Printer's
- 2. Introduction An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment used to communicate the results of data processing carried out by an information processing system(such as a computer) to the outside world.
- 3. What are Printers.....? Printer are the most commonly used output devices that provides the user with a permanent visual record of the output data in human readable form known as hard copy. They can print on plain paper or on specially prepared forms such as invoices, labels, bills, checks and other special purpose forms used in business. Their are several types of printers designed for wide range of application.
- 4. Impact Printers ď‚— Impact printer produces text and images when tiny wire pins on print head strike the ink ribbon by physically contacting the paper. Non Impact Printers ď‚— Non-impact printer produces text and graphics on paper without actually striking the paper.
- 5. Impact vs. Non-impact ď‚— Impact - These printers have a mechanism that touches the paper in order to create an image. There are two main impact technologies: ď‚— Dot matrix printers use a series of small pins to strike a ribbon coated with ink, causing the ink to transfer to the paper at the point of impact. ď‚— Character printers are basically computerized typewriters. They have a ball or series of bars with actual characters (letters and numbers) embossed on the surface. The appropriate character is struck against the ink ribbon, transferring the character's image to the paper. Character printers are fast and sharp for basic text, but very limited for other use. ď‚— Non-impact - These printers do not touch the paper when creating an image. Inkjet printers are part of this group, which includes: ď‚— Inkjet printers, which are described in this article, use a series of nozzles to spray drops of ink directly on the paper. ď‚— Laser printers, covered in-depth in How Laser Printers Work, use dry ink (toner), static electricity, and heat to place and bond the ink onto the paper.
- 6. Types of Impact Impact Printer’s  Dot-matrix printer  Drum printer  Chain printer  Daisy Wheel
- 7. Dot-Matrix Dot Matrix refers to the way the printer creates characters or images on paper. This is done by several tiny pins, aligned in a column, striking an ink ribbon positioned between the pins and the paper, creating dots on the paper. Characters are composed of patterns of these dots by moving the printhead laterally across the page in very small increments.
- 8. Advantages ď‚— Versatile ď‚— Print letters in italics or bold ď‚— Relatively inexpensive ď‚— Used to print carbon copies
- 9. Drum Printer An old line printer technology that used formed character images around a cylindrical drum as its printing mechanism. When the desired character for the selected position rotated around to the hammer line, the hammer hit the paper from behind and pushed it into the ribbon and onto the character.
- 10. Continued…….  Impact Printer - Print head has 9 or 24 pins  Pins strike paper through a ribbon.  24 pins give better print quality – dots closer  NLQ (Near Letter Quality) obtained by printing each line twice, which second pass slightly displaced so as to fill any spaces.  Printers are often bi-directional  Very versatile  Colour possible via 4-colour ribbon – but quality not too good  Can be very noisy
- 11. Working of Drum Printer ď‚— Fixed font character set is engraved onto number of print wheels ď‚— The wheels, joined to form a large drum, and spin at high speed and paper and an inked ribbon are stepped (moved) past the print position The hammer pushes the paper into the type slug when it rotated around to the proper position. Such printer technologies seem ridiculous compared to the quiet, high-speed workings of today's laser printers
- 12. Advantages ď‚— Less Expensive ď‚— Use Less Ink Disadvantages ď‚— Very Noisy ď‚— Slow Speed ď‚— Space Consuming
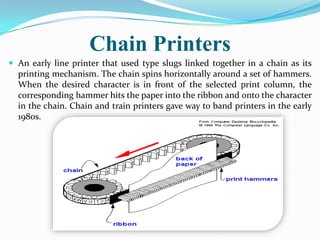
- 13. Chain Printers ď‚— An early line printer that used type slugs linked together in a chain as its printing mechanism. The chain spins horizontally around a set of hammers. When the desired character is in front of the selected print column, the corresponding hammer hits the paper into the ribbon and onto the character in the chain. Chain and train printers gave way to band printers in the early 1980s.
- 14. Working of Chain Printers Chain printers (also known as train printers) placed the type on moving bars (a horizontally-moving chain). As with the drum printer, as the correct character passed by each column, a hammer was fired from behind the paper. By selecting chains that had a smaller character set (for example, just numbers and a few punctuation marks), the printer could print much faster than if the chain contained the entire upper- and lower-case alphabet, numbers, and all special symbols. This was because, with many more instances of the numbers appearing in the chain, the time spent waiting for the correct character to "pass by" was greatly reduced. IBM was probably the best-known chain printer manufacturer and the IBM 1403 is probably the most famous example of a chain printer.
- 15. Daisy Wheel Printers Daisy wheel printers use an impact printing technology invented in 1969 by David S. Lee at Diablo Data Systems. It uses interchangeable pre-formed type elements, each with 96 glyphs, to generate high-quality output comparable to premium typewriters such as the IBM "Golfball" Selectric, but three times faster. Daisyand-wheel printing was used in electronic typewriters, word processors and computer systems from 1972.
- 16. Working of Daisy Wheel Printer The heart of the system is an interchangeable metal or plastic "daisy wheel" holding an entire character set as raised characters moulded on each "petal". Daisy Printer use a servo motor rotates the daisy wheel to position the required character between the hammer and the ribbon. The solenoid-operated hammer then fires, driving the character type on to the ribbon and paper to print the character on the paper. The daisy wheel and hammer are mounted on a sliding carriage similar to that used by dot matrix printers.
- 17. Advantages ď‚— Different typefaces and sizes can be used ď‚— Possible to use multiple fonts ď‚— Bold type facility
- 18. Electrostatic Printers Electrostatic printers use a special photographic paper that allows characters to be etched onto the paper using a stylus. The stylus, made up of tiny wires, forms characters by placing an electrostatic charged image on the paper. Then, as the paper is moved through a toner solution containing ink particles, the ink adheres to the charges that form a pattern on the paper to develop the character. This type of printer can be used for both printing and plotting (displaying graphic output), and can print up to 5,000 lines per minute
- 19. Types of Non Impact Printers Non Impact Printer’s  Inkjet printers  Laser printers
- 20. Inkjet Printer Inkjet printers are non-impact printers which print text and images by spraying tiny droplets of liquid ink onto paper. They are the most popular printers for home use. The inkjet head design is also divided into two main groups: fixed-head and disposable head. Fixed-head is built into the printer and should last for the whole life of the printer. It produces more accurate output than cheap disposable head. The ink cartridges for fixed head printers are also cheaper as the print head does not need to be replaced. However, if the head is damaged, the entire printer has to be replaced.
- 21. Continued…….  Inkjet Printer  Very popular – often bundled with PC  Cheap with very good resolution, particularly on special papers  Droplets of ink are fired at the paper  Large areas of colour may get the page too wet unless special paper is used  Colour printing can be quite expensive
- 22. Advantages of inkjet printers ď‚— Low cost ď‚— High quality of output, capable of printing fine and smooth details ď‚— Capable of printing in vivid color, good for printing pictures ď‚— Easy to use ď‚— Reasonably fast ď‚— Quieter than dot matrix printer ď‚— No warm up time
- 23. Disadvantages of inkjet printers ď‚— Print head is less durable, prone to clogging and damage ď‚— Expensive replacement ink cartridges ď‚— Not good for high volume printing ď‚— Printing speed is not as fast as laser printers ď‚— Ink bleeding, ink carried sideways causing blurred effects on some papers ď‚— Aqueous ink is sensitive to water; even a small drop of water can cause blurring ď‚— Cannot use highlighter marker on inkjet printouts
- 24. Laser Printer ď‚— Laser printers are non-impact printers which can print text and images in high speed and high quality resolution, ranging from 600 to 1200 dpi. ď‚— Unlike inkjet printers, laser printer use toner (black or colored powder) instead of liquid inks
- 25. Working of Laser Printer A laser printer consists of these major components: drum cartridge, rotating mirror, toner cartridge and roller. The drum cartridge rotates as the paper is fed through. The mirror deflects laser beam across the surface of the drum. Laser beam creates charge that causes the toner to stick to the drum. As the drum rotates and presses on paper, toner is transferred from the drum to paper, creating images. Rollers then use heat and pressure to fuse toner to paper. Colored laser printers add colored toner in three additional passes.
- 26. Advantages ď‚— High resolution ď‚— High print speed ď‚— No smearing ď‚— Low cost per page (compared to inkjet printers) ď‚— Printout is not sensitive to water ď‚— Good for high volume printing
- 27. Disadvantages ď‚— More expensive than inkjet printers ď‚— Except for high end machines, laser printers are less capable of printing vivid colors and high quality images such as photos. ď‚— The cost of toner replacement and drum replacement is high ď‚— Bulkier than inkjet printers ď‚— Warm up time needed
- 28. Printers ď‚— Factors affecting choice ď‚— Volume of output ď‚— High volume require fast, heavy-duty printer ď‚— Quality of print required ď‚— Location of printer ď‚— Are multiple copies required? ď‚— Is colour required?