1 of 12
Download to read offline










Recommended
teamwork2-160303073432.pdf
teamwork2-160303073432.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses teams and teamwork. It defines a team as a group committed to producing a result through cooperation and communication. Benefits of teamwork include quick solutions, improved productivity, diversity of ideas, and better decisions. The stages of team development include forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. Effective communication is vital for team success and includes supporting ideas, listening, and giving feedback. The closing thought emphasizes that the strength of each individual member lies in the team.conceptual frame work.docx
conceptual frame work.docxsaranya443113
╠²
The document describes a structured teaching programme on cord blood banking among staff nurses. It presents a conceptual framework based on a general system theory model that shows demographic variables and source of information as inputs, a pre-interventional knowledge assessment and teaching intervention as the throughput, and knowledge assessment outcomes as either an increase in knowledge or no change as the outputs. The goal is to increase nurses' knowledge about cord blood banking through this teaching programme.4-200414055814.docx
4-200414055814.docxsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses human resource management and recruitment. It defines human resource management as planning, organizing, directing, and controlling various human resource functions like recruitment, training, performance evaluation, compensation, and retention to satisfy organizational and individual needs.
It then discusses the objectives, components and importance of recruitment. The key recruitment steps mentioned are planning, searching, screening, evaluation and control. Internal sources include promotions, referrals and external sources involve advertisements, consultants, campus recruitment. Factors affecting recruitment are organization size, employment conditions, growth rate, compensation offered.typesofvariablesinresearchankitach-181022084515.docx
typesofvariablesinresearchankitach-181022084515.docxsaranya443113
╠²
This document defines and describes different types of variables that are commonly used in research. It begins by explaining that observations or participants can have characteristics that are either constants (the same for all) or variables (differ between participants). The main types of variables discussed are independent variables (factors being studied for their effects) and dependent variables (outcomes being measured). Other variable types covered include moderator variables, quantitative vs qualitative variables, and continuous vs discontinuous variables. Demographic variables are also defined as characteristics used to describe research samples.basicresearchterminologies-180731084714.docx
basicresearchterminologies-180731084714.docxsaranya443113
╠²
This document defines key terms and concepts used in research. It discusses variables, data, samples, populations, hypotheses, limitations, validity, reliability and more. Research involves systematically investigating questions through data collection and analysis in order to generate answers and suggest new questions for further study. Key aspects of research addressed include conceptual frameworks, operational definitions, sampling methods, and reliability and validity.hypotheses-PPT.docx
hypotheses-PPT.docxsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses research hypotheses. It defines a hypothesis as a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. Hypotheses help translate research problems into predicted outcomes and include the variables and population being studied. Formulating hypotheses plays an important role in theory building. The document outlines the importance of hypotheses in providing objectivity, direction, and goals for research. It also discusses the characteristics of good hypotheses, such as being testable and consistent with existing knowledge. Sources of hypotheses include theoretical frameworks, previous research, and real-life experiences. The document concludes by describing different types of hypotheses like simple vs complex and directional vs non-directional.CET U5 FORMULATING OBJECTIVES (1).pdf
CET U5 FORMULATING OBJECTIVES (1).pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses educational objectives and their formulation. It begins by outlining the objectives, contents and introduction to the topic. It then defines educational objectives, lists their characteristics as SMART and FOCUSED, and describes the three types - general, intermediate and instructional. Next, it explains Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives, which categorizes them into cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains. For each domain, it provides the levels and examples of action verbs used to write objectives. The document concludes by assigning students to prepare objectives for a teaching plan and answering review questions.yuvas resource person.pptx
yuvas resource person.pptxsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses different types of tumors and cancer treatments. It explains that cancerous tumors can spread throughout the body while noncancerous tumors are rarely life-threatening. It then describes common cancer treatments like surgery to remove tumors, chemotherapy to kill fast-growing cells, radiation therapy to reduce cancer risks or make other treatments more effective, and hormone therapy for certain cancers that use hormones to grow. The document concludes that having a diagnosis and treatment plan for early-stage cancer will help achieve the goal of overcoming the disease.NUTRITIONAL DEFICENCYS IN CHILDREN.pdf
NUTRITIONAL DEFICENCYS IN CHILDREN.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
Nutritional deficiencies in children can cause significant health problems. Protein deficiencies like marasmus and kwashiorkor result in wasting and edema. Vitamin deficiencies such as vitamins A, D, B1, B2 and niacin can cause conditions like rickets, beriberi, and pellagra. Children are especially vulnerable due to their high nutritional needs for growth. Proper nutrition is essential for normal development and long-term health.factorsaffectinggrowthanddevelopment-210602032247.pdf
factorsaffectinggrowthanddevelopment-210602032247.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
Genetic, environmental, and prenatal factors all influence child growth and development. Genetic factors like a child's sex, race, and any genetic disorders can impact development. The prenatal environment, including maternal health, nutrition, infections, and substance use also affect fetal growth. After birth, postnatal factors like nutrition, illness, physical environment, socioeconomic status, and learning experiences further shape development. Growth and development are complex, multifactorial processes determined by an interaction of hereditary and environmental influences from conception onwards.principlesofgrowthanddevelopment-210601080242.pdf
principlesofgrowthanddevelopment-210601080242.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
The document discusses key concepts related to child growth and development. It defines growth as the process of physical maturation resulting in an increase in size, while development refers to functional and physiological maturation and the progressive increase in skills and capacity. It outlines several principles of growth and development, including that it proceeds from head to tail, center to periphery, general to specific, and is continuous, sequential, and predictable. Development depends on maturation and learning and is influenced by heredity and environment.commonneonataldisorders-160915052933.pdf
commonneonataldisorders-160915052933.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses several common neonatal disorders classified by type. Birth injuries include caput succedaneum (edema of the scalp from pressure during labor), cephalhematoma (collection of blood under the skull from birth trauma), fractures, facial paralysis, and Erb's/Brachial palsy. Disorders related to physiological factors include hyperbilirubinemia, hemolytic disease of the newborn, and respiratory distress syndrome. Infectious disorders include sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis. Disorders related to maternal conditions include infants of diabetic mothers. Specific details are provided on hemolytic disease of the newborn, respiratory distress syndrome, nursing care for injuries to the head, and ErbCET U5 INTRODUCTION.pdf
CET U5 INTRODUCTION.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses principles of education and the teaching-learning process. It begins by defining key terms like education, philosophy, and educational philosophies. It then examines several philosophies of education in detail, including naturalism, idealism, realism, and pragmatism. For each philosophy, it outlines the chief proponents, basic concepts, aims and principles of education, organization of education, curriculum, teaching methods, discipline approaches, and the role of the teacher. The document provides an overview of major educational philosophies to help understand principles that guide the teaching and learning process.CET U5 LESSON PLANNING.pdf
CET U5 LESSON PLANNING.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document provides information on lesson planning for nursing students, including:
- The objectives, contents, introduction, definition, functions, significance, prerequisites, characteristics, steps, and format of lesson planning.
- Key aspects of effective lesson planning include setting clear objectives, selecting appropriate content, utilizing various teaching methods and assessment strategies, and ensuring active student participation.
- The document outlines the various sections that should be included in a lesson plan such as the cover page, basic lesson plan information, time allotment and teaching-learning activities for each objective, assessment strategies, assignment, and references.essentialnewborncare-210819043505.pdf
essentialnewborncare-210819043505.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
The document provides information on essential newborn care including the 8 steps of essential newborn care such as drying the baby, assessing breathing, cord care, and warming the baby. It discusses principles like immediate drying, skin-to-skin contact, and delaying bathing and weighing. Components include neonatal resuscitation, thermal protection, infection prevention, and initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour. Risk factors for low birth weight babies and prevention measures are outlined. Optimal infant feeding practices of exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months and introducing complementary foods at 6 months are also summarized.normalnewbornamalkhalil-150107071628-conversion-gate02.pdf
normalnewbornamalkhalil-150107071628-conversion-gate02.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
1. The document defines the neonatal period as the time from birth to 4 weeks postnatal. During this period, newborns are observed and stabilized in the normal newborn nursery or on the maternity floor.
2. The roles of nurses and physicians in the normal newborn nursery include admission care like assessments, history taking, and ensuring identification; ongoing assessments using tools like the APGAR score; and providing routine neonatal care like maintaining temperature and establishing breastfeeding.
3. Physical examinations of newborns assess various body systems and features like reflexes, fontanels, skin characteristics, and vital signs to evaluate overall health and normalcy. Any abnormalities are noted.journal club print.docx
journal club print.docxsaranya443113
╠²
The document summarizes a study that assessed the effectiveness of a structured teaching program on mothers' knowledge of preventing pediatric emergencies and providing first aid for children under 5. 50 mothers participated in the study. Their knowledge was tested before and after the teaching program using a 25 question survey. The results showed that after the program, none of the mothers had inadequate knowledge while all had adequate knowledge, indicating the program was effective. The study also found significant associations between mothers' knowledge and several demographic factors like age, education level, occupation, number of children, and information sources.CET U5-TEACHING -LEARNING PROCESS.pdf
CET U5-TEACHING -LEARNING PROCESS.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses the teaching-learning process in a nursing education context. It begins by outlining the objectives and aims of education, including the individual, social, and democratic aims. It then defines learning as a modification of behavior through experience according to various psychological views. The principles of learning include that it is progressive, motivated, universal, and goal-directed. Teaching is defined as aimed at changing another's behavior potential and includes stimulation, guidance and encouragement of learning. The nature of teaching is described as interactive, multi-level, and requiring planning and effective communication. Evaluation questions are provided to test understanding of the key topics.More Related Content
More from saranya443113 (10)
NUTRITIONAL DEFICENCYS IN CHILDREN.pdf
NUTRITIONAL DEFICENCYS IN CHILDREN.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
Nutritional deficiencies in children can cause significant health problems. Protein deficiencies like marasmus and kwashiorkor result in wasting and edema. Vitamin deficiencies such as vitamins A, D, B1, B2 and niacin can cause conditions like rickets, beriberi, and pellagra. Children are especially vulnerable due to their high nutritional needs for growth. Proper nutrition is essential for normal development and long-term health.factorsaffectinggrowthanddevelopment-210602032247.pdf
factorsaffectinggrowthanddevelopment-210602032247.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
Genetic, environmental, and prenatal factors all influence child growth and development. Genetic factors like a child's sex, race, and any genetic disorders can impact development. The prenatal environment, including maternal health, nutrition, infections, and substance use also affect fetal growth. After birth, postnatal factors like nutrition, illness, physical environment, socioeconomic status, and learning experiences further shape development. Growth and development are complex, multifactorial processes determined by an interaction of hereditary and environmental influences from conception onwards.principlesofgrowthanddevelopment-210601080242.pdf
principlesofgrowthanddevelopment-210601080242.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
The document discusses key concepts related to child growth and development. It defines growth as the process of physical maturation resulting in an increase in size, while development refers to functional and physiological maturation and the progressive increase in skills and capacity. It outlines several principles of growth and development, including that it proceeds from head to tail, center to periphery, general to specific, and is continuous, sequential, and predictable. Development depends on maturation and learning and is influenced by heredity and environment.commonneonataldisorders-160915052933.pdf
commonneonataldisorders-160915052933.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses several common neonatal disorders classified by type. Birth injuries include caput succedaneum (edema of the scalp from pressure during labor), cephalhematoma (collection of blood under the skull from birth trauma), fractures, facial paralysis, and Erb's/Brachial palsy. Disorders related to physiological factors include hyperbilirubinemia, hemolytic disease of the newborn, and respiratory distress syndrome. Infectious disorders include sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis. Disorders related to maternal conditions include infants of diabetic mothers. Specific details are provided on hemolytic disease of the newborn, respiratory distress syndrome, nursing care for injuries to the head, and ErbCET U5 INTRODUCTION.pdf
CET U5 INTRODUCTION.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses principles of education and the teaching-learning process. It begins by defining key terms like education, philosophy, and educational philosophies. It then examines several philosophies of education in detail, including naturalism, idealism, realism, and pragmatism. For each philosophy, it outlines the chief proponents, basic concepts, aims and principles of education, organization of education, curriculum, teaching methods, discipline approaches, and the role of the teacher. The document provides an overview of major educational philosophies to help understand principles that guide the teaching and learning process.CET U5 LESSON PLANNING.pdf
CET U5 LESSON PLANNING.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document provides information on lesson planning for nursing students, including:
- The objectives, contents, introduction, definition, functions, significance, prerequisites, characteristics, steps, and format of lesson planning.
- Key aspects of effective lesson planning include setting clear objectives, selecting appropriate content, utilizing various teaching methods and assessment strategies, and ensuring active student participation.
- The document outlines the various sections that should be included in a lesson plan such as the cover page, basic lesson plan information, time allotment and teaching-learning activities for each objective, assessment strategies, assignment, and references.essentialnewborncare-210819043505.pdf
essentialnewborncare-210819043505.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
The document provides information on essential newborn care including the 8 steps of essential newborn care such as drying the baby, assessing breathing, cord care, and warming the baby. It discusses principles like immediate drying, skin-to-skin contact, and delaying bathing and weighing. Components include neonatal resuscitation, thermal protection, infection prevention, and initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour. Risk factors for low birth weight babies and prevention measures are outlined. Optimal infant feeding practices of exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months and introducing complementary foods at 6 months are also summarized.normalnewbornamalkhalil-150107071628-conversion-gate02.pdf
normalnewbornamalkhalil-150107071628-conversion-gate02.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
1. The document defines the neonatal period as the time from birth to 4 weeks postnatal. During this period, newborns are observed and stabilized in the normal newborn nursery or on the maternity floor.
2. The roles of nurses and physicians in the normal newborn nursery include admission care like assessments, history taking, and ensuring identification; ongoing assessments using tools like the APGAR score; and providing routine neonatal care like maintaining temperature and establishing breastfeeding.
3. Physical examinations of newborns assess various body systems and features like reflexes, fontanels, skin characteristics, and vital signs to evaluate overall health and normalcy. Any abnormalities are noted.journal club print.docx
journal club print.docxsaranya443113
╠²
The document summarizes a study that assessed the effectiveness of a structured teaching program on mothers' knowledge of preventing pediatric emergencies and providing first aid for children under 5. 50 mothers participated in the study. Their knowledge was tested before and after the teaching program using a 25 question survey. The results showed that after the program, none of the mothers had inadequate knowledge while all had adequate knowledge, indicating the program was effective. The study also found significant associations between mothers' knowledge and several demographic factors like age, education level, occupation, number of children, and information sources.CET U5-TEACHING -LEARNING PROCESS.pdf
CET U5-TEACHING -LEARNING PROCESS.pdfsaranya443113
╠²
This document discusses the teaching-learning process in a nursing education context. It begins by outlining the objectives and aims of education, including the individual, social, and democratic aims. It then defines learning as a modification of behavior through experience according to various psychological views. The principles of learning include that it is progressive, motivated, universal, and goal-directed. Teaching is defined as aimed at changing another's behavior potential and includes stimulation, guidance and encouragement of learning. The nature of teaching is described as interactive, multi-level, and requiring planning and effective communication. Evaluation questions are provided to test understanding of the key topics.PRESENTATION.pptx
- 2. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit ADD A FOOTER 2
- 3. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, constituter adipescent elit ŌĆó Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, constituter adipescent elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. ŌĆó Fusce posuere, magna sed pulvinar ultricies, purus lectus malesuada libero, sit amet commodo magna eros quis urna. ŌĆó Nunc viverra imperdiet enim. Fusce est. Vivamus a tellus. ŌĆó Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Proin pharetra nonummy pede. Mauris et orci. ADD A FOOTER 3
- 4. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, constituter adipescent elit Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, constituter adipescent elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Fusce posuere, magna sed pulvinar ultricies ŌĆó Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, constituter adipescent elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Nunc viverra imperdiet enim. Fusce est. Vivamus a tellus. ŌĆó Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Proin pharetra nonummy pede. Mauris et orci. ADD A FOOTER 4
- 5. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa SECTION 1 TITLE ŌĆó Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Fusce posuere, magna sed pulvinar ultricies, purus lectus malesuada libero, sit amet commodo magna eros quis urna. ŌĆó Nunc viverra imperdiet enim. Fusce est. Vivamus a tellus. ŌĆó Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Proin pharetra nonummy pede. Mauris et orci. SECTION 2 TITLE ŌĆó Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. ŌĆó Nunc viverra imperdiet enim. Fusce est. Vivamus a tellus. ŌĆó Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Proin pharetra nonummy pede. Mauris et orci. ADD A FOOTER 5
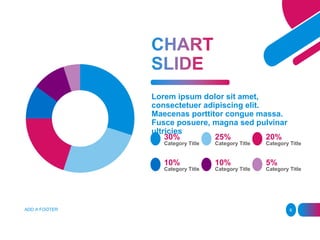
- 6. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Fusce posuere, magna sed pulvinar ultricies 30% Category Title 25% Category Title 20% Category Title 10% Category Title 10% Category Title 5% Category Title ADD A FOOTER 6
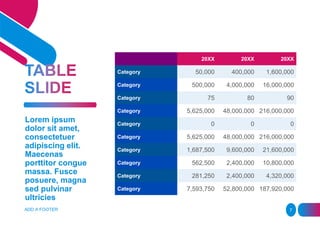
- 7. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Fusce posuere, magna sed pulvinar ultricies 20XX 20XX 20XX Category 50,000 400,000 1,600,000 Category 500,000 4,000,000 16,000,000 Category 75 80 90 Category 5,625,000 48,000,000 216,000,000 Category 0 0 0 Category 5,625,000 48,000,000 216,000,000 Category 1,687,500 9,600,000 21,600,000 Category 562,500 2,400,000 10,800,000 Category 281,250 2,400,000 4,320,000 Category 7,593,750 52,800,000 187,920,000 ADD A FOOTER 7
- 8. BIG IMAGE Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa ADD A FOOTER 8
- 9. ADD A FOOTER 9
- 10. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa ADD A FOOTER 10