programmed learning
- 1. Introduction ïThe term Programmed learning has been coined from principles of operant learning or conditioning developed at the psychological laboratories on the basis of experimental studies conducted on animals by B.F.Skinner of Harvard University. This concept was used to development of self learning material or programmed learning and teaching machines. ïB.F.Skinner and his companions had first started âprogrammed learningâ in 1943
- 2. ï― B.F.Skinner published a paper entitled âScience of Learning and art of Teachingâ . This paper leads the way for the programmed instruction. He claimed that desirable behavior can be brought out by continuous feed back. ï― Thereafter, Sidney L.Pressey designed a teaching machine for teaching purpose.
- 3. Meaning of Programmed Learning ïProgrammed instruction is the process of arranging the material to be learned into a series of sequential steps that is from known to unknown. ------ Smith and Moore ïProgrammed learning is a method of designing a reproducible sequence of instructional events to produce a measurable and consistent effect on behavior of each and every acceptable students. ------ Susan Markle
- 4. Principles of Programmed Learning âĒ Principle of Small Steps âĒ Principle of Active Response âĒ Principle of Immediate Reinforcement âĒ Principle of self âPacing âĒ Principle of Self Evaluation
- 5. ïķIndividualized Instruction ïķLogical Sequence of material (Small Steps) ïķInteraction between the learner and the programmed ïķImmediate Knowledge of results ïķOrganized nature of Knowledge ïķLearners Own Speed (Self Pacing) ïķConstant Evaluation
- 6. âĒ To help the students for learning by doing. âĒ To provide the situation to learn at his/her own speed. âĒ To help the student to learn without the presence of teacher. âĒ To present the mater in a logical manner. âĒ To study himself. âĒ To evaluate himself. âĒ To compare his/her answer with the key .
- 8. Linear Programming âĒ This was developed by B.F.Skinner and his associates. âĒ In this method the subject method will be divided into very small steps each of which is called as frame. âĒ In each frame, the student to do something. âĒ After giving the answer for the question immediately he can check whether his answer in correct or wrong F 1 F 2 F 3 F 4 F 5 F 6
- 9. Branching Programming âĒ This was developed by Norman, A. Crowder (1960) and it was called as intrinsic programmed. âĒ In this method the subject should select the answer for the question(Objective Type). âĒ If subjectâs answer is correct he will lead to the next frame. âĒ If subjectâs answer is wrong he will lead to the remedial frame. âĒ After the remedial frame he will directed to the main frame. F1 IfAnswerisWrong If Answer is Correct F2 F1.1
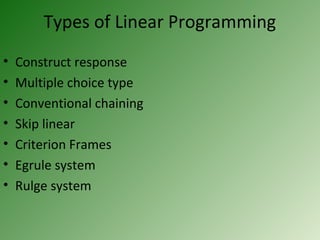
- 10. Types of Linear Programming âĒ Construct response âĒ Multiple choice type âĒ Conventional chaining âĒ Skip linear âĒ Criterion Frames âĒ Egrule system âĒ Rulge system
- 11. Features of Linear Programming âĒ Linear Arrangement âĒ Small Steps âĒ Controlled Responses âĒ Active Responding âĒ Immediate Feedback âĒ Prompting âĒ Self- Pacing âĒ Simple Mechanism âĒ Minimum error
- 12. Limitation of Linear Programming âĒ Lack of Motivation âĒ No Freedom of choice âĒ No development of discriminative power âĒ No student centered âĒ No specific role of teacher âĒ Difficulty in finding background
- 13. Branching Programming Basic Assumptions:- ï§ Needs of the learner ï§ Meaningful units ï§ New material ï§ Traditional Methods ï§ No hindrance by errors ï§ Multiple choice items ï§ Sufficient freedom
- 15. Features Of Branching Programming A. Based on traditional tutorial method B. Larger frame C. Multiple choice questions D. Alertness of learners E. Easier to develop frames F. Teaching and instruction G. Psychological and social motivation
- 16. Limitations Of Branching Programming ïķGuessing ïķDifficulty in multiple choice questions ïķDifficulty in arranging the Branching Programme ïķ Not Suitable for small children ïķCostly ïķNo suitable feedback ïķProgrammerâs immagination