Presentation 3 drilling bits
- 1. OPERATIONS GEOLOGY PRESENTATIONS Presentation 3: Drilling Bits 07 October 2016Ali Trichelli
- 2.  Drilling Bits  Bit Types  Bit Classification  Bit Grading Legend
- 3.  Drill bits are the most critical item of a rotary rig operation. They are the most refined rig tools, available in many styles and sizes. There are two main types of drilling bits and there are several variations within these types of bits.  The two types of bits are:  Roller Cone Bits (Tri-cone bits)  Milled Tooth Bits  Insert Bits  Fixed Cutter Bits  Drag Bits  PDC (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact) & Diamond Bits  TSP (Thermally Stable PDC) Bits Introduction
- 4. These bits have steel teeth milled on the cones. These teeth vary in size and shape, depending on the formation they are expected to drill. Roller Cone Bits (Tri-cone bits)- Milled Tooth Bits
- 5. Roller Cone Bits (Tri-cone bits)- Insert Bits  These bits have tungten carbide teeth (buttons) inserted into the cones and not milled into them. These bits are very much harder and last longer when drilling hard formations ( and of course are more expensive). Teeth vary in size and shape, depending on the formation they are expected to drill.
- 6. Common Features of the Roller Cone Bits (Tri-cone bits)  Fluid Courses: To allow the drilling fluid to circulate through the bit and carry away the cuttings. These courses were conventional at first then jet nozzles were introduced as wells were drilled deeper and hydraulic force was needed to clean the hole.
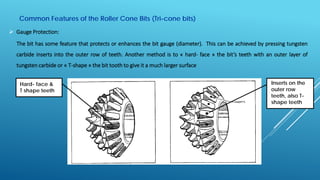
- 7. Common Features of the Roller Cone Bits (Tri-cone bits)  Gauge Protection: The bit has some feature that protects or enhances the bit gauge (diameter). This can be achieved by pressing tungsten carbide inserts into the outer row of teeth. Another method is to « hard- face » the bit’s teeth with an outer layer of tungsten carbide or « T-shape » the bit tooth to give it a much larger surface Inserts on the outer row teeth, also T- shape teeth Hard- face & T shape teeth
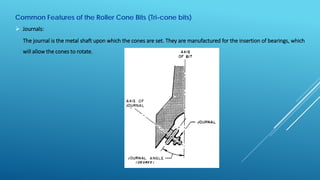
- 8. Common Features of the Roller Cone Bits (Tri-cone bits)  Journals: The journal is the metal shaft upon which the cones are set. They are manufactured for the insertion of bearings, which will allow the cones to rotate.
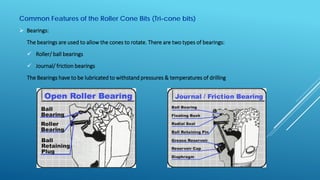
- 9. Common Features of the Roller Cone Bits (Tri-cone bits)  Bearings: The bearings are used to allow the cones to rotate. There are two types of bearings:  Roller/ ball bearings  Journal/ friction bearings The Bearings have to be lubricated to withstand pressures & temperatures of drilling
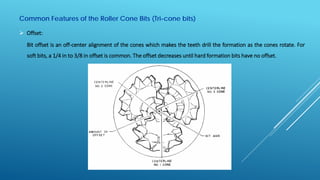
- 10. Common Features of the Roller Cone Bits (Tri-cone bits)  Offset: Bit offset is an off-center alignment of the cones which makes the teeth drill the formation as the cones rotate. For soft bits, a 1/4 in to 3/8 in offset is common. The offset decreases until hard formation bits have no offset.
- 11. Fixed Cutter Bits – Drag Bits  These bits are the earliest types. The cutting structure is sharpened steel and can only be used in soft formations; they are rarely used today.
- 12. Fixed Cutter Bits – PDC (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact) & Diamond Bits  Diamond bits use natural diamond as the cutting structure. They are usually slightly smaller than tri-cone bits to prevent diamond damage while RIH. These bits have no bearings and hence they can be run for long periods and drill almost any formation.  PDC bits have cutting structures which are composed of man-made diamond dust / crystals bonded to tungsten carbide stud. These studs are either pressed or molded into the bit body. The cutters are self sharpening (by exposing new crystals while others are broken off). These bits are used to drill soft to medium and hard formations.
- 13. Fixed Cutter Bits – TSP (Thermally Stable PDC) Bits  These bits are manufactured in the same manner as PDC bits but are tolerant to much higher temperatures than PDC bits.
- 14. Drill Bit Classification  Drill bits are classified by IADC 5International Association of Drilling Contractor) to identify similar bit types made from different manufacturers.  Roller Cone (Tri-cone) bit Classification:  Fixed Cutter Bit Classification: First Digit: an alphabet to define the type of cutter and the body material. D: natural diamond matrix body M: matrix body PDC S: steel body PDC T: matrix body TSP O: others
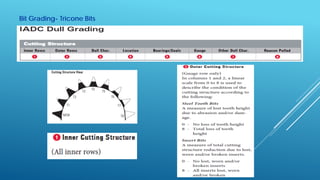
- 15. Bit Grading- Tricone Bits
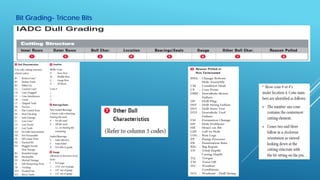
- 16. Bit Grading- Tricone Bits
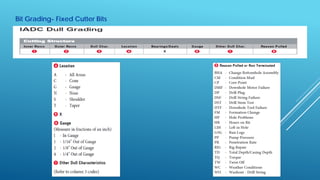
- 17. Bit Grading- Fixed Cutter Bits
- 18. Bit Grading- Fixed Cutter Bits
- 19. Bit Grading- Fixed Cutter Bits
- 20. Next Presentation Mudlogging  Inside the Mudlogging Unit  Main Mudlogging Services  Major Responsibilities of the Mudloggers  Lag Time Determination  Typical Monitored Parameters  Standard Mudlogging Sensors  The Gas System  Real Time Data Display & Transmission  Deliverables of the Mudlogging Contractor  Issues with Mudlogging