presentationdnagrade10-110608052713-phpapp01.pdf
- 1. INHERITANCE AND CHANGE: DNA ¡è CHARACTERISTICS AND INHERITANCE Compiled by: Madre¡¯ Nortje BIOLOGY
- 2. A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 2 A Brief Introduction to Genetics is a short documentary film created using motion graphics as the main visual component. It is a film that explores the history of genetics & genomics and the... 823 views since Aug 15, 2010 submitted by: dmetzky ASSIGNMENT GOOD WEB PAGE: http://www.genomebc.ca/education/
- 3. A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS HTTP://WWW.SCIVEE.TV/NODE/20869 S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 3 http://www.scivee.tv/node/20869
- 4. CHARACTERISTICS AND INHERITANCE S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 4 HOMOLOGOUS ? An organ that is similar to another in: structure, function, position and development.
- 5. HOMOLOGOUS ? After the fusion of the egg and sperm the chromosomes in the zygote now exist as 23 pairs. 23 from each sex cell. ? Homologous chromosomes exist as they have the same genes for particular characteristics at the same location on the chromosomes. ? The zygote has two genes for each characteristic ¨C one from each parent. S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 5
- 6. GREGOR MENDEL 1822 -1884 ¡°FATHER OF GENETICS¡± www.dobermann-review.com S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 6
- 7. Mendel Pea Theory 8/06/2011 Science grade 10/DNA 7 ? www.schools-wikipedia.org ?Pure breeding means that parents produce offspring off same colour only.
- 8. Mendel Pea Theory 8/06/2011 Science grade 10/DNA 8 ? www.scq.ubc.ca
- 9. GENETIC PEAS 8/06/2011 Science grade 10/DNA 9 ? Gene controlling the colour ? Pea plants with the alternate alleles ? CG dark green ¨C incompletely dominant ? CY yellow ¨C defective chlorophyll ¨C unable to photosynthesize ¨C die ? youngGenetic-Coding.gif ? 200 ¡Á 349 - ... insight into the DNA of the pea, by unravelling its genetic coding. ? www.topnews.in www.topnews.in
- 10. GENETIC PEAS TYPE 8/06/2011 Science grade 10/DNA 10 ?GENOTYPE PHENOTYPE ?CG CG Dark green ?CG CY Light green ?CY CY Yellow ?Plants grown from Genotype CGCY X CGCY ?Pea plants are self fertilizing ¨C cross giving rise to Genotype seed CG CG : 2CG CY : CY CY
- 11. GENETIC BARLEY 8/06/2011 Science grade 10/DNA 11 ? Gene controlling pigment ? Producing the alternate alleles ? A: Pigment produced ¨C green (dominant) ? ¡®a: No pigment ¨C albino / or white (recessive) www.southernbiological.com
- 12. GENETIC BARLEY TYPE http://www.albertabarley.com/barley 8/06/2011 Science grade 10/DNA 12 ? Plants grown from Genotype Aa x Aa ? Germinated seeds, can grow into ? AA ¨C green ? Aa ¨C green ? Aa ¨C albino / white ? ? Plants obtained ratio ¨C ? 3 green: 1 white
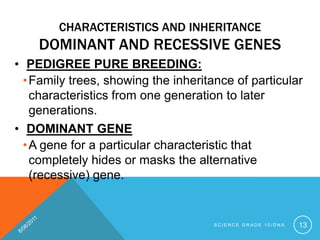
- 13. CHARACTERISTICS AND INHERITANCE DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE GENES ? PEDIGREE PURE BREEDING: ?Family trees, showing the inheritance of particular characteristics from one generation to later generations. ? DOMINANT GENE ?A gene for a particular characteristic that completely hides or masks the alternative (recessive) gene. S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 13
- 14. CHARACTERISTICS AND INHERITANCE DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE GENES ? RECESSIVE GENE ?A gene for a particular characteristic that is completely hidden or masked by the alternative (dominant) gene ? ALLELES OF GENES ?Alleles (a-LEELs): different forms of the same gene; each allele produces variations in inherited characteristics, e.g. eye colour S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 14
- 15. ? HOMOZYGOUS ?Homozygous (HO-mo-ZYE-gus): where the genes for particular characteristic are the same; a pure breeder ? HETEROZYGOUS ?Heterozygous (HET-er-o-ZYE-gus): where the genes for a particular characteristic are different; a hybrid S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 15 CHARACTERISTICS AND INHERITANCE DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE GENES
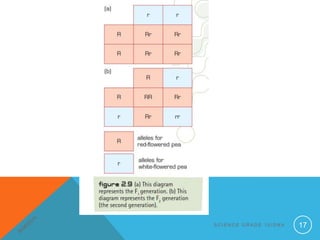
- 16. DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE GENES ? The RR and rr combinations of alleles where the offspring is identical to parent are HOMOZYGOUS ? The Rr combinations of alleles is known as HETEROZYGOUS. S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 16
- 17. S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 17
- 18. OTHER PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 18 THE DETERMINATION OF OUR PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS IS COMPLEX THREE FORMS: 1. INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE ? GENOTYPE ?Genotype (JEE-no-type): the type of genes possess in an organism (BB, BW and WW) for specific characteristic (pg. 131 ¨C Black, White or Blue ¨C grey feathers) ? PHENOTYPE ?Phenotype (FEE-no-type): the physical appearance or characteristics of an organism (pg. 131 ¨C the colour Black, White or Blue ¨C grey)
- 19. . ?INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE ?some genes do not have dominant or recessive alleles and results in a heterozygous individual (blended) ?e.g. black-feathered (BB) and white-feathered (WW) chickens mating to create a blue/grey-feathered (BW) offspring ?The terms BB, WW and BW are called genotypes. ?The physical characteristic (feather colour) is called the phenotype S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 19 OTHER PATTERNS¡.NOT ALL GENES ARE INHERITED AS SIMPLE RECESSIVE OR DOMINANT GENES
- 20. OTHER PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 20 THREE FORMS continue: 2. CO ¨C DOMINANCE ? BOTH OFFSPRING ARE EXPRESSED IN THE PHENOTYPE ¨C e.g. Blood groups www.biologycorner.com
- 21. CO ¨C DOMINANCE ON HAND OF BLOOD TYPE ?Some cases have both alleles in the heterozygous offspring expressed in the phenotype ?E.g. ¨C blood type ?Three alleles for blood type gene and the types A, B, O and AB exist ?AB can form both A or B and has characteristics of both A and B but is not a blend ?A and B are dominant to O thus O will only occur in OO homozygous individual S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 21
- 22. OTHER PATTERS OF INHERITANCE S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 22 THREE FORMS continue: 3. SEX ¨C LINKING / SEX DETERMINATION ?Chromosomes: objects found in the nucleus of a cell that carry the genetic information ? SEX CHROMOSOMES ? XX - female ? XY - male ? AUTOSOMES ? All other chromosomes are referred to as autosomes
- 23. ? X and Y chromosomes ? The only two chromosomes that determine what sex you will be ? All other chromosomes are referred to as autosomes ? XX - female ? XY - male S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 23 X & Y ¡â ¡á
- 24. ALLELE FOR COLOUR-BLINDNESS: S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 24 X CHROMOSO ME
- 25. DIFFERENCE FEMALE ? Eggs will have 23 chromosomes one of which will be X MALE ? Sperm will have 23 chromosomes, but half of the sperm carry X chromosome and the other half carry Y chromosome S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 25
- 26. FERTILISATION: ¡á MALE ¡ú¡â If a male sperm¡. ? Containing X fertilizes an egg ? female (XX) ?Containing Y fertilises and egg ? male (XY) S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 26
- 27. SEX LINKAGE Sex-linked genes - found on X chromosome and not on Y and vice versa. E.g.: ?Colour blindness ?Haemophilia ?Duchenne¡¯s muscular dystrophy S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 27
- 28. S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 28
- 29. CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES ? MUTATION ? Permanent changes in genes, they may be caused by exposure to a ¡ú ? MUTAGEN ? Something that causes a mutation ? KNOWN MUTAGENS ? UV radiation ? X ¨C Ray ? Agricultural and Industrial Chemicals S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 29
- 30. HANDOUTS TO BE COMPLETE ¨C HAND BACK ON TUESDAY NEXT WEEK 1.Questions: How to find Your Learning Style 2. Online Questionnaire on Learning Styles http://www.engr.ncsu.edu/learningstyles/ilsweb.html 3. How to make your own DNA Code Bracelet S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 30
- 31. You all NOW have the GREAT Opportunity to learn more about genetic disorders YOUR BIOLOGY Assignment!!!! Test what you know? Questions 2.2 p 135 S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 31 HOMEWORK: QUESTIONS 2.2 - P135
- 32. NATURAL SELECTION ? Selection of certain characteristics for survival in nature ? Organisms possess structural, functional and behavioural characteristics that enable them to survive in their environments ? Those that do not are less likely to survive and thus less likely to reproduce and not pass on those weaknesses Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 32
- 33. Just means change. Also the name given to the process whereby new life forms develop Influenced by such things as physical barriers (mountains, rivers, oceans) known as geographic isolation EVOLUTION Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 33
- 34. EVOLUTION ? If a species is separated by such, they may develop different adaptation so much so that they can no longer interbreed ? This is referred to as Speciation Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 34 EVOLUTIO N
- 35. EVOLUTION ? Best summarised in 5 points 1. Variation exists within any population of organisms 2. All organism face a daily struggle to survive and reproduce, whether to find mates, seek shelter/food, escape predators 3. Those that are best able to survive and reproduce will do so Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 35
- 36. EVOLUTION 4. Those that reproduce pass on the advantageous characteristics to their offspring 5. Over time, the population will become better suited to its environment ? The theory of evolution can explain how plants and animals have gradually changed into new, different kinds over long periods of time Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 36
- 37. SUMMARY Questions Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 37
- 38. But remember¡. ?So what is the evidence for Evolution ?? ? If an environment changes too rapidly and the genes required for survival in the changed environment are not present in the gene pool¡.EXTINCTION may occur. Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 38
- 39. FOSSIL EVIDENCE ? Study of skeletal structure from fossils ? Evidence of locations ? Evidence of past environments Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 39
- 40. But remember¡. Fossils..... ?So what is the evidence for Evolution ?? Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 40
- 41. Comparative Embryology Science grade 10/DNA 8/06/2011 41 ? In certain stages of development, embryos of organisms in the same group e.g. vertebrates, have similar structures (a) pig (b) cow (c) Rabbit (d) human
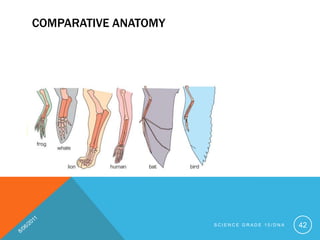
- 42. COMPARATIVE ANATOMY S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 42
- 43. DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT: STEPS TO FOLLOW - CLEAR AND SIMPLE P 20 GRADE 8 S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 43 EXPERIMENT Title Aim Hypothesis Variables Control Material METHOD Tables & Drawings Observation RESULTS Discussion EVALUATION Conclusion
- 44. REVISION: SCIENCE ALPHA TABLE(I) DATE UPDATED: 18/05/2011 S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 44 Word Meaning A Atmosphere B C Carbon Dioxide C Catalyst is a chemical that alters the rate of a chemical reaction but is not consumed by the reaction C Chemical Equation Reactions are described by C Concentration D Dry Ice E F Fermenting G Gas e.g. X 3 H Hydrogen H Hypothesis I J
- 45. REVISION: SCIENCE ALPHA TABLE (II) DATE UPDATED: 18/05/2011 S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 45 Word Meaning K L M N O Observation O Oxygen P Photosynthesis P Precipitate Q R Respiration Rate R S
- 46. REVISION: SCIENCE ALPHA TABLE (III) DATE UPDATED: 18/05/2011 S C I E N C E G R A D E 1 0 / D N A 46 Word Meaning O Observation O Oxygen P Photosynthesis P Precipitate Q R Respiration Rate R S T U V Variable W X Y Z