Presentation on
- 1. PRESENTATION ON QCAD BY AMRIT PAL GOYAL B. Tech. ( CIVIL ) ROLL NO. 100121 SECTION - D1
- 3. ABOUT SOFTWARE QCad is an application for computer aided drafting in two dimensions (2d). With QCad you can create technical drawings such as plans for buildings, interiors, mechanical parts or schemas and diagrams. Fortunately QCAD is one of the most economic CAD packages available. The source code of the QCAD community edition is released under the GPL (Open Source). QCAD runs on any reasonably modern hardware configuration. In QCAD we can use the mouse wheel to quickly navigate around in the drawing.
- 4. Main Features ŌĆó Layers ŌĆó Blocks (grouping) ŌĆó 35 CAD fonts included ŌĆó Metrical and Imperial units ŌĆó DXF input I output ŌĆó Printing to scale ŌĆó Over 40 construction tools ŌĆó Over 20 modification tools ŌĆó Construction and modification of points, lines, arcs, circles, ellipses, splines, polylines, texts, dimensions, hatches, fills, raster images ŌĆó Various powerful entity selection tools ŌĆó Object snaps ŌĆó Measuring tools ŌĆó Part library with over 4800 CAD parts ŌĆó Scripting interface
- 5. ╠² Basic CAD Concepts Entities Entities are graphical objects in a CAD system. Typical entities which are supported by most CAD systems are: points, lines and circular and elliptical arcs. More complex and CAD specific entities include polylines, texts, dimensioning, hatches and splines. Attributes Every entity has certain attributes such as its color, line type and line width.
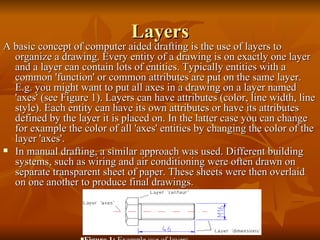
- 6. Layers A basic concept of computer aided drafting is the use of layers to organize a drawing. Every entity of a drawing is on exactly one layer and a layer can contain lots of entities. Typically entities with a common 'function' or common attributes are put on the same layer. E.g. you might want to put all axes in a drawing on a layer named 'axes' (see Figure 1). Layers can have attributes (color, line width, line style). Each entity can have its own attributes or have its attributes defined by the layer it is placed on. In the latter case you can change for example the color of all 'axes' entities by changing the color of the layer 'axes'. In manual drafting, a similar approach was used. Different building systems, such as wiring and air conditioning were often drawn on separate transparent sheet of paper. These sheets were then overlaid on one another to produce final drawings. Figure 1:╠² Example use of layers
- 7. Blocks A Block is a group of entities. Blocks can be inserted into the same graphic more than once with different Attributes and different locations, scaling factors and rotation angles (see Figure 2). Such an instance of a block is usually called an Insert. Inserts have attributes just like entities and layers. An Entity that is part of an Insert can have its own attributes or share the attributes of the Insert. Once created, Inserts are still linked to the Block they instantiate. The power of inserts is, that you can modify the Block once and all Inserts will be updated accordingly. Figure 2:╠² Three instances (Inserts) of a Block with different colors, angles and scalings.
- 8. Drafting in CAD In many ways, CAD is similar to traditional drafting. When drawing a plan or a view of an object on a paper, you would use tools such as a ruler to draw lines. In CAD systems there is a variety of tools available to achieve the same goal. The big advantage of a CAD system is the fact that you can change every entity of your drawing easily after you've created it. This might be the most difficult thing to learn when moving from paper to CAD. When working with a CAD system you will very often create lines that won't be on the final printout or which don't have the correct length and need to be trimmed later (see Figure 3). A common mistake of CAD beginners is wanting to create the final drawing right away. Figure 3:╠² Three possible steps to quickly create a drawing using supportive constructions and the ability of a CAD system to change existing entities.
- 9. Co-ordinate Systems A good understanding of how co-ordinates work is absolutely crucial if you are to make the best use of any CAD program. If you're not familiar with co-ordinates it's highly recommended that you take some time to familiarize yourself with the basic concepts. Origin The origin of the drawing is the point where the X and Y axis cross each other. It's the absolute zero of the drawing. In addition to the origin there's a relative zero point in QCAD. This is a helpful spot that changes it's position depending on the current user interactions. The relative zero point can also be moved around by the user.
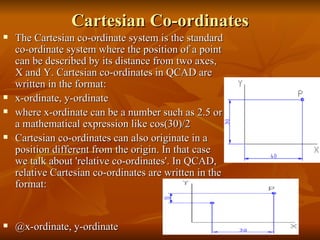
- 10. Cartesian Co-ordinates The Cartesian co-ordinate system is the standard co-ordinate system where the position of a point can be described by its distance from two axes, X and Y. Cartesian co-ordinates in QCAD are written in the format: x-ordinate, y-ordinate where x-ordinate can be a number such as╠²2.5╠²or a mathematical expression like╠²cos(30)/2╠² Cartesian co-ordinates can also originate in a position different from the origin. In that case we talk about 'relative co-ordinates'. In QCAD, relative Cartesian co-ordinates are written in the format: @x-ordinate, y-ordinate
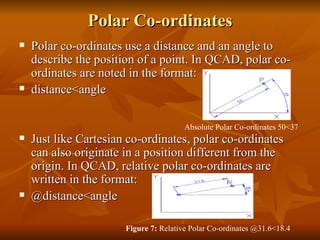
- 11. Polar Co-ordinates Polar co-ordinates use a distance and an angle to describe the position of a point. In QCAD, polar co-ordinates are noted in the format: distance<angle Just like Cartesian co-ordinates, polar co-ordinates can also originate in a position different from the origin. In QCAD, relative polar co-ordinates are written in the format: @distance<angle Absolute Polar Co-ordinates╠²50<37╠² Figure 7:╠² Relative Polar Co-ordinates╠²@31.6<18.4╠²
- 12. Basic Editing Basic Editing Entities can be inserted, selected, and, once selected, can be deleted, transformed or duplicated. To insert an entity means to draw it by selecting the appropriate drawing tool, such as line, arc, etc., and by locating points that define the object to be drawn, such as the endpoints of a line. Entity Selection An entity must be selected before it can be deleted, duplicated, or transformed. Entity selection is one of the most basic of CAD operations. QCAD offers a wide variety of selection tools to quickly select groups of entities, entities within a range, connected entities, etc. Deletion Deleting an entity means to remove it from the drawing.
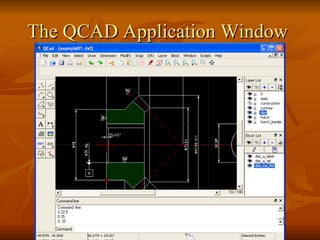
- 13. The QCAD Application Window
- 14. PRICE LIST OF QCAD VERSION PRICE 1 .QCad Professional for Windows EUR 24 2.QCad Professional for Linux EUR 24 3.QCad Professional for Mac OS X EUR 24 4.QCad Professional for Solaris EUR 24 5.QCad Professional for FreeBSD EUR 24 6.QCad Professional Site License EUR 223
- 15. License Copyright Copyright ┬® 1999-2003 by Ribbon-Soft, Andrew Mustun.╠² Published 2003╠² Switzerland╠² Document ID: ╠²$Date: 2004-02-01 22:21:23 +0100 (Sun, 01 Feb 2004) $╠² Release: ╠²September 2003 Trademarks Intel is a registered trademark and 80286, 80386, 286, 386, 486, Pentium and Pentium Pro are trademarks of Intel Corp.╠² Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.╠² TrueType is a registered trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.╠² Microsoft, and MS are registered trademarks and Windows, Windows 95, Windows 98 and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corp.╠² IBM is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corp.╠²
- 16. ╠²