Presentation on Computer Mouse
Download as PPTX, PDF28 likes26,054 views
What is Mouse ? | Invention | Activities | Types | How mouse works ? | Mouse ports | How has the design being changed ?
1 of 18
Downloaded 222 times














Recommended
Presentation on Mouse



Presentation on MouseHaseeb ur Rehman
?
A mouse is a handheld input device that controls the on-screen cursor and allows users to select, open, and manipulate items in a graphical user interface (GUI). It contains buttons that perform tasks like selecting objects and opening programs. Mice connect to computers through ports like USB or wirelessly. There are different types of mice including mechanical mice with rolling balls, optical mice that use light sensors, and wireless mice that connect without wires. The mouse was invented in 1968 by Douglas Engelbart to help users control computers.Computer keyboard



Computer keyboardCheneta Kenny Calvo
?
A keyboard is an input device that contains keys users press to enter data and instructions into a computer. Christopher Latham Sholes invented the modern keyboard design in 1868 with his patent of the typewriter. There are several types of keyboards including standard, laptop, gaming, ergonomic, laser/infrared, and rollup keyboards. Keyboards can connect via wired connections like USB or wireless connections like Bluetooth. Keyboards contain letter keys, number keys, function keys, navigation keys, and special keys like shift, tab, escape and control keys. Computer Mouse



Computer MouseFathimaLidiya
?
what is computer mouse? Mouse is an input device. Parts of a mouse, uses and different types of mouse actions. Different types of mouse click are left click, right click, double click and dragging. Parts of mouse include left button, right button and scroll wheel.Input and output devices ppt



Input and output devices pptbjslides
?
Input devices capture information from the external environment and translate it into a format readable by computers. Common input devices include keyboards, pointing devices like mice and trackballs, game controllers, scanners, styluses, microphones, and digital cameras. Output devices take the information processed by computers and present it to users in a form they can understand, like monitors to display visual information and speakers to output audio.Parts of a Computer



Parts of a ComputerMatt Shea
?
The parts of a computer slideshow for grades 3-4. Includes a quiz and activity. The activity is supposed to have the students act out the parts of a computer.
*ROM is READ ONLY MEMORY - I had a typo...sorry!Scanners



ScannersBits
?
Scanner is a device that translates hard copy into soft copy.
It translates data on a sheet of paper to a form that can be stored on a computer.
In other words converting of a document into digital format.
Data can be in either form of text or graphics.
Output devices of Computer



Output devices of ComputerShaikh Alam
?
An output device is computer hardware that uses received data and commands from a computer in order to perform a task.
Any peripheral that receives data from a computer, usually for display, projection, or physical reproduction.
Computer hardware equipment used to communicate the results of data processing carried out by a computer to the outside world.
Presentation on input devices



Presentation on input devicesNitish Xavier Tirkey
?
This document discusses different types of input devices for computers. It describes keyboards, mice, scanners, joysticks, and digital cameras. Keyboards allow data entry by pressing keys and come in standard, multimedia, and wireless varieties. Mice are popular pointing devices that have buttons and can be clicked to perform tasks. Scanners are used to input data directly from documents and include MICR, OMR, OCR, and barcode readers. Joysticks are used for game controls and have a ball and stick. Digital cameras create digital images that computers can process and interpret.Using the Mouse



Using the MouseLisa Hartman
?
The document discusses the basic functions and uses of a computer mouse. It describes the left button, right button, and scroll wheel. The main mouse functions covered are clicking, double-clicking, dragging to move or highlight items, and right-clicking for shortcuts. Different mouse pointer symbols and their meanings are also outlined.Output devices



Output devicesyaseen baig
?
The document discusses various types of computer output devices. It describes monitors, printers, speakers, and other devices. It provides details on different monitor technologies like LCD, plasma, and CRT. It also explains different printer types such as inkjet, laser, and dot matrix printers. Other output devices covered include projectors, interactive whiteboards, and accessories for games. The document emphasizes that output devices are critical for users to experience and interact with processed data from a computer."MOUSE" HARDWARE 



"MOUSE" HARDWARE Aqsa Mushtaq
?
The document discusses the history and types of computer mice. It explains that the mouse was invented in 1968 by Douglas Engelbart to control the movement of the cursor on a screen. Mice come in various forms such as optical mice which use light sensors rather than a ball, wireless mice which communicate via radio signals, and trackball mice where the ball is stationary and rolled by the thumb. The mouse's design has evolved over time from square wooden models to smaller, more ergonomic designs with additional features like scroll wheels.Computer Components



Computer ComponentsBeth Sockman
?
This document provides an overview of common computer components and terms. It describes typical hardware components like the monitor, motherboard, CPU, RAM memory, expansion cards, power supply, storage drives, keyboard and mouse. It also discusses software types, input/output devices, memory units, networking, and other concepts. Diagrams show the relationship between input, CPU, and output devices, as well as examples of RAM usage.Input devices



Input devicesAdnan Malak
?
This document discusses various types of computer input devices. It describes keyboards, mice, joysticks, light pens, trackballs, scanners, microphones, optical character readers, bar code readers, and voice recognition chips as common input devices. Keyboards and mice are highlighted as the most popular input devices, with keyboards allowing text input and mice used to control cursor movement.Computer Keyboard



Computer KeyboardFathimaLidiya
?
Keyboard is an input device. It has various keys with specific functions. Keys like Alphabet keys, Number keys, Enter keys, delete key, space bar key, caps lock key, Num lock key, Function key, Shift key, etc. This slide will take you through different keys and its functions. For better understanding, I have included pictures of different types of keys.PPT on Keyboard



PPT on KeyboardSanjuktaSahoo5
?
This PPT talks about all the components of a keyboard, who invented it and advice for increasing speed. It is based on class 9 IT (subject code-402) Chapter 7 'Data Entry and Keyboard Skills'.Presentation on input devices... 



Presentation on input devices... simmi khera
?
The document discusses various input devices used to input data and instructions into computers. It describes keyboards, mice, joysticks, touch screens, microphones, scanners, and bar code readers. Keyboards are the most commonly used input device and come in normal and multimedia varieties. Mice can be traditional ball mice or newer optical mice. Scanners convert printed images to digital form, and can be flatbed or handheld models.PPT on INPUT & OUTPUT DEVICES



PPT on INPUT & OUTPUT DEVICESHarsh Raj
?
Input And Output Devices
Prepared By Harsh ,Mehar , Astha and Kalpana
Students Of Birla Institute Of Technology,Patna Campus
Department: BBA Session 2016-2019
Guided By : Ritesh Ravi Sir (Our Computer Teacher)Computer Software introduction



Computer Software introductionfaisalahmed2017
?
in Short words we explain Computer software introduction , it will give u a short introduction about software Central Processing Unit(CPU)



Central Processing Unit(CPU)ANSANS8
?
The CPU, or central processing unit, is the brain of the computer that performs all data processing and controls other parts. It contains at least one processor chip that can have multiple processing cores and operates at a clock speed measured in megahertz or gigahertz. The CPU fetches instructions from memory, decodes and executes them by performing calculations in its arithmetic logic unit and control unit, and stores results back in memory. It has registers for temporary storage and a memory unit for primary storage.Basic of Computer fundamental 



Basic of Computer fundamental Sohan Grover
?
This PPT Cover all basic Fundamental Concept Of Computer Fundamental.
If any Query contact Me :-99964-02177The mouse



The mousejimmygav
?
The mouse was invented in the 1960s at Stanford University and helped popularize graphical user interfaces. It controls an on-screen pointer to select items, access menus, and interact with programs. Early mice were blocky but evolved into sleeker designs from many companies. The mouse established computers as tools for graphics and popularized input techniques like clicking, dragging, and right-clicking. Variants include trackballs, trackpads, and keyboard pointers for less space than a traditional mouse.Basic of computer



Basic of computerM? ?we?ome
?
The document describes the basic components and functions of a computer system. It explains that the monitor displays visual output, while the CPU contains the computer's processor and can be in desktop or tower cases. The document outlines different input devices like keyboards, mice, scanners, and their functions. It also discusses internal memory components like RAM and ROM that help the CPU process and store information, as well as long-term storage devices like hard disk drives. Finally, it mentions that the motherboard coordinates communication between all computer components and is essential to the computer's operation.Types of input-output devices



Types of input-output devicesriyadingria
?
Input devices such as keyboards, mice, scanners, and touchscreens convert human instructions and data into a format computers can understand. These devices allow users to enter information and control the computer. Output devices like monitors, printers, and speakers take the processed data from computers and present it to users in a human-readable form such as displaying images or playing sounds.Types of computer



Types of computerFrya Lora
?
Computers are classified into three main types based on size and capacity: mainframe computers which are large and powerful used by many users at once in large organizations; minicomputers which are medium-sized used by many users at once in small organizations; and microcomputers or personal computers which are small and meant for individual use like desktops, laptops, and other mobile devices.Peripheral devices



Peripheral devicesAnnie Farooq
?
Peripheral devices connect to computers and are controlled by them. They can be either input devices, like keyboards and mice, which allow data to enter the computer, or output devices, like monitors and printers, which allow the computer to present information. Common input devices include keyboards, mice, cameras, and microphones. Common output devices are monitors, printers, and speakers.Beginning computer basics 



Beginning computer basics Vicente Antofina
?
This document provides an introduction to basic computer concepts. It begins by outlining the goals of learning common computer terms, hardware, software and the desktop. It then defines a computer as a device that accepts input, processes data, stores and retrieves information, and provides output. Hardware is described as the physical components like the console, monitor, mouse, keyboard and printers. Software is defined as the set of instructions that directs the hardware. The desktop, icons, taskbar, start button and system tray are introduced as core elements of the graphical user interface. Basic mouse and keyboard functions are also reviewed.Input devices presentation



Input devices presentationTayyab Hussain
?
Input devices allow users to enter data and interact with computers. Some common input devices are keyboards, mice, touchpads, joysticks, touch screens, scanners, and graphics tablets. Keyboards allow text entry and come in various sizes. Mice control on-screen cursors by detecting finger movement on surfaces. Touchpads are alternatives to mice for laptops. Joysticks are used for game controls. Touch screens are displays that can detect touch input. Scanners digitize images. Graphics tablets enable hand drawing of images and graphics.Introduction to Basic Computer Concepts Presentation



Introduction to Basic Computer Concepts PresentationAna Tan
?
The document discusses the history and evolution of computers from early calculating aids like the abacus to modern computers. It describes inventions like the Pascaline, the first mechanical calculator, the Difference Engine, an early mechanical computer, and the ENIAC, one of the first general-purpose electronic computers. It then discusses the development of personal computers starting in the 1970s and the introduction of devices like the Apple I, IBM PC, and early netbooks.Moues



MouesRavi Kodoli
?
Douglas Engelbart invented the computer mouse in 1964 to facilitate graphical user interfaces and pointing on digital displays. The mouse uses an optical or mechanical system to detect movement over a surface and translate it to on-screen cursor movement. It consists of a ball or optical sensor, buttons, and an electronic circuit board that encodes motion data for transmission to and interpretation by the connected computer. Modern mice use optical sensors rather than mechanical components, improving durability and versatility.computer-mouse-sir-tariq.pptx



computer-mouse-sir-tariq.pptxTalhaHussain58
?
The document discusses the history and types of computer mice. It begins by defining a mouse as a device that allows users to control the cursor and select objects on screen. The first mouse was invented in 1968 and used a rolling ball to detect movement. Over time, mice evolved to use optical sensors instead of balls and became wireless. Different types of mice include optical, wireless, trackball, and vertical mice. The mouse design has changed significantly over time to be smaller and more ergonomic while improving motion detection.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Using the Mouse



Using the MouseLisa Hartman
?
The document discusses the basic functions and uses of a computer mouse. It describes the left button, right button, and scroll wheel. The main mouse functions covered are clicking, double-clicking, dragging to move or highlight items, and right-clicking for shortcuts. Different mouse pointer symbols and their meanings are also outlined.Output devices



Output devicesyaseen baig
?
The document discusses various types of computer output devices. It describes monitors, printers, speakers, and other devices. It provides details on different monitor technologies like LCD, plasma, and CRT. It also explains different printer types such as inkjet, laser, and dot matrix printers. Other output devices covered include projectors, interactive whiteboards, and accessories for games. The document emphasizes that output devices are critical for users to experience and interact with processed data from a computer."MOUSE" HARDWARE 



"MOUSE" HARDWARE Aqsa Mushtaq
?
The document discusses the history and types of computer mice. It explains that the mouse was invented in 1968 by Douglas Engelbart to control the movement of the cursor on a screen. Mice come in various forms such as optical mice which use light sensors rather than a ball, wireless mice which communicate via radio signals, and trackball mice where the ball is stationary and rolled by the thumb. The mouse's design has evolved over time from square wooden models to smaller, more ergonomic designs with additional features like scroll wheels.Computer Components



Computer ComponentsBeth Sockman
?
This document provides an overview of common computer components and terms. It describes typical hardware components like the monitor, motherboard, CPU, RAM memory, expansion cards, power supply, storage drives, keyboard and mouse. It also discusses software types, input/output devices, memory units, networking, and other concepts. Diagrams show the relationship between input, CPU, and output devices, as well as examples of RAM usage.Input devices



Input devicesAdnan Malak
?
This document discusses various types of computer input devices. It describes keyboards, mice, joysticks, light pens, trackballs, scanners, microphones, optical character readers, bar code readers, and voice recognition chips as common input devices. Keyboards and mice are highlighted as the most popular input devices, with keyboards allowing text input and mice used to control cursor movement.Computer Keyboard



Computer KeyboardFathimaLidiya
?
Keyboard is an input device. It has various keys with specific functions. Keys like Alphabet keys, Number keys, Enter keys, delete key, space bar key, caps lock key, Num lock key, Function key, Shift key, etc. This slide will take you through different keys and its functions. For better understanding, I have included pictures of different types of keys.PPT on Keyboard



PPT on KeyboardSanjuktaSahoo5
?
This PPT talks about all the components of a keyboard, who invented it and advice for increasing speed. It is based on class 9 IT (subject code-402) Chapter 7 'Data Entry and Keyboard Skills'.Presentation on input devices... 



Presentation on input devices... simmi khera
?
The document discusses various input devices used to input data and instructions into computers. It describes keyboards, mice, joysticks, touch screens, microphones, scanners, and bar code readers. Keyboards are the most commonly used input device and come in normal and multimedia varieties. Mice can be traditional ball mice or newer optical mice. Scanners convert printed images to digital form, and can be flatbed or handheld models.PPT on INPUT & OUTPUT DEVICES



PPT on INPUT & OUTPUT DEVICESHarsh Raj
?
Input And Output Devices
Prepared By Harsh ,Mehar , Astha and Kalpana
Students Of Birla Institute Of Technology,Patna Campus
Department: BBA Session 2016-2019
Guided By : Ritesh Ravi Sir (Our Computer Teacher)Computer Software introduction



Computer Software introductionfaisalahmed2017
?
in Short words we explain Computer software introduction , it will give u a short introduction about software Central Processing Unit(CPU)



Central Processing Unit(CPU)ANSANS8
?
The CPU, or central processing unit, is the brain of the computer that performs all data processing and controls other parts. It contains at least one processor chip that can have multiple processing cores and operates at a clock speed measured in megahertz or gigahertz. The CPU fetches instructions from memory, decodes and executes them by performing calculations in its arithmetic logic unit and control unit, and stores results back in memory. It has registers for temporary storage and a memory unit for primary storage.Basic of Computer fundamental 



Basic of Computer fundamental Sohan Grover
?
This PPT Cover all basic Fundamental Concept Of Computer Fundamental.
If any Query contact Me :-99964-02177The mouse



The mousejimmygav
?
The mouse was invented in the 1960s at Stanford University and helped popularize graphical user interfaces. It controls an on-screen pointer to select items, access menus, and interact with programs. Early mice were blocky but evolved into sleeker designs from many companies. The mouse established computers as tools for graphics and popularized input techniques like clicking, dragging, and right-clicking. Variants include trackballs, trackpads, and keyboard pointers for less space than a traditional mouse.Basic of computer



Basic of computerM? ?we?ome
?
The document describes the basic components and functions of a computer system. It explains that the monitor displays visual output, while the CPU contains the computer's processor and can be in desktop or tower cases. The document outlines different input devices like keyboards, mice, scanners, and their functions. It also discusses internal memory components like RAM and ROM that help the CPU process and store information, as well as long-term storage devices like hard disk drives. Finally, it mentions that the motherboard coordinates communication between all computer components and is essential to the computer's operation.Types of input-output devices



Types of input-output devicesriyadingria
?
Input devices such as keyboards, mice, scanners, and touchscreens convert human instructions and data into a format computers can understand. These devices allow users to enter information and control the computer. Output devices like monitors, printers, and speakers take the processed data from computers and present it to users in a human-readable form such as displaying images or playing sounds.Types of computer



Types of computerFrya Lora
?
Computers are classified into three main types based on size and capacity: mainframe computers which are large and powerful used by many users at once in large organizations; minicomputers which are medium-sized used by many users at once in small organizations; and microcomputers or personal computers which are small and meant for individual use like desktops, laptops, and other mobile devices.Peripheral devices



Peripheral devicesAnnie Farooq
?
Peripheral devices connect to computers and are controlled by them. They can be either input devices, like keyboards and mice, which allow data to enter the computer, or output devices, like monitors and printers, which allow the computer to present information. Common input devices include keyboards, mice, cameras, and microphones. Common output devices are monitors, printers, and speakers.Beginning computer basics 



Beginning computer basics Vicente Antofina
?
This document provides an introduction to basic computer concepts. It begins by outlining the goals of learning common computer terms, hardware, software and the desktop. It then defines a computer as a device that accepts input, processes data, stores and retrieves information, and provides output. Hardware is described as the physical components like the console, monitor, mouse, keyboard and printers. Software is defined as the set of instructions that directs the hardware. The desktop, icons, taskbar, start button and system tray are introduced as core elements of the graphical user interface. Basic mouse and keyboard functions are also reviewed.Input devices presentation



Input devices presentationTayyab Hussain
?
Input devices allow users to enter data and interact with computers. Some common input devices are keyboards, mice, touchpads, joysticks, touch screens, scanners, and graphics tablets. Keyboards allow text entry and come in various sizes. Mice control on-screen cursors by detecting finger movement on surfaces. Touchpads are alternatives to mice for laptops. Joysticks are used for game controls. Touch screens are displays that can detect touch input. Scanners digitize images. Graphics tablets enable hand drawing of images and graphics.Introduction to Basic Computer Concepts Presentation



Introduction to Basic Computer Concepts PresentationAna Tan
?
The document discusses the history and evolution of computers from early calculating aids like the abacus to modern computers. It describes inventions like the Pascaline, the first mechanical calculator, the Difference Engine, an early mechanical computer, and the ENIAC, one of the first general-purpose electronic computers. It then discusses the development of personal computers starting in the 1970s and the introduction of devices like the Apple I, IBM PC, and early netbooks.Similar to Presentation on Computer Mouse (20)
Moues



MouesRavi Kodoli
?
Douglas Engelbart invented the computer mouse in 1964 to facilitate graphical user interfaces and pointing on digital displays. The mouse uses an optical or mechanical system to detect movement over a surface and translate it to on-screen cursor movement. It consists of a ball or optical sensor, buttons, and an electronic circuit board that encodes motion data for transmission to and interpretation by the connected computer. Modern mice use optical sensors rather than mechanical components, improving durability and versatility.computer-mouse-sir-tariq.pptx



computer-mouse-sir-tariq.pptxTalhaHussain58
?
The document discusses the history and types of computer mice. It begins by defining a mouse as a device that allows users to control the cursor and select objects on screen. The first mouse was invented in 1968 and used a rolling ball to detect movement. Over time, mice evolved to use optical sensors instead of balls and became wireless. Different types of mice include optical, wireless, trackball, and vertical mice. The mouse design has changed significantly over time to be smaller and more ergonomic while improving motion detection.Computer mouse 



Computer mouse TariqGhayyur3
?
The document discusses the history and types of computer mice. It begins by defining a mouse as a hardware device that allows users to control the cursor and select objects on screen. The first mouse was invented in 1968 and used a rolling ball to detect movement. Over time, mice evolved to use optical sensors instead of balls and became wireless. Different types of mice include optical mice, wireless mice, trackballs, and trackpoint devices used on laptops. Touchscreens serve as mice on smartphones and tablets. The design of mice has changed significantly over the years to be smaller and more ergonomic.Keyboard & Mouse basics 



Keyboard & Mouse basics United International University
?
A standard keyboard has around 110 keys in a QWERTY layout. It can produce characters through pressing keys which the keyboard controller detects and sends to the computer via an interrupt. A computer mouse is a common input device that was invented in 1968 and uses optical, mechanical, or other methods to track movement and send it to the computer.How computer mice work



How computer mice workRaxTonProduction
?
Mice translate hand motion into signals the computer understands using five main components: a ball that rolls when the mouse moves, rollers that detect motion, an encoding disk with holes, infrared LEDs and sensors that count pulses of light, and a processor chip. Modern optical mice use a camera to take 1500 pictures per second and detect pattern movement to determine cursor movement. Mice send data through connectors like PS/2 using a protocol that reports button states, direction of movement, and movement values in bytes sent 40 times per second.Mouse



MousePrashath Kurunegala
?
The document summarizes how an optical mouse works. It detects motion by taking 1500 pictures per second of the surface below it using an LED and camera sensor. A processor analyzes the pictures to detect pattern changes and determine distance and direction moved. It sends coordinate data to the computer up to 40 times per second using a PS/2, serial, or USB connection and interface.Chap2 input devices



Chap2 input devicesraksharao
?
Importance of I/O devices,Types of input devices,keyboard
Pointing devices,Speech recognition,Digital camera
Webcam,Scanners,OCR,OMR,MICR,Bar-code reader
Basic fundamental Computer input/output Accessories



Basic fundamental Computer input/output Accessoriessuraj pandey
?
The document discusses various computer input and output devices. For input, it describes keyboards, mice, joysticks, light pens, touch screens, data gloves, tablets, digitizers, scanners, optical character recognition, optical mark readers, bar code readers, voice recognition, electronic cards, digital cameras, and webcams. For output, it discusses monitors including CRT, LCD, LED, plasma displays, printers, and impact vs non-impact printers.Computer system Input and Output Devices



Computer system Input and Output DevicesDr. Chandrakant Divate
?
Computer system Input and Output DevicesSpace mouse report 



Space mouse report Anish Sarkar
?
The document discusses the space mouse, a 3D input device originally developed at the German Aerospace Center for controlling robots. It allows 6 degrees of freedom motion control through an ergonomic design based on mechatronics engineering principles. The space mouse works like a standard mouse but enables 3D manipulation of graphic objects through translation and rotation in all axes. It has various applications in mechanical design, animation, and simulation where 3D interaction is required.Introduction of Computers & C++ Programming 



Introduction of Computers & C++ Programming Mujeeb UR Rahman
?
Section 1.
History of Computers, Generations, Models.
Section 2.
C++ Programming, Stings, Loops etc....THINGS ABOUT MOUSE



THINGS ABOUT MOUSEjeevagan nagarajan
?
1. Mice use an optical system to track motion by taking pictures with a camera sensor and detecting pattern changes between images to determine movement.
2. Inside the mouse is a ball that rolls and turns rollers connected to an encoding disk with holes. Infrared LEDs and sensors count light pulses from the disk to translate motion into digital data.
3. This data is sent through the mouse's PS/2 connector to the computer as three bytes per report, indicating button states, direction flags, and movement amounts in X and Y coordinates.hardware chapter computer o level and ram and rom



hardware chapter computer o level and ram and romquratyousaf8
?
Input and output devices allow computers to receive and display information. Common input devices include keyboards, mice, and touchscreens which translate human actions into digital data. Output devices such as monitors, printers and speakers convey the processed data in a human understandable form. Data storage devices like hard disk drives, solid state drives and optical discs are used to permanently store large amounts of digital data in binary format using magnetic charges or physical marks. Networks allow computers to share and exchange information through connections and communication protocols. Network interface cards are used to connect devices to networks while routers direct data traffic between networks.Input & output unit processor



Input & output unit processorHumayunKobir6
?
The input unit accepts data and instructions from external devices and converts them to a binary format understood by the computer. Common input devices include the keyboard, mouse, joystick, scanner, microphone, and touchscreen. The output unit converts the computer's binary output to a human readable format and presents it via output devices such as monitors, printers, speakers, projectors, and plotters. The processor, or CPU, fetches instructions from memory, decodes and executes them, and writes results back to memory in four steps: fetch, decode, execute, and write back. It controls the overall functioning of the computer.Activity based Teaching learning



Activity based Teaching learningKetan Sahu
?
The document discusses a presentation created for an ICT exhibition on the theme of activity-based teaching. It covers related data on activity-based teaching at multiple educational levels. Various diagrams, equations, and data are included to demonstrate and tie together the concepts using ICT presentation tools.Input and output devices 



Input and output devices sajuthomas123
?
The document provides an overview of common computer input and output devices. It describes keyboards, mice, scanners, and sensors as examples of input devices used to capture and send data to a computer. It also discusses monitors, printers, and speakers as examples of output devices that display or convey information from a computer in visual, audio, or physical forms. The document contains detailed descriptions and comparisons of specific input devices like different types of mice, keyboards, scanners, and sensors. It also examines characteristics of output displays like monitor resolution, refresh rates, and types of displays including CRT, LCD, LED, and plasma screens.Unit 2 ºÝºÝߣs



Unit 2 ºÝºÝߣsVikram Nandini
?
The document discusses various computer input and output devices. It describes keyboards, mice, scanners, and other common input devices. It also covers monitors, printers, and other output devices used to display and print information from computers. The keyboard section provides details on standard keyboard keys and features of multimedia and wireless keyboards. Mice types discussed include optical mice, wireless mice, and trackballs.Input / Output Devices



Input / Output DevicesWe Learn - A Continuous Learning Forum from Welingkar's Distance Learning Program.
?
Secondary storage devices are required mainly because primary storage devices are volatile and information is lost the moment power is switched off. Floppy Disks and Drive, Hard Disks, CD/DVD drive, Pen drive and magnetic tapes are some of the secondary storage devices.
For more such innovative content on management studies, join WeSchool PGDM-DLP Program: http://bit.ly/ZEcPAcCse space-mouse-report



Cse space-mouse-reportImkarthikreddy
?
This document appears to be a seminar report on the topic of a Space Mouse. It includes an acknowledgments section thanking various people for their assistance. It also includes preface expressing gratitude to a guide for their help. The introduction defines a Space Mouse as a 3D controller for manipulating objects in 3D environments that allows control of all six degrees of freedom. Chapter 1 provides more details on how computer mice work by translating hand motions into signals using components like a ball, rollers, encoding disk, and infrared sensors. Chapter 2 discusses mechatronics engineering and its goals of designing intelligent systems that integrate mechanical and electronic systems using sensors and microprocessors.Recently uploaded (20)
Revolutionizing-Government-Communication-The-OSWAN-Success-Story



Revolutionizing-Government-Communication-The-OSWAN-Success-Storyssuser52ad5e
?
? ????? ??????? ????? ?
???????? ??????????? is proud to be a part of the ?????? ????? ???? ???? ??????? (?????) success story! By delivering seamless, secure, and high-speed connectivity, OSWAN has revolutionized e-?????????? ?? ??????, enabling efficient communication between government departments and enhancing citizen services.
Through our innovative solutions, ???????? ?????????? has contributed to making governance smarter, faster, and more transparent. This milestone reflects our commitment to driving digital transformation and empowering communities.
? ?????????? ??????, ?????????? ??????????!
DevNexus - Building 10x Development Organizations.pdf



DevNexus - Building 10x Development Organizations.pdfJustin Reock
?
Developer Experience is Dead! Long Live Developer Experience!
In this keynote-style session, we¡¯ll take a detailed, granular look at the barriers to productivity developers face today and modern approaches for removing them. 10x developers may be a myth, but 10x organizations are very real, as proven by the influential study performed in the 1980s, ¡®The Coding War Games.¡¯
Right now, here in early 2025, we seem to be experiencing YAPP (Yet Another Productivity Philosophy), and that philosophy is converging on developer experience. It seems that with every new method, we invent to deliver products, whether physical or virtual, we reinvent productivity philosophies to go alongside them.
But which of these approaches works? DORA? SPACE? DevEx? What should we invest in and create urgency behind today so we don¡¯t have the same discussion again in a decade?A Framework for Model-Driven Digital Twin Engineering



A Framework for Model-Driven Digital Twin EngineeringDaniel Lehner
?
ºÝºÝߣs from my PhD Defense at Johannes Kepler University, held on Janurary 10, 2025.
The full thesis is available here: https://epub.jku.at/urn/urn:nbn:at:at-ubl:1-83896Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptx



Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptxkaylagaze
?
In this presentation, I explore how technology has changed consumer behaviour and its impact on consumers and businesses. I will focus on internet access, digital devices, how customers search for information and what they buy online, video consumption, and lastly consumer trends.Computational Photography: How Technology is Changing Way We Capture the World



Computational Photography: How Technology is Changing Way We Capture the WorldHusseinMalikMammadli
?
? Computational Photography (Computer Vision/Image): How Technology is Changing the Way We Capture the World
He? d¨¹?¨¹nm¨¹s¨¹n¨¹zm¨¹, m¨¹asir smartfonlar v? kameralar nec? bu q?d?r g?z?l g?r¨¹nt¨¹l?r yarad?r? Bunun sirri Computational Fotoqrafiyas?nda(Computer Vision/Imaging) gizlidir¡ª??kill?ri ??km? v? emal etm? ¨¹sulumuzu t?kmill??dir?n, komp¨¹ter elmi il? fotoqrafiyan?n inqilabi birl??m?si.[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web AppsSafe Software
?
Ready to simplify workflow sharing across your organization without diving into complex coding? With FME Flow Apps, you can build no-code web apps that make your data work harder for you ¡ª fast.
In this webinar, we¡¯ll show you how to:
Build and deploy Workspace Apps to create an intuitive user interface for self-serve data processing and validation.
Automate processes using Automation Apps. Learn to create a no-code web app to kick off workflows tailored to your needs, trigger multiple workspaces and external actions, and use conditional filtering within automations to control your workflows.
Create a centralized portal with Gallery Apps to share a collection of no-code web apps across your organization.
Through real-world examples and practical demos, you¡¯ll learn how to transform your workflows into intuitive, self-serve solutions that empower your team and save you time. We can¡¯t wait to show you what¡¯s possible!Transform Your Future with Front-End Development Training



Transform Your Future with Front-End Development TrainingVtechlabs
?
Kickstart your career in web development with our front-end web development course in Vadodara. Learn HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, and more through hands-on projects and expert mentorship. Our front-end development course with placement includes real-world training, mock interviews, and job assistance to help you secure top roles like Front-End Developer, UI/UX Developer, and Web Designer.
Join VtechLabs today and build a successful career in the booming IT industry!DealBook of Ukraine: 2025 edition | AVentures Capital



DealBook of Ukraine: 2025 edition | AVentures CapitalYevgen Sysoyev
?
The DealBook is our annual overview of the Ukrainian tech investment industry. This edition comprehensively covers the full year 2024 and the first deals of 2025. Fl studio crack version 12.9 Free Download



Fl studio crack version 12.9 Free Downloadkherorpacca127
?
https://ncracked.com/7961-2/
Note: >>?? Please copy the link and paste it into Google New Tab now Download link
The ultimate guide to FL Studio 12.9 Crack, the revolutionary digital audio workstation that empowers musicians and producers of all levels. This software has become a cornerstone in the music industry, offering unparalleled creative capabilities, cutting-edge features, and an intuitive workflow.
With FL Studio 12.9 Crack, you gain access to a vast arsenal of instruments, effects, and plugins, seamlessly integrated into a user-friendly interface. Its signature Piano Roll Editor provides an exceptional level of musical expression, while the advanced automation features empower you to create complex and dynamic compositions.EaseUS Partition Master Crack 2025 + Serial Key



EaseUS Partition Master Crack 2025 + Serial Keykherorpacca127
?
https://ncracked.com/7961-2/
Note: >> Please copy the link and paste it into Google New Tab now Download link
EASEUS Partition Master Crack is a professional hard disk partition management tool and system partition optimization software. It is an all-in-one PC and server disk management toolkit for IT professionals, system administrators, technicians, and consultants to provide technical services to customers with unlimited use.
EASEUS Partition Master 18.0 Technician Edition Crack interface is clean and tidy, so all options are at your fingertips. Whether you want to resize, move, copy, merge, browse, check, convert partitions, or change their labels, you can do everything with a few clicks. The defragmentation tool is also designed to merge fragmented files and folders and store them in contiguous locations on the hard drive.
Future-Proof Your Career with AI Options



Future-Proof Your Career with AI OptionsDianaGray10
?
Learn about the difference between automation, AI and agentic and ways you can harness these to further your career. In this session you will learn:
Introduction to automation, AI, agentic
Trends in the marketplace
Take advantage of UiPath training and certification
In demand skills needed to strategically position yourself to stay ahead
? If you have any questions or feedback, please refer to the "Women in Automation 2025" dedicated Forum thread. You can find there extra details and updates.DAO UTokyo 2025 DLT mass adoption case studies IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)



DAO UTokyo 2025 DLT mass adoption case studies IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)Tsuyoshi Hirayama
?
DAO UTokyo 2025
–|¾©´óѧÇéˆóѧh ¥Ö¥í¥Ã¥¯¥Á¥§©`¥óÑо¿¥¤¥Ë¥·¥¢¥Æ¥£¥Ö
https://utbciii.com/2024/12/12/announcing-dao-utokyo-2025-conference/
Session 1 :DLT mass adoption
IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)Inside Freshworks' Migration from Cassandra to ScyllaDB by Premkumar Patturaj



Inside Freshworks' Migration from Cassandra to ScyllaDB by Premkumar PatturajScyllaDB
?
Freshworks migrated from Cassandra to ScyllaDB to handle growing audit log data efficiently. Cassandra required frequent scaling, complex repairs, and had non-linear scaling. ScyllaDB reduced costs with fewer machines and improved operations. Using Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM), they bulk-migrated data, performed dual writes, and validated consistency.SMART SENTRY CYBER THREAT INTELLIGENCE IN IIOT



SMART SENTRY CYBER THREAT INTELLIGENCE IN IIOTTanmaiArni
?
SMART SENTRY CYBER THREAT INTELLIGENCE IN IIOTEarly Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)



Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)nick896721
?
Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation preview by User Interviews.Gojek Clone Multi-Service Super App.pptx



Gojek Clone Multi-Service Super App.pptxV3cube
?
Gojek Clone is a versatile multi-service super app that offers ride-hailing, food delivery, payment services, and more, providing a seamless experience for users and businesses alike on a single platform.Cloud of everything Tech of the 21 century in Aviation



Cloud of everything Tech of the 21 century in AviationAssem mousa
?
AI, Block chain, Digital Currency, Cloud, Cloud of Things, Tactile Internet, Digital Twins, IOT, AR, VR, MR, U commerce, data and robotics."
L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardness



L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardnessRostislavDaniel
?
Introduction to NanoindentationPresentation on Computer Mouse
- 1. Presentation on Computer Mouse Peripheral & Interfacing Sub Code : CSE-432 Bangladesh University
- 2. Submitted by : Md. Sadiqur Rahman Id : 201531043092 Batch : 43 (Day) Dept : CSE Bangladesh University Submitted to : Khan Md. Hasib Lecturer, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Bangladesh University
- 3. Computer Mouse Key Points ? What is Mouse ? Invention of Mouse ? Activities of Mouse ? Types of Mice / Mouses ? How Mouse Works ? Computer Mouse Ports ? How has the Design being changed
- 4. What is Mouse ? ? A computer mouse is a hand-held pointing device that detects two- dimentional motion relative to a surface. ? This motion is typically translated into the motion of a pointer on a display, which allows a smooth control of the graphical user interface. Why it is named as ¡°Mouse¡± ? ? With the cord coming out of the back of the mouse Douglas said the device reminded him of the rodent mouse and the name stuck. ? It's a lot easier to remember than a ¡±X-Y Position Indicator for a Display System¡±.
- 5. Invention of Mouse ? In 1968, a man named Douglas Engelbart created this special tool to help people control their computers. ? It was a small wooden block on wheels, and there was a long cable sticking out of the back, kind of like a tail!
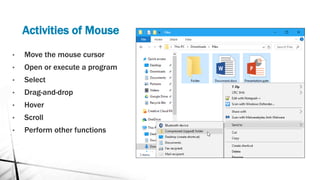
- 6. Activities of Mouse ? Move the mouse cursor ? Open or execute a program ? Select ? Drag-and-drop ? Hover ? Scroll ? Perform other functions
- 7. Types of Mice / Mouses ? Cordless (Wireless) ? Footmouse ? IntelliMouse (Wheel mouse) ? J-Tech Mouse ? Joystick ? Optical Mouse ? Gest ? gStick Mouse ? Touchpad (Glidepoint) ? Mechanical ? Trackball ? TrackPoint
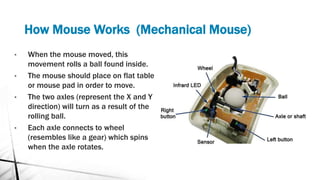
- 8. How Mouse Works (Mechanical Mouse) ? When the mouse moved, this movement rolls a ball found inside. ? The mouse should place on flat table or mouse pad in order to move. ? The two axles (represent the X and Y direction) will turn as a result of the rolling ball. ? Each axle connects to wheel (resembles like a gear) which spins when the axle rotates.
- 9. ? Beside each rotating wheel, there are an infrared LED (light- emitting diode) and infrared Sensor. ? The LED sends a path of light to the wheel. ? The sensor, found on the other side of the wheel, detects the pulses of light interrupted by rotating wheel. ? The mouse on-board processor chip reads the pulses from the sensor and translates into computer usable format (binary data). ? This tells the mouse position and speed which is displayed in the movement of a cursor on a screen. How Mouse Works (Mechanical Mouse)
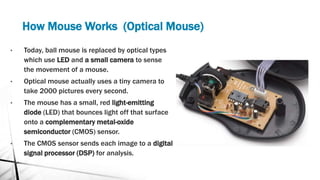
- 10. How Mouse Works (Optical Mouse) ? Today, ball mouse is replaced by optical types which use LED and a small camera to sense the movement of a mouse. ? Optical mouse actually uses a tiny camera to take 2000 pictures every second. ? The mouse has a small, red light-emitting diode (LED) that bounces light off that surface onto a complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensor. ? The CMOS sensor sends each image to a digital signal processor (DSP) for analysis.
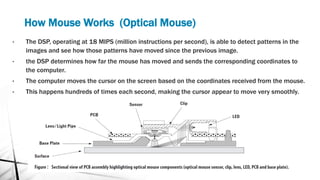
- 11. How Mouse Works (Optical Mouse) ? The DSP, operating at 18 MIPS (million instructions per second), is able to detect patterns in the images and see how those patterns have moved since the previous image. ? the DSP determines how far the mouse has moved and sends the corresponding coordinates to the computer. ? The computer moves the cursor on the screen based on the coordinates received from the mouse. ? This happens hundreds of times each second, making the cursor appear to move very smoothly.
- 12. Most modern Mouse has the following parts ? Case ? On-board processor chip ? Two buttons ? A wheel between the two buttons (used to scroll up and down, Zoom IN and Zoom Out in applications like AutoCAD) ? Battery (if it is wireless) ? Connection interface such as USB or Infrared
- 13. Computer mouse ports ? Bluetooth ? PS/2 Port ? Serial Port ? USB ? Infrared Today, most computer mice connect to a computer using a USB port. Below is a listing of all the type of ports and wireless connections that a mouse is capable of using or has used in the past.
- 14. How has the Design being changed ? The computer mouse has definitely changed size, getting smaller and smaller. ? The design has also become more comfortable to hold, as the first computer mouse was quite square. ? Motion detectors have changed from a tracking ball, to an LED light, and now a laser.
- 15. How has the Design being changed ? This improves the quality of motion we see on the screen, and also eliminated the use of the mouse pads. ? A ¡®scroll wheel¡¯ is also available on most mouses, making it easier to view web pages and folders.
- 16. How Mouse Works (Mechanical Mouse)
- 17. How Mouse Works (Optical Mouse)
- 18. Thank You . . .


