Presentation.pptx
- 2. z Definition Spatial Concepts Points1 : The elements of space Geometric figures1 : finite sets of points (i.e., subsets of space, which can be point, lines or regions) Spatial objects1 : âAn object with spatial attributesâ Spatial attribute1 : is specifies the object's geometric coordinates. Layer1 : is a representation of a spatial attribute or a layer is a set of geometric figures. .
- 3. z
- 4. z Definition Temporal Concepts ï§ We assume a linear ordered time line, isomorphic to a finite subset of the natural numbers. The elements of this set are termed chronons. ï§ Time points : is considered as one chronon. ï§ Time intervals [tk...tm] : with tkâĶtm, time point sand k<m, has duration and is defined as set of chronons. ï§ Time period : defined as a set of time points, time intervals or any combination thereof.
- 5. z Definition Temporal Concepts ï§ An event occurs at an exact time point, i.e., an event has no duration. Example events are a âcar crashâ, âsunriseâ etc. ï§ A state is defined for each chronon in a time interval, hence it has a duration. For example, a âexamâ takes place from loam until lpm.
- 6. z Time series models ï§ Autoregressive (AR) models ï§ Moving-average (MA) models ï§ Autoregressive moving-average (ARMA) models
- 7. z Definition Spatiotemporal Concepts ï§ We combine the concepts of spatial and temporal by simply recording the spatial view (i.e., objects and layers) in time (time point and time interval); ï§ For a moving âvehicleâ in a route network we can record its ânewâ position in time points ï§ t1âĶtk. In the same way, as a âland parcelâ changes its shape (eg. split , expanded etc.),we capture snapshots of such spatial object in time.
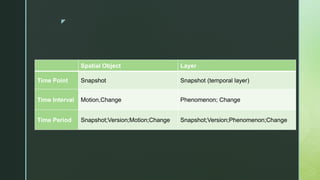
- 8. z Spatial Object Layer Time Point Snapshot Snapshot (temporal layer) Time Interval Motion,Change Phenomenon; Change Time Period Snapshot;Version;Motion;Change Snapshot;Version;Phenomenon;Change
- 9. z
- 10. z âĒ Snapshot model (Armstrong 1988) âĒ Spatiotemporal composite model (Langran and Chrisman 1988) âĒ Event-based spatiotemporal data model (Peuquet and Duan 1995) âĒ Three-domain data model (Yuan 1999) âĒ Geo-atom model (Goodchild et al. 2007, Chen et al. 2012) âĒ Object-oriental models (Wang and Cheng 2001)
- 11. z âĒ spatiotemporal data model based on the CLR technique(Bi Yu Chen 2015)
- 12. z References Xiaoyu Wang, Xiaofang Zhou . âSpatiotemporal Data Modelling and Management: a Surveyâ Pebesma, Edzer, and others. 2012. âSpacetime: Spatio-Temporal Data in r.â Journal of Statistical Software 51 (7): 1â30. Ãnnerfors, à sa, Mariana Kotzeva, TeodÃģra BrandmÞller, and others. 2019. âEurostat Regional Yearbook 2019 Edition.â Rowe, Francisco, Nikos Patias, and Dani Arribas-Bel. 2020. âPolicy Brief: Neighbourhood Change and Trajectories of Inequality in Britain, 1971-2011.â Rowe, Francisco, and Nikos Patias. 2020. âMapping the Spatial Patterns of Internal Migration in Europe.â Regional Studies, Regional Science 7 (1): 390â93. Kwan, Mei-Po, and Jiyeong Lee. 2004. âGeovisualization of Human Activity Patterns Using 3d GIS: A Time-Geographic Approach.â Spatially Integrated Social Science 27: 721â44.
- 13. z References Bi Yu Chen, Hui Yuan, Qingquan Li, Shih-Lung Shaw, William H.K. Lam & Xiaoling Chen (2016) Spatiotemporal data model for network time geographic analysis in the era of big data, International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 30:6, 1041-1071,


![z
Definition
Temporal Concepts
ï§ We assume a linear ordered time line, isomorphic to a finite subset of the natural
numbers. The elements of this set are termed chronons.
ï§ Time points : is considered as one chronon.
ï§ Time intervals [tk...tm] : with tkâĶtm, time point sand k<m, has duration and is
defined as set of chronons.
ï§ Time period : defined as a set of time points, time intervals or any combination
thereof.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-220923222022-21f4a0cb/85/Presentation-pptx-4-320.jpg)