Presentation1
- 1. MACRO ANALYSIS OF INDIAN THERMAL POWER GENERATION SECTOR PROJECT GUIDE: PROF.H.J.JANI SUBMITTED BY: AKASH CHOKSI (1OM44) ANIL CHAUHAN (10F45) MADHURRAM CHUDASAMA (10M63) TEJAS VASAVA (10F76) VIREN PATEL (10M79) G.H.PATEL POST GRADUATE INSTITUTE OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT SARDAR PATEL UNIVERSITY VALLABH VIDYANAGAR (388120)
- 2. INTRODUCTION TO POWER GENERATION SECTOR ï Power Generation Overview ï History of Power Generation
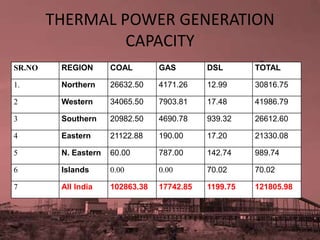
- 4. THERMAL POWER GENERATION CAPACITY SR.NO REGION COAL GAS DSL TOTAL 1. Northern 26632.50 4171.26 12.99 30816.75 2 Western 34065.50 7903.81 17.48 41986.79 3 Southern 20982.50 4690.78 939.32 26612.60 4 Eastern 21122.88 190.00 17.20 21330.08 5 N. Eastern 60.00 787.00 142.74 989.74 6 Islands 0.00 0.00 70.02 70.02 7 All India 102863.38 17742.85 1199.75 121805.98
- 5. POWER SECTOR REFORMS âĒ Evolution of Indian Power Industry âĒ Mega Power Policy âĒ National Electricity Policy âĒ National Tariff Policy âĒ Electricity Act 2003
- 6. ECONOMICS OF THERMAL POWER GENRATION SECTOR âĒ Introduction to Economics of Power Generation âĒ Selection of Type of Generation âĒ Tariff
- 7. LOGISITC MANAGEMENT âĒ COAL - The Primary Energy Resource Endowment - Skewed Regional Distribution of Coal Reserves - Creating an Integrated Rail System For Planning Optimum Outcome
- 8. âĒ Gas Trans National Pipelines
- 9. Current Trends in Thermal Power Generation Sector âĒ Economics and Energy Indicators âĒ Energy Consumption âĒ Regional and Sect oral Variations âĒ Resources Availability âĒ Resources for Thermal Power Generation
- 10. TYPES AND SOURCES OF FINANCE âĒ Debt âĒ Equity âĒ Key Power Sector Financing
- 11. FINANCIAL ANALYSIS âĒ Ratio Analysis âĒ ROCE âĒ RONW âĒ EPS AND DPS
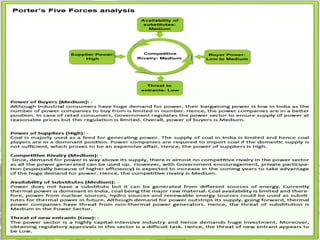
- 13. SWOT ANALYSIS Strength âĒ Highly qualified engineering and technical personnel âĒ Regulatory framework is further facilitated with enactment of Electricity Bill 2003. âĒ Emergence of strong and globally comparable central utilities (power grid NTPC) Opportunity âĒ Coal based plants at pithead or coastal locations (imported coal) âĒ Natural Gas/CNG based turbines at load centres or near gas terminals
- 14. Weakness -More ever, government provides power to agriculture sector at subsidized rates. This factors have resulted in financial disorder of state electricity board (SEBs) -Poor return to utilities, which affect their profitability and capacity to make further investment -Lack of optimum utilization of the existing generation capacity Threats -Waste generation leading to environmental damage -High AT & C losses (Aggregate technical and commercial losses) AT&C loss (defined as the difference between the input energy and the units of energy from which the payment is actually realized) has come down further in 2006/07, to 32.07%. Compared to the last two years, this marks an improvement in efficiency, of over 2%
- 15. FUTURSTIC SCENARIO OF THE INDUSTRY -Thermal generation, comprising coal, gas and oil, is expected to grow by 5.6% per annum during the period to 2015, but growth looks set to accelerate later in the decade. -Expect gas-fired power generation to climb 16.7% per annum between 2011 and 2015, with an average annual growth rate of 16.1% forecast to 2020.
- 16. REFERANCES âĒ Er. Nath Rakesh;Paper âPower sector reforms-sharing of resources is the key to economical growth and sucessâ;Octobar 2003 âĒ Nag P.K. âPower plant engineering â; 2005 âĒ Power ministry of India; âAnnual report 2010-11â Websites: âĒ www.powermin.nic.in âĒ planningcommission.nic.in/ âĒ www.coal.nic.in/ âĒ www.ntpcindia.com/ âĒ www.cercind.gov.in/ âĒ www.cea.nic.in âĒ www.indiainfrastructure.com/ âĒ www.indiacore.com âĒ www.kpmg.com/ âĒ cg.gov.in/opportunities/Annexure%203.2.pdf âĒ www.indiaenergyportal.org/overview_detail.php âĒ www.scribd.com âš Research âš Business & Economics