principles of managemet foe management studirs
- 2. INTRODUCTION BUSINESS ORGANISATION NON-BUSINESS ORGANISATION SOCIAL LIFE M A N A G E M E N T
- 3. INTRODUCTION Management is the key to success in achievement of goals WHERE YOU ARE WHERE YOU WANT TO BE MANAGEMENT APRIL FEBRUARY BOARD EXAMS MANAGE YOUR STUDIES & TIME 80 ŌĆō 90%
- 4. 5M OF MANAGEMENT MAN METHODS MATERIAL MACHINERY MONEY
- 5. MEANING & DEFINITION OF PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT MEANING ’éĢWhile achieving a goal of an individual or an organization, it is always important to use different systems or techniques ’éĢSome of these techniques are accepted universally, hence they are called as Principles DEFINITION ’éĢPrinciple is defined as Fundamental Truth or a proposition that serves as the foundation for a system of belief or behavior or for a chain of reasoning ’éĢIn simple words ŌĆō Techniques / Systems which give one directional result are called as Principles
- 6. NATURE OF PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT 1. UNIVERSAL APPLICATION ’üČ UNIVERSAL IN NATURE ’üČ CAN BE APPLIED TO ALL TYPES OF ORGANISATIONS ’üČ IT IS APPLICABLE TO ALL LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT
- 7. NATURE OF PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT 2. GENERAL GUIDELINES ’üČ PROVIDES GUIDELINES IN TACKLING THE ORGANIZATIONAL SITUATION & SOLVING ’üČ THEY ARE NOT RIGID ’üČ MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES ARE APPLIED DEPENDING ON THE SIZE, SITUATION & NATURE OF THE ORGANIZATION 3. PRINCIPLES ARE FORMED BY PRACTISE & EXERCISE ’üČ THE MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES ARE DEVELOPED GRADUALLY ŌĆó THROUGH RESEARCH WORK ŌĆó SYSTEMATIC OBSERVATION ŌĆó EXPERIMENTS
- 8. NATURE OF PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT 4. FLEXIBILITY ’üČ FLEXIBLE IN NATURE ’üČ THEY CAN BE FORMED / MODIFIED ACCORDING TO THE SITUATIONS Eg. A situation arises between two groups of employees in an organization. Eg. There is a shortage of production due to machinery failure. 5. BEHAVIOURAL IN NATURE ’üČ MANAGEMENT IS A GROUP ACTIVITY ’üČ ORGANISATION GOALS ARE ACHIEVED THROUGH A GROUP OF HUMAN BEINGS ’üČ THESE PRINCIPLES ARE DESIRED TO INFLUENCE HUMAN BEINGS POSITIVE WAY
- 9. NATURE OF PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT 6. CAUSE & EFFECT RELATIONSHIP ’üČ PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT ARE A BASE OF TAKING DECISIONS Eg. Payment of good wages and incentives helps in increasing the output of workers or making effective advertisements helps in sale of products. 5. ALL PRINCIPLES ARE OF EQUAL IMPORTANCE ’üČ TO GET THE BEST RESULTS IN THE FORM OF ACHIEVEMENTS OF PRE DEFINED GOALS ALL PRINCIPLES SHOULD BE USED
- 11. HENRY FAYOLŌĆÖS 14 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT July 29, 1841 - November 19, 1925 French mining engineer, mining executive Became a leading industrialist and a successful manager Rose to the position of the chief managing director Father of Modern Management He wrote a book entitled, General and Industrial Management He also laid down the 14 Principles of Management
- 12. HENRY FAYOLŌĆÖS 14 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT LEARN IT THE EASY WAY!!! DAD U C USSR DIVISION OF WORK AUTHORITY & RESPONSIBILITY DISCIPLINE UNITY OF COMMAND CENTRALISATION & DECENTRALISATION UNITY OF DIRECTION SCALAR CHAIN OF COMMAND STABILITY OF TENURE REMUNERATION O I SEE ORDER INITIATIVE SUBORDINATION OF INTEREST TO GENERAL INTEREST EQUITY ESPIRIT DE CORPS
- 13. DIVISION OF WORK ’üČThe principle suggests that total work should be sub ŌĆō divided into small parts. ’üČEach part of the work should be allocated as to who is the expert in that part of the work ’üČThis leads to specialization ’üČLess wastage ’üČReduces Risk
- 14. AUTHORITY & RESPONSIBILITY ’üČAuthority means power to take decisions ’üČResponsibility means obligation to complete the assigned job on time. ’üČAuthority & Responsibility go hand in hand ’üČAuthority without responsibility results in an irresponsible behavior
- 15. DISCIPLINE ’üČDiscipline is obedience, application, energy, behavior and respect shown by employees ’üČIt is of 2 types ŌĆō ŌĆó Self imposed discipline: Comes from within the individual ŌĆó Command discipline: comes from authority, expressed through rules, regulations and customs
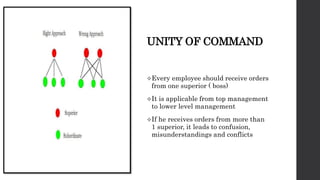
- 16. UNITY OF COMMAND ’üČEvery employee should receive orders from one superior ( boss) ’üČIt is applicable from top management to lower level management ’üČIf he receives orders from more than 1 superior, it leads to confusion, misunderstandings and conflicts
- 17. CENTRALISATION & DECENTRALISATION ŌĆó Centralization means concentration of power and authority of an organization in one hand. ŌĆó Decentralization means concentration of power and authority of an organization in more than one hands / few hands. ABC Sports & Games Ltd. Co. Centralization Decentralization Manager Sporting Goods Manager Board Games Manager Computer Games Division managers report to President Sporting Goods Division Board Games Division Computer Games Division President retains direct control over each business unit