Presentation photosynthesis
Download as PPT, PDF1 like2,181 views
This document summarizes the key discoveries and experiments that led to the modern understanding of photosynthesis. It describes how van Helmont, Priestly, and Ingenhousz performed early experiments in the 17th-18th centuries that showed plants absorb materials from water and soil and release oxygen when exposed to sunlight. Later scientists like Julius Mayer proposed that plants convert sunlight into chemical energy. The document then provides details on the structures and processes involved in photosynthesis, including chloroplasts, chlorophyll, thylakoids, and the two main stages - the light-dependent reactions that convert solar energy to chemical energy and the light-independent Calvin cycle that uses this energy to produce sugars.
1 of 21
Downloaded 27 times



















![REFERENCES
Bryant DA, Frigaard NU (November 2006). "Prokaryotic photosynthesis
and phototrophy illuminated".╠²Trends Microbiol.╠²14╠²(11): 488ŌĆō96]
Buick R (August 2008).╠²"When did oxygenic photosynthesis
evolve?".╠²Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci.╠²363╠²Olson
JM (May 2006). "Photosynthesis in the Archean era".╠²Photosyn.
Res.╠²88╠²(2): 109ŌĆō17.
Online Sources
http://bioenergy.asu.edu/photosyn/stuy.html
http://hdgc.epp.cmu.edu/teachersguide/teachersguide.htm
╠²](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationphotosynthesis-140305073325-phpapp01/85/Presentation-photosynthesis-21-320.jpg)
Recommended
Photosynthesis as an Energy Transfer Process



Photosynthesis as an Energy Transfer ProcessJaya Kumar
╠²
Photosynthesis involves two main sets of reactions: light-dependent reactions where light energy is absorbed and electron transport is used to make ATP and NADPH; and light-independent reactions where CO2 is fixed into sugars using the energy from the light reactions. The light reactions take place in the chloroplasts and involve the absorption of light by pigments and the splitting of water to provide electrons and protons. The Calvin cycle fixes CO2 into carbohydrates using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions. Factors like light intensity, temperature, and CO2 concentration can limit the rate of photosynthesis.A level biology photosynthesis



A level biology photosynthesisBilegdemberel Magadaa
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use energy from sunlight to produce food from carbon dioxide and water. It occurs in two main stages:
1. Light-dependent reactions trap light energy from the sun using chlorophyll and use it to split water molecules and produce ATP and NADPH. This takes place in the thylakoid membranes inside chloroplasts.
2. Light-independent reactions use the ATP and NADPH to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into organic carbohydrates like glucose. This occurs in the chloroplast stroma and is known as the Calvin cycle. The overall equation is 6CO2 + 6H2O ŌåÆ C6H12O6 + 6O2.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisKarl Pointer
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. Chlorophyll, located in chloroplasts, absorbs sunlight and uses the energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose through a two-step process - the light reactions and Calvin cycle. Plants appear green because chlorophyll, the main photosynthetic pigment, absorbs most wavelengths of visible light except green, which it reflects, giving leaves their green color.Ecological succession



Ecological successionJaya Prakash
╠²
Ecological succession is the process of change in species composition of an ecological community over time. There are two main types: primary succession, which occurs in areas without previous life, and secondary succession, which occurs after a disturbance in an existing ecosystem. Succession will continue through different stages as species colonize an area and change the environment, eventually reaching a climax community that is stable and able to reproduce itself until the next disturbance. Humans can impact ecological succession through activities like agriculture that clear land and disrupt existing ecosystems.photosynthesis ppt



photosynthesis pptSindhu Pretty
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of food (sugars). It occurs in two stages: (1) the light reactions where sunlight is absorbed and converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, and (2) the dark reactions where carbon dioxide is fixed using the ATP and NADPH to produce sugars like glucose. The overall equation is: 6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight ŌåÆ C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2. Photosynthesis provides a critical source of food for organisms and oxygen for respiration.Light reaction of photosynthesis



Light reaction of photosynthesisArif Majid
╠²
1. The light reaction of photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and involves the absorption of light by photosynthetic pigments.
2. Energy from the absorbed light is used to transfer electrons along an electron transport chain, powering the synthesis of ATP through photophosphorylation and reducing NADP+ to NADPH.
3. The products of the light reaction, ATP and NADPH, are used in the Calvin cycle to fix carbon from CO2 into organic molecules like glucose.Plants Evolution



Plants EvolutionMuhammad Asif Muneer
╠²
- Green algae are thought to be the ancestors of modern plants. They may have lived on land over 500 million years ago.
- Plants evolved adaptations like roots, leaves, and vascular tissue to survive on land. They obtain water and minerals from roots and CO2 from the air through leaves.
- Plants have alternation of generations, where the haploid gametophyte produces gametes and the diploid sporophyte produces spores through meiosis. This life cycle is seen in mosses, ferns, and seed plants.powerpoint presentation on topic photosynthesis



powerpoint presentation on topic photosynthesisDadu Brutally Innocent
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages - the light-dependent reactions where sunlight is absorbed to make ATP and NADPH using chlorophyll, and the light-independent Calvin cycle where carbon is fixed into sugars like glucose using ATP and NADPH. Photosynthesis provides food for plants and oxygen for other organisms while consuming carbon dioxide.Energy flow in ecosystem



Energy flow in ecosystemNanda Palit
╠²
It is quite interesting to note that the only producer of food in the entire world is PLANT. All others are consumers, and depend only on plants to provide food to all the living organisms and species.Plant divisions mosses and ferns



Plant divisions mosses and fernseziennker
╠²
The document summarizes the characteristics and life cycles of nonvascular and seedless vascular plants. It describes two divisions of plants - nonvascular plants like moss that lack roots, stems, and leaves, and vascular plants that have transport tissues. Moss and liverworts are examples of nonvascular plants that reproduce via alternation of generations between sporophyte and gametophyte stages. Ferns are an example of seedless vascular plants that have true stems, roots, and leaves called fronds. Their life cycle also involves alternation between sporophyte and gametophyte stages. Ferns and other seedless plants were important in forming peat bogs and peat, which was used as fuel.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisBajrangKusro
╠²
Photosynthesis is a oxidation reduction process in which water is oxidized and carbon dioxide is reduced to carbohydrate level, the water and oxygen being by product.A Level Biology - Classification and Biodiversity



A Level Biology - Classification and Biodiversitymrexham
╠²
This is a PowerPoint presentation for Topic 3 in the Edexcel Biology B A Level course that starts in 2015.
This is a free sample, the full PowerPoint presentation is available to purchase here: https://sellfy.com/MrExhamPhotosynthesis carbon fixation



Photosynthesis carbon fixationSudhir Devadiga
╠²
The document summarizes key aspects of photosynthesis, including:
1) The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to the three-carbon sugar glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) through carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration phases.
2) Some plants like cacti and succulents have evolved alternative carbon fixation mechanisms like CAM to minimize photorespiration and be more efficient in hot, dry climates.
3) Photosynthesis converts sunlight into chemical energy stored in sugars, providing energy and materials for plants and the global biosphere.Photosynthesis



Photosynthesisgohil sanjay bhagvanji
╠²
This document provides an overview of photosynthesis. It begins by defining photosynthesis as the process by which plants and algae use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It then discusses the historical background and discovery of photosynthesis. The remainder of the document describes the key components of photosynthesis, including the two photochemical processes (photosystems I and II), the light-dependent reactions, and the mechanisms of cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation that generate ATP using energy from excited electrons. In closing, it summarizes the similarities and differences between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.AS Level Biology - 1) Biological Molecules



AS Level Biology - 1) Biological MoleculesArm Punyathorn
╠²
To understand Biology, one must first understand the basic chemistry of it - which is relatively simple as opposed to normal chemistry. All you have to know about is Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein and Water.Energy flow in ecosystem



Energy flow in ecosystemNanda Palit
╠²
1) Energy from the sun powers photosynthesis in green plants, which convert carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight into glucose.
2) This chemical energy from glucose is transferred through ecosystems as organisms eat each other, forming food chains.
3) Producers like plants capture energy from the sun which is then consumed by primary consumers like herbivores, and passed up through secondary and tertiary consumers in a trophic pyramid, with decomposers recycling nutrients.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisJessabeth Aluba
╠²
Plants and algae perform photosynthesis, which converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts and uses chlorophyll to absorb light, which drives the production of ATP and NADPH that fuel the Calvin cycle to produce glucose from carbon dioxide. It is an essential process that generates oxygen and forms the base of the food chain sustaining all life on Earth.Photosynthesis Notes



Photosynthesis Notesjlehmkuhler
╠²
Photosynthesis involves two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. In the light-dependent reactions, chlorophyll uses light energy to split water molecules, producing oxygen and energized electrons. These electrons are used to convert NADP+ into NADPH through an electron transport chain, while hydrogen ions create a proton gradient used to make ATP. In the Calvin cycle, which takes place in the stroma, CO2 is fixed into three-carbon molecules using ATP and NADPH produced previously. These molecules are then reduced, regenerated, and used to form new sugars like glucose. Together these stages convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds to fuel plant growth.Cyclic phosphorylation



Cyclic phosphorylationFarhanaShiekh
╠²
This document presents a topic on cyclic photophosphorylation. It begins with an introduction to photophosphorylation and defines cyclic photophosphorylation. There are two types of photophosphorylation: cyclic and non-cyclic. Cyclic photophosphorylation involves the same excited electron returning to the excited chlorophyll, producing one ATP molecule. The mechanism involves an electron being energized in photosystem I and passing through an electron transport system before returning to the reaction center. This releases energy to produce ATP. The steps involve an electron moving from P700 to acceptors to the cytochrome complex and back to P700, producing one ATP via chemiosmosis.Chloroplasts



ChloroplastsDilip Pandya
╠²
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plants and algae that carry out photosynthesis. They have an inner and outer membrane, with an intermembrane space between them. Inside is the stroma, which contains thylakoids that are arranged in stacks called grana. Chloroplasts contain their own genome and divide independently. According to the endosymbiotic theory, chloroplasts originated from cyanobacteria that were engulfed by other cells but not destroyed. Chloroplasts import most proteins from the cytosol through translocation complexes in the inner and outer membranes. They perform photosynthesis through light and dark reactions, using solar energy to fix carbon dioxide and produce oxygen and carbohydrates.Ap Bio Ch7 Power Point



Ap Bio Ch7 Power PointAnthony DePhillips
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages: in the light-dependent reactions, sunlight is absorbed and used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, producing oxygen as a byproduct. In the light-independent reactions, the glucose is then assembled from carbon dioxide using energy from the light reactions. The light reactions take place in chloroplasts within plant cells, while the dark reactions occur in the chloroplast stroma. Photosynthesis is essential for producing oxygen and food on Earth.Light reaction of Photosynthesis



Light reaction of PhotosynthesisAlakesh Das
╠²
Photosynthesis converts light energy to chemical energy through light reaction. Light reaction occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, where photosystems use light to transfer electrons and pump protons, generating ATP and NADPH. There are two photosystems - PSII uses water as the electron donor and evolves oxygen, while PSI and cytochrome b6f complex generate a proton gradient used for ATP synthesis via ATP synthase. Both oxygenic and anoxygenic bacteria perform similar light reactions, though they use different electron donors and may contain only one photosystem. Light reaction is essential for providing the energy required for carbon fixation in photosynthesis.Organisms and their environments



Organisms and their environmentshilary farlow
╠²
The document discusses key concepts related to ecosystems, including energy flow, trophic levels, food chains, and food webs. It explains that the sun is the primary source of energy for ecosystems and that energy flows through trophic levels from producers to consumers. While chemical elements cycle through an ecosystem, energy is lost at each transfer between trophic levels and must constantly be replenished by the sun. Food chains and food webs illustrate the complex feeding relationships and energy transfers within an ecosystem.AS Level Biology - 4) Membranes



AS Level Biology - 4) MembranesArm Punyathorn
╠²
Transportation of substances in and out of cells can be regulated by the single most underrated and under appreciated organelle in the cell - the phospholipid bilayer membrane.Photosynthesis PowerPoint



Photosynthesis PowerPointBiologyIB
╠²
Photosynthesis converts sunlight into chemical energy through a series of light-dependent and light-independent reactions. The light reactions use energy from sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH, which provide energy and electrons to drive the Calvin cycle. The Calvin cycle fixes carbon from carbon dioxide into organic three-carbon sugars like glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions. One sugar molecule is used for growth, while five are recycled to regenerate the starter molecule for the next round of the Calvin cycle.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisJolie Yu
╠²
The document summarizes photosynthesis, including:
1) Photosynthesis uses light energy, water, carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen through two phases - the light reactions and dark reactions.
2) The light reactions use light to produce ATP and NADPH using chlorophyll and a series of electron carriers in the thylakoid membranes.
3) The dark reactions use ATP and NADPH to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into glucose through the Calvin cycle in the chloroplast stroma.Biology Lecture - Photosynthesis



Biology Lecture - PhotosynthesisLumen Learning
╠²
1. Transition to renewable energy sources like solar and wind to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels.
2. Drive and fly less to lower transportation emissions, and purchase more fuel-efficient vehicles.
3. Practice sustainable habits like recycling and reducing waste to lessen environmental impacts.
4. Support policies that place a price on carbon emissions to incentivize the development of clean technologies.cellular respiration



cellular respirationYang Durana
╠²
The document discusses cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells break down food molecules to produce energy in the form of ATP. It describes the three main stages of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and occurs in the cytoplasm, producing a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further breaks down molecules in the mitochondria, producing more ATP and electrons. The electron transport chain uses these electrons and oxygen to produce the most ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen through fermentation.Photosynthesis part 1



Photosynthesis part 1Maria Donohue
╠²
The document summarizes key experiments and discoveries in photosynthesis research from the 1600s to present. Jan van Helmont discovered in 1643 that most of a tree's mass comes from water, not soil. Joseph Priestly showed in 1771 that plants release oxygen. Jan Ingenhousz found in 1779 that plants need sunlight to produce oxygen. Later scientists like Calvin traced the chemical pathway that fixes carbon to form glucose in the Calvin Cycle.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisMaria Donohue
╠²
The document discusses photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds like glucose. It summarizes key experiments by scientists like van Helmont, Priestly, and Ingenhousz that helped discover this process. The document then describes the structures involved like chloroplasts and chlorophyll, and explains that photosynthesis has two main stages - the light-dependent reactions where sunlight is converted to chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent Calvin cycle where sugar is produced using those energy carriers.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Energy flow in ecosystem



Energy flow in ecosystemNanda Palit
╠²
It is quite interesting to note that the only producer of food in the entire world is PLANT. All others are consumers, and depend only on plants to provide food to all the living organisms and species.Plant divisions mosses and ferns



Plant divisions mosses and fernseziennker
╠²
The document summarizes the characteristics and life cycles of nonvascular and seedless vascular plants. It describes two divisions of plants - nonvascular plants like moss that lack roots, stems, and leaves, and vascular plants that have transport tissues. Moss and liverworts are examples of nonvascular plants that reproduce via alternation of generations between sporophyte and gametophyte stages. Ferns are an example of seedless vascular plants that have true stems, roots, and leaves called fronds. Their life cycle also involves alternation between sporophyte and gametophyte stages. Ferns and other seedless plants were important in forming peat bogs and peat, which was used as fuel.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisBajrangKusro
╠²
Photosynthesis is a oxidation reduction process in which water is oxidized and carbon dioxide is reduced to carbohydrate level, the water and oxygen being by product.A Level Biology - Classification and Biodiversity



A Level Biology - Classification and Biodiversitymrexham
╠²
This is a PowerPoint presentation for Topic 3 in the Edexcel Biology B A Level course that starts in 2015.
This is a free sample, the full PowerPoint presentation is available to purchase here: https://sellfy.com/MrExhamPhotosynthesis carbon fixation



Photosynthesis carbon fixationSudhir Devadiga
╠²
The document summarizes key aspects of photosynthesis, including:
1) The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to the three-carbon sugar glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) through carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration phases.
2) Some plants like cacti and succulents have evolved alternative carbon fixation mechanisms like CAM to minimize photorespiration and be more efficient in hot, dry climates.
3) Photosynthesis converts sunlight into chemical energy stored in sugars, providing energy and materials for plants and the global biosphere.Photosynthesis



Photosynthesisgohil sanjay bhagvanji
╠²
This document provides an overview of photosynthesis. It begins by defining photosynthesis as the process by which plants and algae use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It then discusses the historical background and discovery of photosynthesis. The remainder of the document describes the key components of photosynthesis, including the two photochemical processes (photosystems I and II), the light-dependent reactions, and the mechanisms of cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation that generate ATP using energy from excited electrons. In closing, it summarizes the similarities and differences between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.AS Level Biology - 1) Biological Molecules



AS Level Biology - 1) Biological MoleculesArm Punyathorn
╠²
To understand Biology, one must first understand the basic chemistry of it - which is relatively simple as opposed to normal chemistry. All you have to know about is Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein and Water.Energy flow in ecosystem



Energy flow in ecosystemNanda Palit
╠²
1) Energy from the sun powers photosynthesis in green plants, which convert carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight into glucose.
2) This chemical energy from glucose is transferred through ecosystems as organisms eat each other, forming food chains.
3) Producers like plants capture energy from the sun which is then consumed by primary consumers like herbivores, and passed up through secondary and tertiary consumers in a trophic pyramid, with decomposers recycling nutrients.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisJessabeth Aluba
╠²
Plants and algae perform photosynthesis, which converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts and uses chlorophyll to absorb light, which drives the production of ATP and NADPH that fuel the Calvin cycle to produce glucose from carbon dioxide. It is an essential process that generates oxygen and forms the base of the food chain sustaining all life on Earth.Photosynthesis Notes



Photosynthesis Notesjlehmkuhler
╠²
Photosynthesis involves two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. In the light-dependent reactions, chlorophyll uses light energy to split water molecules, producing oxygen and energized electrons. These electrons are used to convert NADP+ into NADPH through an electron transport chain, while hydrogen ions create a proton gradient used to make ATP. In the Calvin cycle, which takes place in the stroma, CO2 is fixed into three-carbon molecules using ATP and NADPH produced previously. These molecules are then reduced, regenerated, and used to form new sugars like glucose. Together these stages convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds to fuel plant growth.Cyclic phosphorylation



Cyclic phosphorylationFarhanaShiekh
╠²
This document presents a topic on cyclic photophosphorylation. It begins with an introduction to photophosphorylation and defines cyclic photophosphorylation. There are two types of photophosphorylation: cyclic and non-cyclic. Cyclic photophosphorylation involves the same excited electron returning to the excited chlorophyll, producing one ATP molecule. The mechanism involves an electron being energized in photosystem I and passing through an electron transport system before returning to the reaction center. This releases energy to produce ATP. The steps involve an electron moving from P700 to acceptors to the cytochrome complex and back to P700, producing one ATP via chemiosmosis.Chloroplasts



ChloroplastsDilip Pandya
╠²
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plants and algae that carry out photosynthesis. They have an inner and outer membrane, with an intermembrane space between them. Inside is the stroma, which contains thylakoids that are arranged in stacks called grana. Chloroplasts contain their own genome and divide independently. According to the endosymbiotic theory, chloroplasts originated from cyanobacteria that were engulfed by other cells but not destroyed. Chloroplasts import most proteins from the cytosol through translocation complexes in the inner and outer membranes. They perform photosynthesis through light and dark reactions, using solar energy to fix carbon dioxide and produce oxygen and carbohydrates.Ap Bio Ch7 Power Point



Ap Bio Ch7 Power PointAnthony DePhillips
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages: in the light-dependent reactions, sunlight is absorbed and used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, producing oxygen as a byproduct. In the light-independent reactions, the glucose is then assembled from carbon dioxide using energy from the light reactions. The light reactions take place in chloroplasts within plant cells, while the dark reactions occur in the chloroplast stroma. Photosynthesis is essential for producing oxygen and food on Earth.Light reaction of Photosynthesis



Light reaction of PhotosynthesisAlakesh Das
╠²
Photosynthesis converts light energy to chemical energy through light reaction. Light reaction occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, where photosystems use light to transfer electrons and pump protons, generating ATP and NADPH. There are two photosystems - PSII uses water as the electron donor and evolves oxygen, while PSI and cytochrome b6f complex generate a proton gradient used for ATP synthesis via ATP synthase. Both oxygenic and anoxygenic bacteria perform similar light reactions, though they use different electron donors and may contain only one photosystem. Light reaction is essential for providing the energy required for carbon fixation in photosynthesis.Organisms and their environments



Organisms and their environmentshilary farlow
╠²
The document discusses key concepts related to ecosystems, including energy flow, trophic levels, food chains, and food webs. It explains that the sun is the primary source of energy for ecosystems and that energy flows through trophic levels from producers to consumers. While chemical elements cycle through an ecosystem, energy is lost at each transfer between trophic levels and must constantly be replenished by the sun. Food chains and food webs illustrate the complex feeding relationships and energy transfers within an ecosystem.AS Level Biology - 4) Membranes



AS Level Biology - 4) MembranesArm Punyathorn
╠²
Transportation of substances in and out of cells can be regulated by the single most underrated and under appreciated organelle in the cell - the phospholipid bilayer membrane.Photosynthesis PowerPoint



Photosynthesis PowerPointBiologyIB
╠²
Photosynthesis converts sunlight into chemical energy through a series of light-dependent and light-independent reactions. The light reactions use energy from sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH, which provide energy and electrons to drive the Calvin cycle. The Calvin cycle fixes carbon from carbon dioxide into organic three-carbon sugars like glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions. One sugar molecule is used for growth, while five are recycled to regenerate the starter molecule for the next round of the Calvin cycle.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisJolie Yu
╠²
The document summarizes photosynthesis, including:
1) Photosynthesis uses light energy, water, carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen through two phases - the light reactions and dark reactions.
2) The light reactions use light to produce ATP and NADPH using chlorophyll and a series of electron carriers in the thylakoid membranes.
3) The dark reactions use ATP and NADPH to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into glucose through the Calvin cycle in the chloroplast stroma.Biology Lecture - Photosynthesis



Biology Lecture - PhotosynthesisLumen Learning
╠²
1. Transition to renewable energy sources like solar and wind to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels.
2. Drive and fly less to lower transportation emissions, and purchase more fuel-efficient vehicles.
3. Practice sustainable habits like recycling and reducing waste to lessen environmental impacts.
4. Support policies that place a price on carbon emissions to incentivize the development of clean technologies.cellular respiration



cellular respirationYang Durana
╠²
The document discusses cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells break down food molecules to produce energy in the form of ATP. It describes the three main stages of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and occurs in the cytoplasm, producing a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further breaks down molecules in the mitochondria, producing more ATP and electrons. The electron transport chain uses these electrons and oxygen to produce the most ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen through fermentation.Similar to Presentation photosynthesis (20)
Photosynthesis part 1



Photosynthesis part 1Maria Donohue
╠²
The document summarizes key experiments and discoveries in photosynthesis research from the 1600s to present. Jan van Helmont discovered in 1643 that most of a tree's mass comes from water, not soil. Joseph Priestly showed in 1771 that plants release oxygen. Jan Ingenhousz found in 1779 that plants need sunlight to produce oxygen. Later scientists like Calvin traced the chemical pathway that fixes carbon to form glucose in the Calvin Cycle.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisMaria Donohue
╠²
The document discusses photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds like glucose. It summarizes key experiments by scientists like van Helmont, Priestly, and Ingenhousz that helped discover this process. The document then describes the structures involved like chloroplasts and chlorophyll, and explains that photosynthesis has two main stages - the light-dependent reactions where sunlight is converted to chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent Calvin cycle where sugar is produced using those energy carriers.Photosynthesis part 1



Photosynthesis part 1Maria Donohue
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. Key early scientists like van Helmont, Priestly and Ingenhousz discovered that plants require sunlight to produce oxygen. The process occurs in chloroplasts and involves two stages - the light-dependent reactions where light energy is absorbed to make ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent Calvin cycle where carbon is fixed into glucose using the energy from the light reactions.Photosynthesis Notes



Photosynthesis NotesHyde Park
╠²
The document provides an overview of photosynthesis, including:
1) Photosynthesis uses light energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen through a two-stage process of light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
2) The light reactions convert solar energy to chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle then uses this chemical energy to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into sugars.
3) Two photosystems, Photosystem I and Photosystem II, work together to drive electron transport and generate a proton gradient used to produce ATP through chemiosmosis.PHOTOSYNTHESIS



PHOTOSYNTHESISsathyananthinis
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages - the light-dependent reactions where sunlight is absorbed to make ATP and NADPH using chlorophyll, and the light-independent Calvin cycle where carbon dioxide is fixed using ATP and NADPH to produce glucose or other carbohydrates. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis, which is essential for aerobic organisms to survive.Photosynthesis Lecture for Lesson 1



Photosynthesis Lecture for Lesson 1Lauren Welker
╠²
This document provides an overview of photosynthesis, including:
- Photosynthesis converts sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into oxygen and glucose through a two-step process in chloroplasts. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which absorbs light energy and the thylakoid membranes where the light-dependent reactions occur.
- Autotrophs like plants use photosynthesis to produce their own food, and release oxygen into the atmosphere as a byproduct. Most of Earth's oxygen comes from phytoplankton in the ocean.
- Photosynthesis is essential to life on Earth as it provides oxygen for humans and animals to breathe and produces glucose that sustains plant life.Chap 8 concept checks



Chap 8 concept checksJavier Aguirre
╠²
The document provides information about photosynthesis including:
1. Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts located in plant leaves. The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes and produce ATP and NADPH.
2. The Calvin cycle uses the products of the light reactions along with CO2 to produce G3P, which can then be converted into glucose and other organic molecules.
3. The two main stages, the light reactions and Calvin cycle, work together to ultimately convert sunlight, water and CO2 into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds through the overall process of photosynthesis.Lesson plan powerpoint



Lesson plan powerpointLauren Welker
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages - the light dependent reactions that take place in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast and produce ATP, NADPH, and oxygen, and the light independent reactions that take place in the chloroplast stroma and use ATP and NADPH to produce glucose from carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis is essential to life on Earth as it provides oxygen for humans and animals to breathe and produces glucose that sustains life in plants.Photosynthesis ppt



Photosynthesis pptDoreen Mhizha
╠²
The document outlines the key processes and components of photosynthesis. It discusses how chloroplasts use light energy from the sun to transform carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-rich glucose through two stages - the light-dependent reactions which generate ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent Calvin cycle which uses these products to fix carbon into sugars. Chlorophylls and other pigments play a crucial role in absorbing sunlight for photosynthesis, which is why plants appear green.Photosynthesis PPT FOR CLASS 9,10 and 11Th students



Photosynthesis PPT FOR CLASS 9,10 and 11Th studentsKumarlalit750
╠²
The document outlines the key processes and components of photosynthesis. It discusses how chloroplasts use light energy harvested by pigments like chlorophyll to drive photophosphorylation, producing ATP and NADPH through electron transport chains. The Calvin cycle then uses these products to fix carbon from CO2 into sugars, providing the basic energy currency and building blocks for life. Plants appear green because chlorophyll predominantly absorbs wavelengths other than green.Photosynthesis



Photosynthesiswcadigpub2009zs
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. Chlorophyll in the chloroplasts absorbs light which is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-storing molecules like glucose. The byproducts of photosynthesis like oxygen and glucose are essential for other organisms to survive.ECOSYSTEM-Life-Energy.pptx



ECOSYSTEM-Life-Energy.pptxPT2JJ
╠²
This presentation discusses the way energy flows and is distributed all throughout the ecosystem, from one member to another. This details how one organism becomes an essential necessity for another and how abiotic components play their role as supportive elements for life.Photosynthesis by iqbal1313



Photosynthesis by iqbal1313subject specialist biology
╠²
By the end of this lecture you will be able to:
Understand that ENERGY can be transformed from one form to another.
Know that energy exist in two forms; free energy - available for doing work or as heat - a form unavailable for doing work.
Appreciate that the Sun provides most of the energy needed for life on Earth.
Explain why photosynthesis is so important to energy and material flow for life on earth.
Know why plants tend to be green in appearance.
Equate the organelle of photosynthesis in eukaryotes with the chloroplast.
Describe the organization of the chloroplast.
Understand that photosynthesis is a two fold process composed of the light-dependent reactions (i.e., light reactions) and the light independent reactions (i.e. Calvin Cycle or Dark Reactions).
Tell where the light reactions and the CO2 fixation reactions occur in the chloroplast.
Define chlorophylls giving their basic composition and structure.
Draw the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll and compare it to the action spectrum of photosynthesis.
Define the Reaction Centers and Antennae and describe how it operates.
Describe cyclic photophosphorylation of photosynthesis.
Describe noncyclic photophosphorylation of photosynthesis. Science 



Science RhyzaRuiz
╠²
Van Helmont, Priestley, and Ingenhousz experiments revealed that plants grow using water and carbon dioxide, and produce oxygen. Photosynthesis uses light, water, carbon dioxide to produce oxygen, ATP, NADPH, and glucose through two stages - the light-dependent reactions in the thylakoid membranes that produce ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent Calvin cycle in the chloroplast stroma that uses ATP and NADPH to produce glucose.Photosynthesis Essay



Photosynthesis EssayCustom Paper Writing Services
╠²
The Importance Of Photosynthesis In Plants
Photosynthesis Lab Hypothesis
Photosynthesis Process
Essay about photosynthesis lab report
Photosynthesis
Process of Photosynthesis Essay
Photosynthesis Research Paper
Photosynthesis Research Paper
Photosynthesis and Respiration
Essay on Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Essay
Photosynthesis Lab Essay
Essay on Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis : The Chemical Energy
Lab Report On Photosynthesis
The Process of Photosynthesis Essay
Photosynthesis Essay example
Lab Report on Photosynthesis Essay15 photosynthesis



15 photosynthesisHazel Joy Chong
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. It occurs in chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll and other pigments. Photosynthesis involves two photosystems which absorb light and use it to split water, producing oxygen, protons, and electrons. The electrons are used to produce ATP through electron transport, and NADPH through oxidative phosphorylation. The ATP and NADPH produced are then used by the Calvin cycle to fix carbon dioxide into sugars.Photosynthesis lecture



Photosynthesis lectureIBslides
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy-rich organic molecules like sugar. It occurs in chloroplasts through two stages: the light-dependent reactions where solar energy is captured to make ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent reactions where carbon dioxide is reduced using ATP and NADPH to form carbohydrates like glucose. Photosynthesis provides a source of energy and organic carbon for nearly all life on Earth.Photosynthesis



PhotosynthesisCollegeof horticulture
╠²
Photosynthesis,Importance of Photosynthesis ,Structural feature of leaf advantage for photosynthesis,Leaf anatomy of C3 and C4 plants: etc.photosynthesis.ppt



photosynthesis.pptPrakhar Pandey
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions where light energy is captured and used to produce ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent reactions where CO2 is incorporated into organic compounds to produce glucose. Photosynthesis is essential as it produces oxygen and glucose, the primary energy source for nearly all life on Earth.Photosynthesis[1]![Photosynthesis[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/photosynthesis1-200331163342-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Photosynthesis[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/photosynthesis1-200331163342-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Photosynthesis[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/photosynthesis1-200331163342-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Photosynthesis[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/photosynthesis1-200331163342-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Photosynthesis[1]TarekGamal14
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages - the light-dependent reaction which converts solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent reaction which uses this chemical energy to fix carbon and produce glucose. Photosynthesis is essential as it produces oxygen and glucose, the primary energy source for nearly all life on Earth.Presentation photosynthesis
- 1. By Ganyaza Z
- 2. Review ’üĄ What is photosynthesis? ’üĄ Process by which energy from sunlight is used to convert water and carbon dioxide into highenergy carbohydrates (sugars and starches) and oxygen as a waste product ’üĄ Who uses photosynthesis? ’üĄ Plants and other producers
- 4. Jan van Helmont ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ 1643 Belgian physician Do plants grow by taking material out of the soil? Mass of soil Mass of seed Watered regularly @ end of 5 yrs, tree was 75 g, soil the same Conclusion: Mass came from water Accounts to the ŌĆ£hydrateŌĆØ portion of carbohydrate produced but what made the ŌĆ£carbo-ŌĆØ portion
- 5. Joseph Priestly ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ 1771 English minister Bell jar, candle, plant Jar over candle’āĀ flame died out Jar over candle with live sprig of mint’āĀ flame didnŌĆÖt die Conclusion: Plant releases oxygen
- 6. Jan Ingenhousz ’üĄ 1779 ’üĄ Dutch scientist ’üĄ Aquatic plants produce bubbles only when light is present ’üĄ Conclusion: Plants need sunlight to produce oxygen
- 7. Julius Robert Mayer ’üĄ 1845 ’üĄ German scientist ’üĄ Proposed that plants convert light into energy into chemical energy
- 8. ’üĄ The experiments performed by van Helmont, Priestly, and Ingenhousz led to work by other scientists who finally discovered that in the presence of light, plants transform carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates, and they also release oxygen ’üĄ Hill, R. (May 1999). "Oxygen Produced by Isolated Chloroplasts". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences 127 (847): 192ŌĆō210
- 9. Review Sunlight ’üĄ White light ’üĄ ROYGBIV ’üĄ Combo of all colors ’üĄ Pigments ’üĄ Chemicals that absorb electromagnetic radiation (visible light) ’üĄ Light absorbing molecules ’üĄ Electromagnetic spectrum ’üĄ Electrons=energy
- 11. Chloroplast (found in cells in leaves) ’üĄ Concentrated in the cells of the mesophyll (inner layer of tissue) in leaf ’üĄ Stomata ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ Tiny pores on surface of leaf Allows carbon dioxide and oxygen in and out of the leaf Veins ’üĄ Carry water and nutrients from roots to leaves ’üĄ Deliver organic molecules produced in leaves to other parts of the plant
- 12. Chloroplast ’üĄ Cellular organelle where photosynthesis takes place ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ Double membrane Outer membrane Stroma (fluid filled space) Inner membrane Thylakoids Granum Intermembrane space Contain chemical compound called Chlorophyll ’üĄ This molecule gives chloroplast its green color
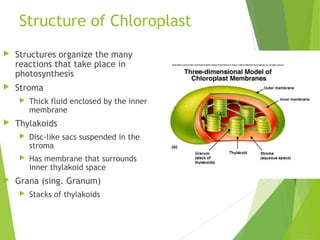
- 13. Structure of Chloroplast ’üĄ Structures organize the many reactions that take place in photosynthesis ’üĄ Stroma ’üĄ ’üĄ Thick fluid enclosed by the inner membrane Thylakoids ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ Disc-like sacs suspended in the stroma Has membrane that surrounds inner thylakoid space Grana (sing. Granum) ’üĄ Stacks of thylakoids
- 16. Chlorophyll Plants principle pigment ’üĄ 2 types ’üĄ ’üĄ Chlorophyll a ’üĄ ’üĄ Absorbs light in the blue-violet and red regions of visible spectrum Chlorophyll b ’üĄ Absorbs light in the blue and red regions of the visible spectrum Chlorophyll does NOT absorb light well in the green portion of the visible spectrum ’üĄ Green light reflected by leaves ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ This is why plants look greenŌĆ”they reflect green light Carotene ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ Secondary plant pigment Red and orange pigments Absorb light in other regions of the spectrum other than red and orange
- 17. 2 main stages ’üĄ Light Dependent Rxn ’üĄ Light-Independent or Calvin Cycle
- 18. Photosynthesis Overview ’üĄ #1 ŌĆ£Light-DependentŌĆØ reactions ’üĄ Convert the E in sunlight to chemical energy ’üĄ Rxns depend on molecules made in membranes of thylakoids ’üĄ Chlorophyll in membr. captures light E ’üĄ Chloroplast use E to remove e- from water ’üĄ Splits water into oxygen (waste) and hydrgen ions ’üĄ ’üĄ ’üĄ e- taken are used to make high-E molecule NADPH (similar to NADH) Chloroplast also use captured E to make ATP Overall Product: convert light E into chemical energy stored in compounds ATP and NADPH
- 19. Photosynthesis Overview # 2 ŌĆ£Light- IndependentŌĆØ Reactions aka The Calvin Cycle ’üĄ Makes sugar from atoms of CO2 and H+ ions and High-E e- carried by NADPH ’üĄ Enzymes for these reactions are dissolved in the stroma (outside thylakoid) ’üĄ ATP made by light Rxns provides E to make sugar (glucose) ’üĄ Called light independent, b/c unlike unlike the light reactions, these do NOT require light tp begin ’üĄ However, this cycle does require two things made by the light reactions: ATP and NADPH ’üĄ This means that the calvin cycle cannot necessarily continue in the dark
- 20. List of references ’üĄ ^╠²"photosynthesis".╠²Online Etymology Dictionary. ’üĄ ╠²(http://bioenergy.asu.edu/photosyn/study.html).
- 21. REFERENCES Bryant DA, Frigaard NU (November 2006). "Prokaryotic photosynthesis and phototrophy illuminated".╠²Trends Microbiol.╠²14╠²(11): 488ŌĆō96] Buick R (August 2008).╠²"When did oxygenic photosynthesis evolve?".╠²Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci.╠²363╠²Olson JM (May 2006). "Photosynthesis in the Archean era".╠²Photosyn. Res.╠²88╠²(2): 109ŌĆō17. Online Sources http://bioenergy.asu.edu/photosyn/stuy.html http://hdgc.epp.cmu.edu/teachersguide/teachersguide.htm ╠²
