LIGHT AND SIGHT
- 1. LIGHT AND SIGHT BY: EN. KAMARUZAMAN BIN ABD SAMAD
- 2. Can be reflect Travel in straight line PROPERTIES OF LIGHT Can be disperse Can be refract
- 3. 2- i (incident angle) = r (reflected angle) 1- Light bounce the surface of object REFLECTION 3- Properties image on plane mirror upright virtual Same size
- 4. i r
- 6. REFRACTION speed of light change when pass from one medium to another medium in different density
- 7. 90 o line (normal) AIR WATER
- 8. 90 o line (normal) AIR WATER
- 9. AIR WATER
- 10. AIR WATER
- 11. DEFECT OF VISION & LIMITATION OF SIGHT
- 12. Learning Objective At the end of the lesson the students must able: 1- Describe the defect of vision 2- State the limitation of sight.
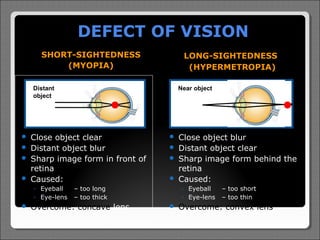
- 13. DEFECT OF VISION SHORT-SIGHTEDNESS (MYOPIA) LONG-SIGHTEDNESS (HYPERMETROPIA) Distant object Near object Close object clear ï Distant object blur ï Sharp image form in front of retina ï Caused: ï âĶ Eyeball âĶ Eye-lens ï Close object blur ï Distant object clear ï Sharp image form behind the retina ï Caused: ï â too long â too thick Overcome: concave lens âĶ Eyeball âĶ Eye-lens ï â too short â too thin Overcome: convex lens
- 15. ContinueâĶ DEFECT OF VISION Colour blindness Astigmatism - Genetic disease. -Caused by irregular surface of - Lack photoreceptor on retina. cornea. - Canât determine red and green. - Sees some part of object more clearly than other part. - Correction: -Surgery -Special lens
- 16. We canât see through opaque object We canât see tiny object We canât see distant object LIMITATION OF SIGHT OPTICAL ILLUSION BLIND SPOT Image form in accurate but misinterpreted by brain Eye cannot detect image that fall on the spot
- 17. Do You See the Bunny or the Duck?
- 18. What do you see at first an old lady or a young woman?