Principles of Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- 1. Presenter: Dr Chandrima Mukherjee Moderator: Dr Rahul Sisodiya Faculty Moderator: Dr Prashanth G MANAGEMENT OF 10/17/2024 1
- 2. âĒ Discuss the CTP & BCLC Criteria and its implications in Mgt of HCC âĒ Broad Principles of Surgery for HCC âĒ Broad Principles of Locoregional Therapy âĒ Basic of Liver transplant âĒ Broad Principles of Radiation Therapy including role of SBRT âĒ Broad Principles of Sytemic Therapy LEARNING OBJECTIVES 10/17/2024 2
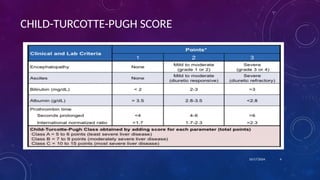
- 3. ISSUES IN MANAGEMENT OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA âĒ Stage of underlying liver disease â Assessed using Child-Turcotte-Pugh Score âĒ Etiology â Viral vs Non Viral âĒ Tumor related factors âĒ Size âĒ Number âĒ Vessel Involvement âĒ Biological Behavior âĒ Response to treatment 10/17/2024 3
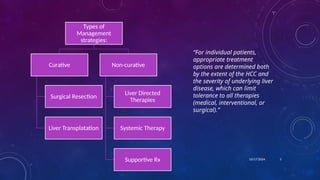
- 5. Types of Management strategies: Curative Surgical Resection Liver Transplatation Non-curative Liver Directed Therapies Systemic Therapy Supportive Rx âFor individual patients, appropriate treatment options are determined both by the extent of the HCC and the severity of underlying liver disease, which can limit tolerance to all therapies (medical, interventional, or surgical).â 10/17/2024 5
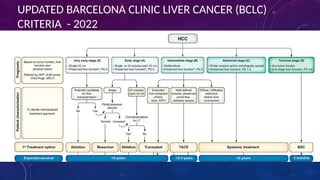
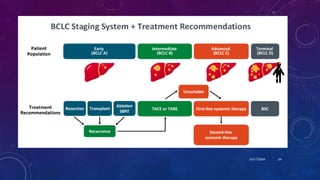
- 6. 10/17/2024 6 UPDATED BARCELONA CLINIC LIVER CANCER (BCLC) CRITERIA - 2022
- 7. 10/17/2024 7
- 8. 10/17/2024 8
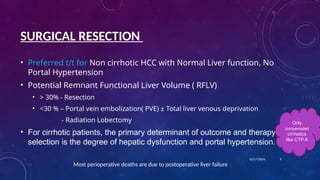
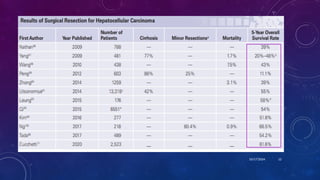
- 9. SURGICAL RESECTION âĒ Preferred t/t for Non cirrhotic HCC with Normal Liver function, No Portal Hypertension âĒ Potential Remnant Functional Liver Volume ( RFLV) âĒ > 30% - Resection âĒ <30 % â Portal vein embolization( PVE) Âą Total liver venous deprivation - Radiation Lobectomy âĒ For cirrhotic patients, the primary determinant of outcome and therapy selection is the degree of hepatic dysfunction and portal hypertension. Most perioperative deaths are due to postoperative liver failure 10/17/2024 9 Only compensated cirrhotics like CTP A
- 10. METHODS TO IMPROVE FLR: 1) Portal Vein Embolization (PVE): Portal vein embolization of the affected segment allows for hypertrophy of the anticipated FLR allowing for more extensive resection. In general, there is a 30% increase in the FLR and 10% increase in SLV at the end of 2 weeks following PVE. 2) Trans Arterial Chemo Embolisation (TACE): TACE has been proposed as a complimentary adjunct to PVE in the preoperative setting. In addition to embolizing the arterial supply to the tumour, it also blocks the small arterio-portal shunts that attenuate the effect of PVE in cirrhotic patients. 3) The Associating Liver Partition with Portal vein ligation for Staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) procedure has also been successfully used to increase FLR in cirrhotic patients with HCC. 4) Radiation Lobectomy - A potential advantage of radiation lobectomy is that it results in tumor control in addition to inducing contralateral hepatic hypertrophy 10/17/2024 10
- 11. CRITERIA FOR RESECTABILITY âĒ Solitary lesion upto 5 cm âĒ Child Pugh A âĒ Confined to liver âĒ No radiographic evidence of invasion of the hepatic vasculature, âĒ No evidence of portal hypertension (splenomegaly, esophagogastric varices, and thrombocytopenia or directly determined by hepatic venous wedge pressures (âĨ10 mmHg). 10/17/2024 11
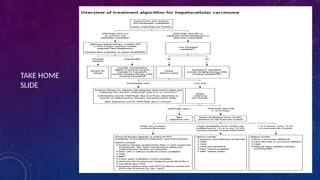
- 12. 10/17/2024 12
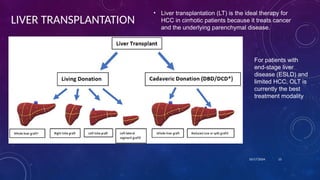
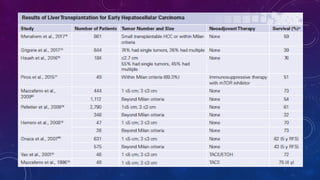
- 13. LIVER TRANSPLANTATION âĒ Liver transplantation (LT) is the ideal therapy for HCC in cirrhotic patients because it treats cancer and the underlying parenchymal disease. 10/17/2024 13 For patients with end-stage liver disease (ESLD) and limited HCC, OLT is currently the best treatment modality
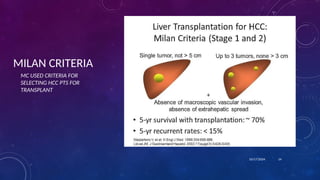
- 14. MILAN CRITERIA 10/17/2024 14 MC USED CRITERIA FOR SELECTING HCC PTS FOR TRANSPLANT
- 15. USCF CRITERIA 10/17/2024 15 The UCSF criteria were associated with 90% and 75% survival at 1 and 5 years, respectively
- 16. 10/17/2024 16
- 17. 10/17/2024 âĒ To qualify for the waitlist, a biopsy or one of the following criteria must be fulfilled: âĒ AFP >500 ng/mL, âĒ arterial enhancement followed by a portal venous washout on computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or âĒ a history of locoregional treatment. âĒ The tumor should be assessed every 3 months by CT scans or MRI to rule out disease progression beyond the established criteria. 17
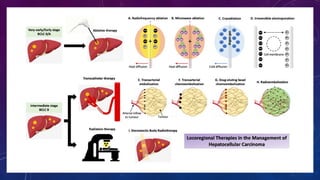
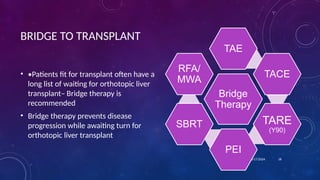
- 18. BRIDGE TO TRANSPLANT âĒ âĒPatients fit for transplant often have a long list of waiting for orthotopic liver transplantâ Bridge therapy is recommended âĒ Bridge therapy prevents disease progression while awaiting turn for orthotopic liver transplant 10/17/2024 18 Bridge Therapy TAE TACE TARE (Y90) PEI SBRT RFA/ MWA
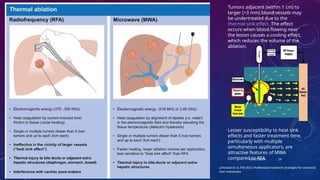
- 19. 10/17/2024 19 Limmatal et al, Feb 2021 Multimodal treatment strategies for colorectal liver metastases Tumors adjacent (within 1 cm) to larger (>3 mm) blood vessels may be undertreated due to the thermal sink effect. The effect occurs when blood flowing near the lesion causes a cooling effect, which reduces the volume of the ablation. Lesser susceptibility to heat sink effects and faster treatment time, particularly with multiple simultaneous applicators, are attractive features of MWA compared to RFA.
- 20. 10/17/2024 Irreversible Electroporation âĒ Irreversible electroporation (IRE) is a relatively new, largely nonthermal electrical ablation technology. âĒ It is less susceptible to the thermal heat sink ïĻ limit the efficacy of thermal ablation devices in treating tumors adjacent to blood vessels ïĻ less likely to damage critical structures, such as major bile ducts. âĒ IRE uses high-power large electrical currents delivered between electrode pairs placed into tumors. 20
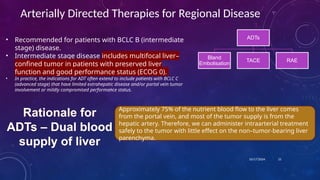
- 21. 10/17/2024 Arterially Directed Therapies for Regional Disease âĒ Recommended for patients with BCLC B (intermediate stage) disease. âĒ Intermediate stage disease includes multifocal liverâ confined tumor in patients with preserved liver function and good performance status (ECOG 0). âĒ In practice, the indications for ADT often extend to include patients with BCLC C (advanced stage) that have limited extrahepatic disease and/or portal vein tumor involvement or mildly compromised performance status. 21 Approximately 75% of the nutrient blood flow to the liver comes from the portal vein, and most of the tumor supply is from the hepatic artery. Therefore, we can administer intraarterial treatment safely to the tumor with little effect on the nonâtumor-bearing liver parenchyma. Rationale for ADTs â Dual blood supply of liver ADTs Bland Embolisation TACE RAE
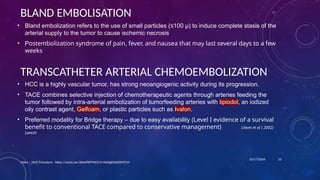
- 22. 10/17/2024 BLAND EMBOLISATION âĒ Bland embolization refers to the use of small particles (âĪ100 Ξ) to induce complete stasis of the arterial supply to the tumor to cause ischemic necrosis âĒ Postembolization syndrome of pain, fever, and nausea that may last several days to a few weeks Video â TACE Procedure - https://youtu.be/36hxiPXPTWQ?si=9eDigBYaX30MZTsV 22 TRANSCATHETER ARTERIAL CHEMOEMBOLIZATION âĒ HCC is a highly vascular tumor, has strong neoangiogenic activity during its progression. âĒ TACE combines selective injection of chemotherapeutic agents through arteries feeding the tumor followed by intra-arterial embolization of tumorfeeding arteries with lipiodol, an iodized oily contrast agent, Gelfoam, or plastic particles such as Ivalon. âĒ Preferred modality for Bridge therapy â due to easy availability (Level I evidence of a survival benefit to conventional TACE compared to conservative management) Llovet et al ( 2002) Lancet
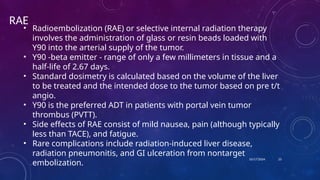
- 23. 10/17/2024 23 RAE âĒ Radioembolization (RAE) or selective internal radiation therapy involves the administration of glass or resin beads loaded with Y90 into the arterial supply of the tumor. âĒ Y90 -beta emitter - range of only a few millimeters in tissue and a half-life of 2.67 days. âĒ Standard dosimetry is calculated based on the volume of the liver to be treated and the intended dose to the tumor based on pre t/t angio. âĒ Y90 is the preferred ADT in patients with portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT). âĒ Side effects of RAE consist of mild nausea, pain (although typically less than TACE), and fatigue. âĒ Rare complications include radiation-induced liver disease, radiation pneumonitis, and GI ulceration from nontarget embolization.
- 24. RADIATION THERAPY AS LOCAL ABLATION âĒ Liver â One of the most Radiosensitive organs â Aim of Planning â Max dose to tumor, min dose to normal tissue âĒ Radiation therapy (RT) for liver tumors was historically limited by hepatic toxicity âĒ Who are the candidates for RT Ablation?? âĒ Unresectable Tumors âĒ Medically Inoperable pts âĒ Size > 3cm âĒ Proximity to Diaphragm , Large Vessel, Gall Bladder 10/17/2024 24 Pts who could not be effectively t/t by RFA
- 25. 10/17/2024 âĒ Radiation segmentectomy and radiation lobectomy - use ablative doses of radiation to improve tumoricidal effect and cause contralateral hepatic hypertrophy, respectively. âĒ In radiation segmentectomy, a tumor localized to a single segment can be selectively treated with a dose calculated for the entire liver lobe, achieving doses of over 400 Gy to cause segmental liver ablation. âĒ Radiation lobectomy is performed to treat tumors and induce ipsilateral lobar atrophy and contralateral hypertrophy in patients who are potential candidates for resection. 25
- 26. SBRT SBRT can be considered as an alternative to ablation/embolization techniques or when these therapies have failed or are contraindicated. ( NCCN 2022) With high doses per fraction, the biologic effect is greater than with the same dose delivered in a standard fractionated course, up to the equivalent of 80 to 150 Gy in 2-Gy fractions Postulated mechs of RT injury: (a) Ablative direct cell kill (b) Endothelial targets â RT increases tumor Ag specific immune response SBRT is used in patients with 1-3 tumors. Parameters in Deciding T/t: 10/17/2024 26 For tumors < 2cm , SBRT = RT ablation For Tumors > 2cm, SBRT gives a better PFS
- 27. SIDE EFFECTS OF RT Primary toxicity of concern is a radiation-induced liver disease (RILD), categorized as classic and non-classic. âĒ Classic RILD is a constellation of anicteric ascites, hepatomegaly, and elevated liver enzymes (particularly alkaline phosphatase), which typically occurs within 4 months of therapy and is a type of veno- occlusive. âĒ Nonclassic RILD, a more recent classification, is characterized by jaundice and markedly elevated serum transaminases (>5 times the upper limit of normal) within 3 months of therapy completion. This is thought to represent direct hepatocyte rather than endothelial injury RILD is typically self-limited but can be severe, even leading to mortality. It is managed symptomatically using diuretics and paracentesis. 10/17/2024 27 Even low doses to the whole liver of 25 Gy in 10 fractions or 32 Gy in 1.5 Gy per fraction twice daily are associated with a >5% risk of RILD, particularly for patients with cirrhosis and already compromised liver function RILD: i) Transaminase / ALP > 2.5-5X ULN ii) Sr Bil > 1.5-3X ULN iii) Non malignant ascites in the absence of disease progression Hallmark â small venous obstruction â central venous congestion & collagen deposition without inflammation Rx: Diuretics, paracentesis, Vit K
- 28. ROLE OF NEOADJUVANT THERAPY âĒ Recurrences, post resection, in HCC tend to be intrahepatic. âĒ Use of trans arterial chemo-embolization (TACE) was done prior to surgery in resectable cases with the aim of decreasing in-liver recurrences and a hope to prolong survival. âĒ A systematic review of 18 studies, including 3 randomized trials demonstrated that the use of TACE in the neoadjuvant setting in resectable HCC was safe and efficacious with a high rate of pathological response. âĒ However, it did not improve survival 10/17/2024 29
- 29. Role of Adjuvant Therapy âĒ STORM, a phase III, randomized controlled trial evaluated the benefit of Sorafenib in the adjuvant setting after resection/ ablation of HCC ïĻ showed no added survival advantage. âĒ The 2018 EASL guidelines do not recommend any neo-adjuvant or adjuvant therapy after curative resection or ablation 10/17/2024 30
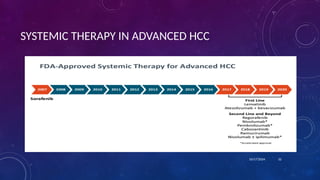
- 30. SYSTEMIC THERAPY FOR HCC âĒ Systemic chemotherapies have had no proven benefits on survival in HCC. * 10/17/2024 31
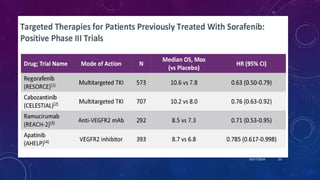
- 31. SYSTEMIC THERAPY IN ADVANCED HCC 10/17/2024 32
- 32. 10/17/2024 33
- 33. 10/17/2024 34
- 34. BIBLIOGRAPHY âĒ Devitaâs Principles & Practices of Oncology â 12th Edition âĒ UptoDate âĒ Pubmed 10/17/2024 35
Editor's Notes
- #9: Next slide: Methods to improve FLR: Portal hypertension can be indirectly assessed clinically by the presence of splenomegaly, esophagogastric varices, and thrombocytopenia (platelet count
- #10: Dynamic LFTs for Liver function test: Tc99m GSA, ICG
- #27: Other tox: Gastric or duodenal bleeding prescribed doses ranged from 40 Gy to 90 Gy
- #28: CONS: No blinding OS benefit of the TACE-RT arm â 55 vs 43 weeks â Not statistically significant Only 3 Pts completed 24 weeks of Sorafenib
- #31: IMBrave