Presentation of sound unit 10
- 1. SUBJECT : SCIENCE BY MS. naila anjum
- 2. Unit :10 Sound
- 3. Overview ŌĆó The Facts of Sound ŌĆó Examples of objects produces sound ŌĆó The Ear and Sound ŌĆó Sound Vocabulary ŌĆó Musical Instruments and Sound
- 4. The Facts Sound ŌĆ” 1. Is a form of energy produced & transmitted by vibrating matter 2. Travels in waves 3. Travels more quickly through solids than liquids or gases
- 5. Kinds of sounds 1. Musical sound: Musical sound results when regular vibrations of the voice or a musical instrument are produced. 2. Noise sound: Noise results when irregular vibrations are made at irregular times.
- 6. Examples of things which produces sounds
- 7. The Ear ŌĆó Sound is carried to our ears through vibrating air molecules. ŌĆó Our ears take in sound waves & turn them into signals that go to our brains. ŌĆó Sound waves move through 3 parts of the ear; outer ear, middle ear, & inner ear. Middle Ear
- 8. Vibration - Back and forth movement of molecules of matter - For example,
- 9. Compression - Where molecules are being pressed together as the sound waves move through matter - For example, - a wave travels through the springs just like sound waves travel through the air - the places where the springs are close together are like compressions in the air.
- 10. Sound Waves - Alternating areas of high & low pressure in the air - ALL sound is carried through matter as sound waves - Sound waves move out in ALL directions from a vibrating object
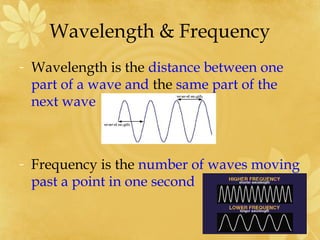
- 11. Wavelength & Frequency - Wavelength is the distance between one part of a wave and the same part of the next wave - Frequency is the number of waves moving past a point in one second
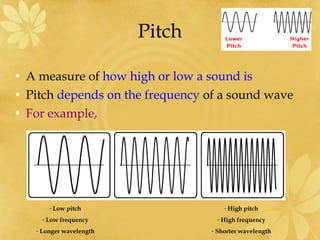
- 12. Pitch ŌĆó A measure of how high or low a sound is ŌĆó Pitch depends on the frequency of a sound wave ŌĆó For example, - Low pitch - High pitch - Low frequency - High frequency - Longer wavelength - Shorter wavelength
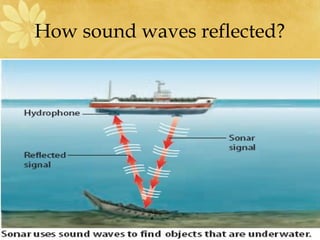
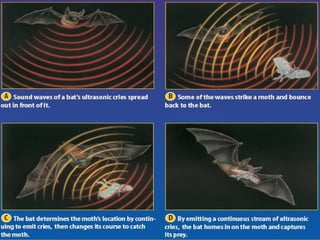
- 13. Reflection of sound - An instrument that uses reflected sound waves to find underwater objects - For example, Humans use sonar to locate or map objects Animals use sonar or echo location to find their prey; these sounds have such a high pitch or frequency that the human ear cannot hear
- 14. How sound waves reflected?
- 17. Sound and Instruments - Instruments can be played at different pitches by changing lengths of different parts. - For example, - Another way to make different pitches is to change the thickness of the material that vibrates. - For example, A tromboneŌĆÖs mute absorbs some of the sound waves produced, thus producing a softer note when played.
- 18. The End