PRINCIPLES OF AC MOTORS AND THEIR TYPESS
- 1. 18 RA 45 ELECTRICAL DRIVES & CONTROL Dr. G. Ezhilarasan, Professor, EEE UNIT 2: AC MOTOR FOR DRIVES
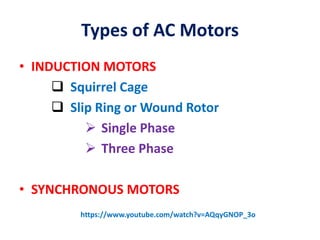
- 2. Types of AC Motors ŌĆó INDUCTION MOTORS ’ü▒ Squirrel Cage ’ü▒ Slip Ring or Wound Rotor ’āś Single Phase ’āś Three Phase ŌĆó SYNCHRONOUS MOTORS https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AQqyGNOP_3o
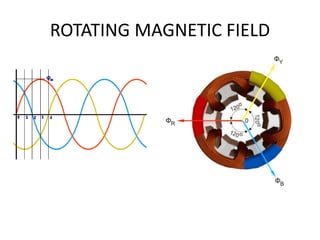
- 3. AC MOTOR BASICS ŌĆó THREE PHASE ELECTRICITY ŌĆó ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION ŌĆó ROTATING MAGNETIC FIELD ŌĆó LORENTZ FORCE ŌĆó SYNCHRONOUS SPEED ŌĆó SLIP ŌĆó SYNCHRONOUS OPERATION ŌĆó ASYNCHRONOUS OPERATION
- 8. SYNCHRONOUS SPEED ŌĆó The synchronous speed is the speed of the revolution of the magnetic field in the stator winding of the motor. ŌĆó P be the total number of field poles, ŌĆó Ns is the speed of the field in revolution per minute (r.p.m), ŌĆó f is the frequency of the generated voltage in hertz.
- 9. SLIP ŌĆó Slip in Induction Motor is the relative speed between the rotating magnetic flux (synchronous speed) and the speed of the rotor (actual Speed) . It is a dimensionless quantity.
- 10. SYNCHRONOUS SPEED TERMS ŌĆó SYNCHRONOUS SPEED ŌĆó ASYNCHRONOUS SPEED ŌĆó SUPER SYNCHRONOUS OPERATION ŌĆó SUB-SYNCHRONOUS OPERATION
- 11. SQUIRREL CAGE AND SLIP RING INDUCTION MOTORS SQUIRREL CAGE ROTOR WOUND ROTOR STATOR
- 12. STATOR OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR ’āś The stator of an induction motor is common for slip ring and squirrel cage induction motors and even for a synchronous motor. ’āś It is made up of a number of stampings, which are slotted to receive the windings. ’āś The stator carries a 3-phase winding and is fed from a 3-phase supply. ’āś The stator winding, when supplied with a 3-phase currents, produce a magnetic flux, which is of constant magnitude but which revolves at synchronous speed (Ns = 120 x f / p). ’āś This revolving magnetic flux induces emf in rotor by mutual induction.
- 13. SQUIRREL CAGE ROTOR ’āś Almost 90 percentage of induction motors are squirrel-cage type, because this type of rotor has the simplest and most rugged construction. ’āś The Rotor consists of cylindrical laminated core with parallel slots for carrying the rotor conductors which, it should be noted clearly, are not wires but consists of heavy bars of copper, aluminum or alloys. ’āś One bar is placed in each slot and are brazed or electrically welded to two heavy end-rings thereby short circuiting all the conductors is called a squirrel cage construction. ’āś The rotor slots are not quite parallel to the shaft but are purposely given a slight skew ŌĆó It helps to make the motor run quietly by reducing the magnetic hum ŌĆó It helps in reducing the locking tendency of the rotor.
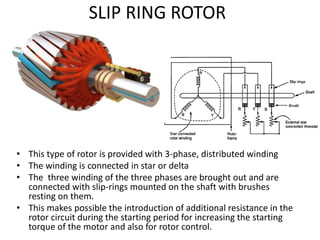
- 14. SLIP RING ROTOR ŌĆó This type of rotor is provided with 3-phase, distributed winding ŌĆó The winding is connected in star or delta ŌĆó The three winding of the three phases are brought out and are connected with slip-rings mounted on the shaft with brushes resting on them. ŌĆó This makes possible the introduction of additional resistance in the rotor circuit during the starting period for increasing the starting torque of the motor and also for rotor control.
- 15. WORKING OF INDUCTION MOTORS ŌĆó Induction motor works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. ŌĆó When three phase supply is given to the stator winding, a rotating magnetic field of constant magnetic field is produced and rotates at synchronous speed ŌĆó This rotating field produces an effect of rotating poles around a rotor. ŌĆó Now the R.M.F. gets cut by rotor conductors as R.M.F. sweeps over rotor conductors. ŌĆó Whenever a conductor cuts the flux, emf. gets induced in it. As rotor forms closed circuit, induced emf. circulates current through rotor called rotor current. ŌĆó Any current carrying conductor produces its own flux. So rotor produces its flux called rotor flux. Now there are two fluxes, one R.M.F. and another rotor flux. ŌĆó Both the fluxes interact with each other hence the conductor experiences a force, due to interaction of the two fluxes. ŌĆó As all rotor conductor experiences a force, overall rotor experiences a torque and starts rotating. ŌĆó So interaction of the two fluxes is very essential for a motoring action. The direction of force is same as that of rotating magnetic field. Hence rotor starts rotating in the same direction as that of R.M.F.
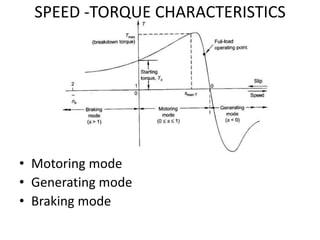
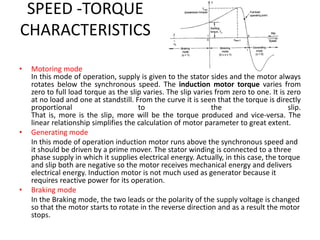
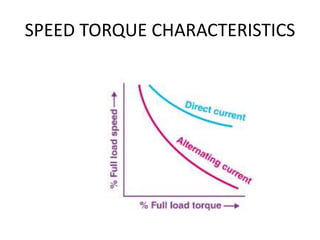
- 16. SPEED -TORQUE CHARACTERISTICS ŌĆó Motoring mode ŌĆó Generating mode ŌĆó Braking mode
- 17. SPEED -TORQUE CHARACTERISTICS ŌĆó Motoring mode In this mode of operation, supply is given to the stator sides and the motor always rotates below the synchronous speed. The induction motor torque varies from zero to full load torque as the slip varies. The slip varies from zero to one. It is zero at no load and one at standstill. From the curve it is seen that the torque is directly proportional to the slip. That is, more is the slip, more will be the torque produced and vice-versa. The linear relationship simplifies the calculation of motor parameter to great extent. ŌĆó Generating mode In this mode of operation induction motor runs above the synchronous speed and it should be driven by a prime mover. The stator winding is connected to a three phase supply in which it supplies electrical energy. Actually, in this case, the torque and slip both are negative so the motor receives mechanical energy and delivers electrical energy. Induction motor is not much used as generator because it requires reactive power for its operation. ŌĆó Braking mode In the Braking mode, the two leads or the polarity of the supply voltage is changed so that the motor starts to rotate in the reverse direction and as a result the motor stops.
- 18. STEPPER MOTORS
- 26. UNIVERSAL MOTOR ŌĆó A universal motor is a special type of motor that runs on both AC and DC power supplies. Universal motors are series- wound (the armature and field windings are in series). The series connection allows them to generate high torque; hence the universal motors are generally built into the device they are meant to drive. ŌĆó Most of the universal motors are meant to operate at speeds as high as 3500 RPM. These motors run at a higher speed on DC supply than they run on AC supply of the same voltage. This is due to the reactance voltage drop that is present only in AC and not in DC.
- 28. Applications Universal motors are used in applications where high speed and good speed control is necessary. Following are the various applications of universal motor: ŌĆó Universal Motors are used in table fans, hairdryers and grinders. ŌĆó They are used in portable drill machines. ŌĆó They are used in polishers, blowers and kitchen appliances.