of type I and type II errors in hypothesis testing and emphasizes the importance of carefully planning study designs.Hypothesis testing 1.0
Hypothesis testing 1.0Dr. C.V. Suresh Babu
Ěý
The document covers the fundamentals of hypothesis testing in research, explaining concepts such as significance levels, p-values, sampling errors, and types of errors in statistical tests. Hypothesis tests assess two conflicting theories regarding population properties, striving to provide evidence against the null hypothesis that assumes no effect. It emphasizes the importance of setting appropriate significance levels to reduce the risk of type I and type II errors in data interpretation.lecture no.7 computation.pptx
lecture no.7 computation.pptxssuser378d7c
Ěý
This document discusses hypothesis testing. It defines a hypothesis as a tentative statement about the relationship between variables. The null hypothesis proposes no relationship, while the alternative hypothesis proposes a relationship. There are two types of errors in hypothesis testing - type I errors occur when a true null hypothesis is rejected, and type II errors occur when a false null hypothesis is not rejected. Key concepts discussed include critical regions, critical values, significance levels, and one-tailed versus two-tailed tests.Hypothesis
HypothesisMmedsc Hahm
Ěý
The document discusses hypothesis testing, including defining the null and alternative hypotheses, types of errors, test statistics, and the process of hypothesis testing. Some key points:
- The null hypothesis states that a population parameter is equal to a specific value. The alternative hypothesis is paired with the null and states inequality.
- Type I errors occur when the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true. Type II errors occur when the null is not rejected when it is false.
- A test statistic is calculated based on sample data and compared to critical values to determine if the null hypothesis can be rejected.
- Hypothesis testing follows steps of stating hypotheses, choosing a significance level, collecting/analyzing data,Rm 3 Hypothesis
Rm 3 Hypothesisitsvineeth209
Ěý
Hypothesis testing is an important tool in research. A hypothesis is a statement or proposition that can be tested through scientific investigation. The null hypothesis represents the default position that there is no relationship between variables or no difference among groups. The alternative hypothesis is what the researcher aims to prove. Through hypothesis testing, researchers aim to reject the null hypothesis by collecting data and calculating the probability of the results if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is then compared to the pre-determined significance level, often 5%, to determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Proper hypothesis testing involves clearly stating the hypotheses, selecting a random sample, determining the appropriate statistical test based on the data, and interpreting the results.Definition of Hypothesis jynyyetbxhzwtrb xb
Definition of Hypothesis jynyyetbxhzwtrb xbgarefed500
Ěý
A hypothesis is a testable statement formulated to explain phenomena, serving as the basis for scientific inquiry. Hypothesis testing involves evaluating data to accept or reject a null hypothesis, with a focus on significance levels and p-values. It also discusses type I and type II errors, highlighting their inverse relationship and the trade-off researchers face when balancing the two.HypothesisT I think I will be in there for the
HypothesisT I think I will be in there for themarialuisarada
Ěý
The document discusses the principles and procedures of hypothesis testing in statistics, detailing how to formulate null and alternative hypotheses, and the significance of p-values. It outlines the six steps of hypothesis testing, including generating hypotheses, checking assumptions, and determining the significance level, while also addressing type I and type II errors. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between statistical significance and clinical importance in research findings.Basis of statistical inference
Basis of statistical inferencezahidacademy
Ěý
Statistical inference involves using probability concepts to draw conclusions about populations based on samples. It includes point and range estimation to estimate population values, as well as hypothesis testing to test hypotheses about populations. Hypothesis testing involves making a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis before collecting sample data. Common hypotheses include claims of no difference or significant differences. Statistical tests like z-tests, t-tests, and chi-square tests are used to either accept or reject the null hypothesis based on the sample data and a significance level, typically 5%. P-values indicate the probability of observing the sample results by chance. Type 1 and type 2 errors can occur when making inferences about hypotheses.Hypothesis Testing.pptx
Hypothesis Testing.pptxMelba Shaya Sweety
Ěý
Hypothesis testing involves making tentative assumptions about population parameters or distributions, called null hypotheses (H0). Alternative hypotheses (Ha) are also defined. Sample data is used to determine if H0 can be rejected. If rejected, the conclusion is that Ha is true. There are two types of errors that can occur - type I errors when a true H0 is rejected, and type II errors when a false H0 is not rejected. The significance level and power aim to control these errors. One-tailed and two-tailed tests look at relationships between variables in different ways.Chapter 20 and 21 combined testing hypotheses about proportions 2013
Chapter 20 and 21 combined testing hypotheses about proportions 2013calculistictt
Ěý
This document discusses hypotheses testing and the reasoning behind it. It explains that hypotheses testing involves proposing a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis based on a parameter of interest. Data is then analyzed to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Specifically:
1) The null hypothesis proposes a baseline model or value for a parameter.
2) Statistics are calculated based on the data and compared to what we would expect if the null hypothesis is true.
3) If the results are inconsistent enough with the null hypothesis, we can reject it in favor of the alternative hypothesis. Otherwise we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
The goal is to quantify how unlikely the results would be if the null hypothesis is true, hypothesis test
hypothesis testUnsa Shakir
Ěý
This document provides an overview of estimation and hypothesis testing. It defines key statistical concepts like population and sample, parameters and estimates, and introduces the two main methods in inferential statistics - estimation and hypothesis testing.
It explains that hypothesis testing involves setting a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (Ha), calculating a test statistic, determining a p-value, and making a decision to accept or reject the null hypothesis based on the p-value and significance level. The four main steps of hypothesis testing are outlined as setting hypotheses, calculating a test statistic, determining the p-value, and making a conclusion.
Examples are provided to demonstrate left-tailed, right-tailed, and two-tailed hypothesis testsTesting Of Hypothesis
Testing Of HypothesisSWATI SINGH
Ěý
The document explains hypothesis testing as a statistical method for evaluating claims about a population parameter, involving a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (H1). It outlines the significance level, types of errors (Type I and Type II), and provides procedures for conducting hypothesis tests using either the rejection region method or p-value estimation method. Additionally, it discusses one-tailed and two-tailed tests, emphasizing the importance of clear hypotheses in guiding research outcomes.Test of hypothesis
Test of hypothesisvikramlawand
Ěý
The document discusses hypothesis testing in research. It defines a hypothesis as a proposition that can be tested scientifically. The key points are:
- A hypothesis aims to explain a phenomenon and can be tested objectively. Common hypotheses compare two groups or variables.
- Statistical hypothesis testing involves a null hypothesis (H0) and alternative hypothesis (Ha). H0 is the initial assumption being tested, while Ha is what would be accepted if H0 is rejected.
- Type I errors incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis. Type II errors fail to reject a false null hypothesis. Hypothesis tests aim to control the probability of type I errors.
- The significance level is the probability of a type I error,Basic Conecepts of Inferential Statistics _ şÝşÝߣshare.pptx
Basic Conecepts of Inferential Statistics _ şÝşÝߣshare.pptxElementary & Secondary Education Department, KP, Pakistan
Ěý
Presentation 2
- 1. RAMESH DEBUR Hypothesis testing
- 2. The Way Back Formulate a research Question Develop a research Methodology Collected Data Sorted Data
- 3. The Way Forward Introduction GENERATE A HYPOTHESIS NULL HYPOTHESIS ALTERNATIVE HYPOTHESIS Significance The p Value Errors TYPE 1 TYPE 2 ACCEPT OR REJECT HYPOTHESIS INFERENCE & PRESENTATION OF THE DATA
- 4. Hypothesis Testing Scientific Hypothesis testing – A Deductive method of accepting or rejecting a hypothetical statement
- 5. Definition A hypothesis consists either of a suggested explanation for a phenomenon Eg: Gastric Juices produces Hunger or A reasoned proposal suggesting a possible correlation between multiple phenomena Eg: People who smoke more cigarettes are at a higher risk of developing lung cancer
- 6. Therefore….. Hypothesis testing implies either accepting or rejecting a certain statement. Generating a Hypothesis In Scientific Research the hypothesis is an offshoot of the research question Eg: Do people who smoke more cigarettes increase their risk of developing Lung Cancer
- 7. The Logic of Hypothesis Testing All hypothesis are false until proven true The farther away from falsification the truer is the hypothesis A Hypothesis is NEVER a Fact. We accept a hypothesis as true until it is falsified Eg: Columbus wants to discover a route to India Columbus Discovers America Every body he sees are called Indian – Hypothesis Later learns they are not Indian – Hypothesis falsified
- 8. The NULL Hypothesis The exact opposite of the perceived effect or change Eg: Gastric Juices DOES NOT cause Hunger Smoking DOES NOT Increase the risk of Developing Lung Cancer
- 9. The Alternate Hypothesis The Exact opposite of the NULL Hypothesis Called alternate because the falsification is the primary logic of hypothesis testing Gastric Juices DOES NOT cause Hunger Smoking DOES NOT Increase the risk of Developing Lung Cancer Easier to Falsify things than prove facts?????
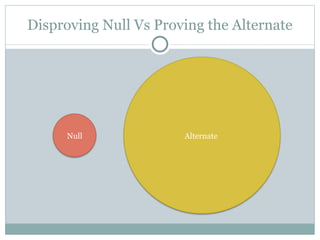
- 10. Disproving Null Vs Proving the Alternate Null Alternate
- 11. THE NEXT QUESTION WHEN DO WE REJECT THE NULL HYPOTHESIS ANSWER : WHEN THE CHANCES OF IT BEING TRUE ARE VERY SLIM ( NON SIGNIFICANT) PROBABILITY TESTING
- 12. Probability (prob·a·bil·i·ty) Similar to Chance: Derived from the Noun Probable What is a probability : The chance of a event occurring at any given time The likelihood of an event having a particular outcome Eg: Flipping a coin All probability is between 0 and 1
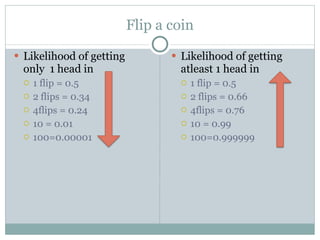
- 13. Flip a coin Likelihood of getting only 1 head in 1 flip = 0.5 2 flips = 0.34 4flips = 0.24 10 = 0.01 100=0.00001 Likelihood of getting atleast 1 head in 1 flip = 0.5 2 flips = 0.66 4flips = 0.76 10 = 0.99 100=0.999999
- 14. Probability as related to hypothesis testing The p value The likelihood that the data collected is equal to or more extreme than the null hypothesis (logic: The Null hypothesis is the extreme value of an experiment) Alternatively: The probability that the expected outcome occurred purely by chance
- 15. Significance - Definition The significance level of a test is the probability that the test statistic will reject the null hypothesis when the [hypothesis] is true .
- 16. IN REAL TERMS Get Test statistic (outcome of research ) Null hypothesis – test statistic if > chance : accept test and reject null If ≤ chance : reject test Generally the significance is kept at 0.05 or 1 chance in 100 or 0.001( 1 in 1000)
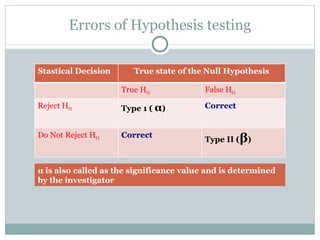
- 17. Errors of Hypothesis testing α is also called as the significance value and is determined by the investigator Stastical Decision True state of the Null Hypothesis True H O False H O Reject H O Type 1 ( α ) Correct Do Not Reject H O Correct Type II ( β )
- 18. A type 1 error is considered much more serious than a type 2 error Why? EG. A new drug is introduced into the market which can potentially cure hypertension but can also cause sudden death. Evaluate the chances of sudden death by the drug Statistical Decision True state of the Null Hypothesis True H O NO Death False H O Death Reject H O Type 1 ( α ) (Accept drug) Correct (Reject drug) Do Not Reject H O Correct (Accept Drug) Type II ( β ) (Reject Drug)