Primary 5 Cycles: Water
- 1. Water
- 3. Introduction Covers three-quarters of the earth surface All living things need water to survive. Water exists in three different states: Solid Liquid Gaseous
- 4. Water in Solid State ice snow hail
- 5. Water in the Liquid State Most of the Earth’s water is sea water. raindrops dew clouds
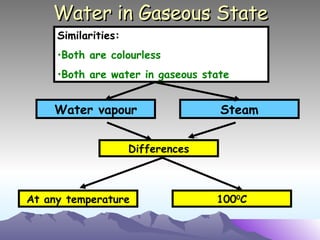
- 6. Water in Gaseous State Water vapour Steam Similarities: Both are colourless Both are water in gaseous state Differences At any temperature 100 0 C
- 7. Changing States of Water: Heat Gained Solid to liquid: Melting (0 0 C) Liquid to Gaseous : Evaporation : Boiling (100 0 C)
- 8. Changing States of Water: Heat Loss Liquid to Solid: Freezing (0 0 C) Gaseous to Liquid : Condensation
- 9. Changing States of Water: Heat Loss Liquid to Solid: Freezing (0 0 C) Liquid to Gaseous : Condensation
- 10. Melting From solid to liquid Gains heat Happens at 0 0 C Ice to water Temperature stays the same Heat gained to change state of water from solid to liquid State of water during melting: solid and liquid
- 11. Freezing From liquid to solid Heat loss from water to the surrounding Happens at 0 0 C Water to Ice Temperature stays the same
- 12. Boiling From liquid to gaseous Gains Heat Happens at 100 0 C Water to Steam Temperature stays the same Heat gained to change state of water from liquid to gaseous State of water: liquid and gaseous
- 13. Evaporation From liquid to gaseous Gains heat Evaporation happens all the time and at any temperature. Water to Water Vapour
- 14. Condensation From gaseous to liquid Loses heat Condensation happens due to temperature difference Water Vapour to Water Steam to Water
- 15. Condensation Faster Slower More water droplets Less water droplets (100 0 C) (10 0 C) (100 0 C) (70 0 C)
- 16. Evaporation The rate of evaporation depends on a few factors: Presence of wind Humidity Temperature Area of exposed surface
- 17. Presence of Wind Water evaporates faster in the presence of wind. When water evaporates, water vapour gathers above the surface of the water . Wind will carry the water vapour away, making space for more water to rise.
- 18. Humidity (Amount of water vapour in the air) High humidity: Large amount of water vapour in the air Higher humidity Slower rate of evaporation There is little or no space in the air for any more water vapour when humidity is high.
- 19. Temperature Higher temperature Faster rate of evaporation
- 20. Area of Exposed Surface The larger the area of the exposed surface, the greater the amount of evaporation. Larger exposed surface area Smaller exposed surface area
- 21. Area of Exposed Surface 0 fold 1fold 2 folds Increase rate of evaporation
- 22. Video on processes of water
- 23. Ěý
- 24. Water Cycle Video 1
- 25. Water Cycle Respiration Animals give out water vapour Stage 1: Evaporation Heat from sun evaporate water from rivers, lakes and sea Transpiration Plants give out water vapour through stomata of leaves
- 26. Water Cycle Stage 2: Condensation Water vapour rises into the air and condenses into water droplets
- 27. Water Cycle Stage 3: Precipitation Clouds become to heavy and fall as rain to the ground
- 28. Water Cycle
- 29. Main source of energy for water cycle
- 30. Water Cycle Song: Processes Water Cycle Song