Presentation 7 casing & cementing
- 1. OPERATIONS GEOLOGY PRESENTATIONS Presentation 7: Casing & Cementing 25 November 2016Ali Trichelli
- 2. LEGEND  Casing & Cementing  Overview  Casing Accessories & Casing Running Tools  Typical Cementing System ( for a land well)  The Cementing Job (of a Casing String)
- 3. Overview  Every well is drilled in sections and each section has to be cased and cemented (see well profile)  Casing is a steel pipe that has to be set in the borehole to prevent it from caving in and to seal off formations  Casing has to be cemented and held in place  Casing comes in different lengths (4.88m to 14.63m) and Diameters (5in to 30in). Casing also comes in differents grades or strengths depending on the well’s characteristics  The main casing types are:  Conductor casing to prevent cave-ins of near surface formations  Surface casing to avoid contamination of the fresh water zone of near surface formations  Intermediate casing to seal off troublesome zones to prevent problems when drilling the deeper formations. Deep wells may require more than one intermediate casing  Production casing or liner to protect and isolate the producing zone
- 4. Casing Accessories & Casing Running Tools  Casing Running Tools include Heavy duty elevators, casing spiders and power casing tongs. These tongs are used to screw the threaded connections of the casing joints together and torque them to the correct amount.  Liner hanger is used in case the production casing is not run all the way to surface Casing Accessories Casing Running Tools Casing Spider Casing Elevator Power Casing Tongs
- 5. Typical Cementing System for a Land Well The one way valve in the float collar lets the casing string float into the well to lessen the load on the hoisting system
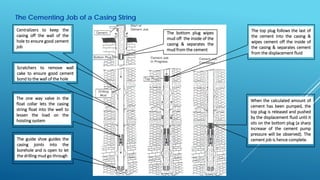
- 6. The Cementing Job of a Casing String The guide shoe guides the casing joints into the borehole and is open to let the drilling mud go through The one way valve in the float collar lets the casing string float into the well to lessen the load on the hoisting system Centralizers to keep the casing off the wall of the hole to ensure good cement job Scratchers to remove wall cake to ensure good cement bond to the wall of the hole The bottom plug wipes mud off the inside of the casing & separates the mud from the cement The top plug follows the last of the cement into the casing & wipes cement off the inside of the casing & separates cement from the displacement fluid When the calculated amount of cement has been pumped, the top plug is released and pushed by the displacement fluid until it sits on the bottom plug (a sharp increase of the cement pump pressure will be observed). The cement job is hence complete.
- 7. Next Presentation  Cutting Sample Examination  Introduction  Source of the Cutting Samples  Lag Time Determination  Cutting Preparation & Sample Types  Handling of the Drill Cutting Samples  Sample Contamination  Cuttings Sample Description  Rock Type  Classification  Color  Hardness/ Induration  Grain Size/ Grain Shape  Sorting  Luster  Cementation/ Matrix  Visual Porosity  Accessories/ Inclusions  Hydrocarbon Show Evaluation- Oil  Hydrocarbon Show Evaluation- Gas  Shipment of the Cutting Samples