Principales of landscape gardening
- 1. Presentation on Principles of Landscape Gardening Course Code: AG 3111 Course Title: Ornamental Horticulture (T) Assigned by Md.Shafiqul Islam Lecturer Dept. of Agriculture Presented by Ohi Alam ASH 1514026M
- 3. W h a t i s L a n d s c a p i n g Landscaping: The use of plants and inanimate objects outdoors to fulfill aesthetic and functional purposes
- 4. Principle of Landscape Gardening Simplicity Balance Focalization Rhythm And Sequence Proportion And Scale & Repetition
- 5. Simplicity âą Simplicity is the harmonious relationship among all elements and characteristics of a garden. âąTo establish unity in a garden, stay simple and minimize.
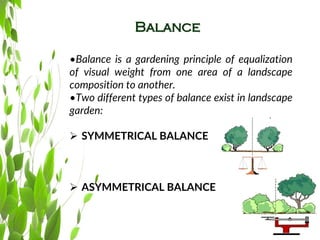
- 6. Balance âąBalance is a gardening principle of equalization of visual weight from one area of a landscape composition to another. âąTwo different types of balance exist in landscape garden: ï SYMMETRICAL BALANCE ï ASYMMETRICAL BALANCE
- 7. Balance SYMMETRICAL BALANCE âą Symmetrical balance is a formal balance. It is sometimes referred to as bi-lateral symmetry. âą In Symmetrical balance the same components are repeated on both sides of the composition. The visual and actual weight is equally distributed on each side.
- 8. Balance ASYMMETRICAL BALANCE âą A symmetrically balanced landscape compares to a level balance scale. Both sides of the scale are level with the exact same weights on each plate. âą Asymmetrical balance is an informal balance. It does not repeat the same plant material in the same quantity or in the same relative position on either side of the center axis. It does not have the âsamenessâ on each side.
- 9. Focalization âą The focal point is the point or area of the landscape that attracts the viewerâs eyes. âą The visual break captures the attention of the viewer and draws it to the focal point. âą Without a point or area on which to focus, the viewerâs eyes become lost and confused throughout the landscape.
- 10. Rhythm And Sequence âą Rhythm and sequence describe the dynamic unity or the related, orderly that they are the apparent flow of lines, textures, and colors that express a feeling of motion rather than confusion. âą Rhythm and sequence lead the viewerâs eyes easily and smoothly along a deliberate, dominant, and visual path.
- 11. Proportion And Scale âą Proportion is the relationship that exists among the components of a landscape. It also describes the relationship between the components of the landscape âą Proportion involves the size relationships, the mathematical relationships among the dimensions of space and site components making up the landscape garden. âąFor example, corner plantings next to a house that are two thirds the distance from the ground to the eave are proportional to the house. The height of the corner plantings is proportional to the height of the eave.
- 12. Repetition âą Repetition involves repeating or using an element more than once âą It helps establish and add order and unity to a design.