Progesterone and related drugs
- 1. Progesterone and related drugs Prepared by: Soma rashad jawad Azheen kanabi muhammad Tamara bakr rasul
- 2. ŌĆó Introduction ŌĆó Defintion ŌĆó History ŌĆó Effects of progesterone on the body ŌĆó Drugs related to progesterone ŌĆó Progesterone antagonists ŌĆó Oral contraceptives
- 4. Willard M. Allen Willard Myron Allen along with George W. Corner isolated the hormone from corpora lutea of sows and named it progestin in 1933
- 5. Progesterone favours pregnancyby: ŌĆó Preventingendomaterial shedding ŌĆó reducingUterine motility ŌĆó Inhibitingimmunological reaction toward the foetus
- 8. males Secrete 1-5 mg /day Plasma level 0.03mcg/dl females During the follicular phase the level is only slightly higherthanthat of males But during the luteal phase The plasma levels range from 0.5 to 2 mcg/dl Reaches peak in in the 3rd trimester of pregancy Effect=?
- 9. receptors The progesterone receptor (PR) is a progestin- activated steroid receptor Also known as NR3C3 ; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 3 It is an intranuclear receptor It has 2 isoforms : PR A PR B PR is expressed in the following organs: central nervous system (CNS) Endocrine gastrointestinal immune reproductive cardiovascular respiratory Uterus ovary cerebellum spinal cord hypothalamus
- 11. Effects of progesterone on the body
- 12. Uterus: Progesterone brings about the secretory changes in the endometruim
- 13. Cervix : Progesterone causes the production of a viscid cervical secretion Vagina: It causes leukocyte infiltration in the epithelium Breast: Progesterone cause proliferation of the acini in the mammary glands CNS: High levels may cause sedation Body tempretaure: It causes a slight 0.5 rise in body tempreture Metabolism: Impairs glucose tolerance They may tend to raise LDL and lower HDL It stimulates respiration Pituitary: They have anti ovulatory activity by reducing LH secretion
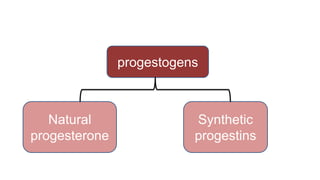
- 16. Synthetic progestin (Agonist)s Progesterone derivatives (21 C) 19-nortestosterone derivatives (18 C)
- 17. Synthetic progestin (Agonist)s Progesterone derivatives (21 C) These are pure progestins. They have weaker anti-ovulatory action and are used primarily as adjutants to estrogens for HRT, threatened abortion and edometriosis. 19-nortestosterone derivatives (18 C) They have weak estrogenic, androgenic and anabolic action but have potent anti- ovulatory action. They are mainly used in combined contraceptive pills. Like desogestrel and norgestimate (prodrug)
- 18. Progesterone derivatives (21 C) Medroxyprogesterone acetate Megestrol acetate Dydrogesterone Hydroxyprogesterone caproate Newer compound Nomegestrol acetate 19-nortestosterone derivatives (18 C) old Norethindrone (Norethisterone) Lynestrenol (Ethinylestrenol) Allylestrenol Levonorgestrel (Gonane) 19-nortestosterone derivatives (18 C) new (Gonanes ) Desogestrel Norgestimate Gestodene
- 19. Pharmacokinetics ŌĆó Progesterone undergo high 1st pass metabolism , hence mostly given by i.m in oily solution . ŌĆó they have a short half life in the plasma , so usually prescribed for twice or thrice-daily administration. ŌĆó A micronized preparation of progesterone is rapidly absorbed after its administrated by any route, Absorption
- 20. Distribution Progesterone is extensively bound to plasma proteins, primarily albumin (50 to 54%) and cortisol-binding protein (43 to 48%)
- 21. ŌĆó reduction to pregnanediol, pregnanetriol and pregnanolone. ŌĆó Subsequent conjugation results in the formation of glucuronide and sulfate metabolites. ŌĆó The metabolites of pregnanediol and pregnanolone are excreted ŌåÆurine or bile ŌĆó ŌĆó enterohepatic recycling or feces. Metabolism Excretion
- 22. Clinical uses of progestins 1.Rectify hormonal deficiency and HRT. 2. Contraception. 3.Control of dysfunctional uterine bleeding. 4.Treatment of dysmenorrhea. 6.Management of endometriosis. 5.Suppression of postpartum lactation. 7.Treatment of endometrial carcinoma.
- 23. CONTRAINDICATIONS Other contraindications ŌĆó Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding. ŌĆó Missed abortion. ŌĆó Known sensitivity to Progesterone injection.
- 24. 1.Breast engorgement, headache, Ōåæin body temperature, acne, esophageal reflux and mood swings . 2.Irregular bleeding or amenorrhoea . 3.The 19- nortestosterone derivatives Ōåōplasma HDL level . 4.In HRT may Ōåæthe risk of breast cancer . 5. Diabetes may be precipitated by long term uses of potent agents like levonorgestrol.
- 26. 19-norsteroid. with potent competitive anti-progestational, anti-glucocorticoid, anti-androgenic and partial agonist activity. It is administered during different phases of ovarian cycle. Mifepristone Pharmacokinetics Is orally active , bioavailability ŌåÆ 25% Mainly metabolized ŌåÆ liver & excreted ŌåÆ bile.
- 27. Uses 1.termination of early pregnancy 2.As a contraceptive given once a month 3.Cervical ripening 4.cushingŌĆÖs syndrome Side effects Main side effects are significant uterine bleeding and possibility of an incomplete abortion Also Uterine cramps
- 28. Contraceptive
- 29. The birth control pill (also called "the Pill") is a daily pill that contains hormones to change the way the body works and prevent pregnancy. Hormones are chemical substances that control the functioning of the body's organs. In this case, the hormones in the Pill control the ovaries and the uterus.
- 30. Major classes of oral contraceptive
- 31. Combination pills ŌĆó Products containing a combination of an estrogen and progestin are the most common type of oral contraceptives . ’āśThe estrogens that are commonly used in combination pills are Ethinyl estradiol and mestranol ’āśThe progestin in this preparations is norethindrone
- 32. Progestin pills Products containing a progestin only usually ŌĆó Norethindrone or norgestrel (called a ŌĆ£mini_pillŌĆØ)
- 33. Progestin implants ŌĆó Subdermal capsules containing levonorgestrel offer long term contraception ŌĆó Six capsules each the size of a matchstick are placed subcutaneously in the upper arm the progestin is slowly released from the capsules ŌĆó Provide contraceptive protection for approximately five years Totally reversible if the implants are surgically removed
- 34. Mechanism ŌĆó Inhibition of release of FSH and LH ŌĆó Increase viscosity of cervical mucus ŌĆó Endometrial changes ŌĆó Contraction of cervix , uterus and fallopian tube
- 35. Effects on the body
- 37. Therapeutic uses ŌĆó Numerous studies have shown that oral contraceptives (OC) provide protection against a wide variety of illnesses and conditions, including :
- 39. Adverse effects
- 43. ŌĆó Richard AH , Pamela CC .Lippincotts illustrated reviews .3rd edition . Donnelley W : USA ; 2006. ŌĆó K.D.Tripathi.Essentials of medical pharmacology.3rd edition.jitender p vij:new delhi;2008. ŌĆó Laurance L. Brunton , john S.Lazo , Keith L.Parker . Goodman and gilmanŌĆÖs the pharmacologicalbasis of theraputics.11th edition.mcGraw-hill:New york;2005.
- 44. List of refrences (cont.): ŌĆó Bertram g. Katzung , Susan B.Masters, Anthony J.Trevor. Basic and clinical pharmacology.12th edition. mcGraw-hill :New york;2012. ŌĆó James M. Ritter , Lionel DL , Timothy GK , Albert f . Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics . Fifth edition . Great britain: Hodder armond ;2008 . ŌĆó Teferra A , Srinivasa A , Amare M , Solomomon W , Eshetu L , Musie A , Dawet . Lecture notes for health science students .ethiopia 2004
- 45. List of refrences (cont.): ŌĆó progeterone receptors [Internet] :NURSA; 2014[cited 25 April 2015] Available from: https://www.nursa.org/nursa/molecules/nr.jsf?doi=10.1621/9 NIE3U3DI6 ŌĆó progesterone[Internet] :Drugs.com;2013[cited 25 April 2015] .Available from: http://www.drugs.com/pro/progesterone.html ŌĆó Therapeutic use of contraceptive [Internet] london: contraceptive; 1999 [cited 2015 april 15 ].available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10342095
- 46. List of refrences (cont.): ŌĆó Combined oral contraceptive pill [internet] U.S.A :contraindications of contraceptive ; 2015 [cited 2015 april 21] . Available from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combined_oral_contraceptive_ pill#Development_of_an_effective_combined_oral_contrace ptive












































![List of refrences (cont.):
ŌĆó progeterone receptors [Internet] :NURSA; 2014[cited 25 April
2015] Available from:
https://www.nursa.org/nursa/molecules/nr.jsf?doi=10.1621/9
NIE3U3DI6
ŌĆó progesterone[Internet] :Drugs.com;2013[cited 25 April 2015]
.Available from:
http://www.drugs.com/pro/progesterone.html
ŌĆó Therapeutic use of contraceptive [Internet] london:
contraceptive; 1999 [cited 2015 april 15 ].available from:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10342095](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/progesteroneandrelateddrugs-150428132253-conversion-gate02/85/Progesterone-and-related-drugs-45-320.jpg)
![List of refrences (cont.):
ŌĆó Combined oral contraceptive pill [internet] U.S.A
:contraindications of contraceptive ; 2015 [cited 2015 april
21] . Available from:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combined_oral_contraceptive_
pill#Development_of_an_effective_combined_oral_contrace
ptive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/progesteroneandrelateddrugs-150428132253-conversion-gate02/85/Progesterone-and-related-drugs-46-320.jpg)