Prohibition of interest IN DIFFERENT CIVILIZATION
- 1. Prohibition of Interest: Evidences from Different Civilizations 123/11/2015
- 2. Synonyms of Interest ï Usury ï Interest ï Riba 223/11/2015
- 4. Usury: Definition USURY: MEANING Ancient Ages (3300 BC-1400 BC): ï Any premium for a loan of money, or of any kind of property ï The gain of anything above the principal, or that which was lent whether it be in money, corn, wares or the like." 423/11/2015
- 5. Usury: Definition Modern Ages (1400 AD -2015 AD): ï Interest at unreasonably high rates ï ï Interest rate at Usurious rate ï Interest rate above the rate fixed by the govt./Law ï Interest rate above the legal rate 523/11/2015
- 6. Interest: Definition Meaning of Interest: ï A premium for a loan of money ï Extra amount charged on principal money in lending and borrowing ï Extra amount on Loan- Legally approved by the state 623/11/2015
- 7. Interest as a substitute for usury (14th -21st century) ï The word âInterestâ- First appeared in the fourteenth century ï End of the 13th century: declining the influence of the Orthodox Church ï Development of trade and commerce, investment ï Interest on loans for commercial and productive purposes 723/11/2015
- 8. Interest as a substitute for usury (14th -21st century) ï 1483-1546: Reforms movement Led by Reformist Luther and Zwingli ï Mid-16th century: Calvin and Molinaeus ï 1545: the King (and the Church) of England fixed a legal maximum interest; any amount in excess of the maximum was usury 823/11/2015
- 9. Interest as a substitute for usury (14th -21st century) Proposal of Calvin and Molinaeus: Mid- 16th century: ï interest on commercial loans- Permitted ï interest on loans to the needy-forbidden ï They are responsible for modern interest rate (for all including needy) 923/11/2015
- 10. Interest as a substitute for usury (14th -21st century) 1620s-1780s: Age of Enlightenment/ Enlightenment Movement/ Age of Reason: ï Religion vs. Secularism ï Emphasized on reason, analysis, and individualism ï Separations of religions and ethics from practical life ï Interest is common practice in the world 1023/11/2015
- 11. Riba: Definition ï Arabic term ï Wider concept than Usury or Interest ï Literally Meaning: to excess, addition and surplus ï Terminology of the Shariah: An addition, however slight, over and above the principal of a loan or debt 1123/11/2015
- 12. Riba: Characteristics ï Positive and fixed ex-ante; ï Tied to the time period and the amount of the loan; ï Payment is guaranteed regardless of the outcome or the purposes for which the principal was borrowed; ï The state apparatus sanctions and enforces its collection 1223/11/2015
- 13. Riba: Types 1. Riba al - nasiah deals with riba in money- to â money exchanges(Money Riba) 2. Riba al- fadl deals with hand - to - hand or barter exchange (Commodity Riba) 1323/11/2015
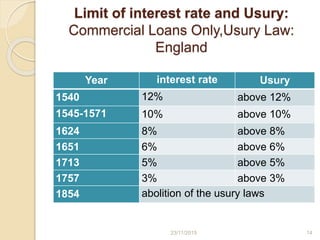
- 14. Limit of interest rate and Usury: Commercial Loans Only,Usury Law: England Year interest rate Usury 1540 12% above 12% 1545-1571 10% above 10% 1624 8% above 8% 1651 6% above 6% 1713 5% above 5% 1757 3% above 3% 1854 abolition of the usury laws 1423/11/2015
- 15. Interest rate vs. Usury: Modern day ï Modern day Banking Interest rate: 16- 18% ï Isnât usury? ï Yes: So it is haram ï No!!!!!! Double standard??? ï The legal rate of Interest in Islam is Zero ï So interest=Usury=Riba ï All are Haram 1523/11/2015
- 16. Interest in Ancient Civilizations: Mesopotamian: 3300 â 750 BC ï Babylonia: The legal interest rate : 30 % (money), 50 % (grain) ï Assyria: no upper limit for interest rate. ï Sumeria: 20 % (money), 33 % (grain) Consequence: ï The farmers were often so deep in debt that they starved to death along with their families. ï If failed to pay interest, Slavery is the ultimate fate 1623/11/2015
- 17. Mesopotamian: 3300 â 750 BC Example of cruelty City of Uruk in Sumer: ï There lived two brothers who lent money with interest. ï When a borrower no longer could repay his loan, ï He lost his house and had to start working for free for the brothers. ï The slave could be lent also to other employers. ï Slaves are Sold to overseas ï This is a classical example of economic slavery. 1723/11/2015
- 18. Prohibition of interest in Mesopotamia ï By the ruler of Babylon, Hammurabi (1848-1805 B.C.) ï Legal acts (containing 93 paragraphs) ï Severe punishment for Breaking the law ï Halakhic ruling: money disappears if charging interest 1823/11/2015
- 19. Interest in Ancient Civilizations: Persian: 730-330 BC ï Collateral: land and vineyards ï The Greek moneychangers-money lender ï They acquired huge property by lending money ï Become influential in Persian Empire ï 445 BC: Nehemiah, the governor of Judea, prohibited interest ï Nehemiah builds a wall around Jerusalem to save his people from money changers 1923/11/2015
- 20. Interest in Ancient Civilizations: Greek: 2700BC-600 AD ï Interest rate: 12 - 24 % ï Small proprietors or metayers, became indebted to the rich ï Debtor were practically slaves ï Usury had given all the power of the state to a small plutocracy ï 594 BC: Solon's laws contained many provisions for the relief of poor debtors 2023/11/2015
- 21. Interest in Ancient Civilizations: Greek: 2700 BC-600 AD ï Charging interest was regulated, but not forbidden ï Prohibited and condemned by philosopher and Lawmakers Aristotle: ï Usury is the unnatural breeding of money from money ï Contrary to justice and the Natural Law ï Medium of exchange, not commodity ï It could not beget another piece of money Plato: ï Usury is the social evils ï It showed a lack of generosity toward poor a ï Contrary to the welfare ï Setting one class against the other 2123/11/2015
- 22. Interest in Ancient Civilizations: Roman: 600BC-400 AD ï Jews of Rome was moneychangers/usurer ï Money-changers monopolized usury, ï Monopolized the precious mineral trade ï Start the businesses of prostitution (including pedophilia and homosexuality), ï Start the slavery 2223/11/2015
- 23. Interest in Ancient Civilizations: Roman: 600BC-400 AD Effects: ï 98-117 A.D: the reign of Trajan: high taxes for borrowing money at interest ï Reversal of its earlier commerce policies ï High taxes, pervasive regulation and debasement of the currency ï Rome was bankrupt and was collapsing 2323/11/2015
- 24. Interest in Ancient Civilizations: Roman: 600BC-400 AD Prohibition: ï 342 BC: Prohibited by Law Genucia ï 325AD: by Constantine, the Roman emperor ï Canon and ecumenical councils forbade the interest for clergy and laity ï 212 AD: by the Law Caracalla: confine rights of Jews in the Roman Empire, ï Up to 14th century: also prohibited by Church, pope, Pope Clement V, 2423/11/2015
- 25. Prohibition of Usury In England ï 1189-1275 AD: debtors massacred the Jews usurer at London and York ï 1275 AD: king Edward I: Law-Statute of Jewry: usury illegal and linked it to blasphemy ï Scores of English Jews were arrested, ï 300 were hanged ï Their property went to the Crown ï 1290 AD: all Jews were expelled from England, ï Allowed to take only what they could carry; ï The rest of their property became the Crown's 2523/11/2015
- 26. Interest in Ancient Civilizations: Ancient India: 3000BC-500 BC Prohibition ï 2000â1400 BC: Vedic Hindu texts in Ancient India ï 700â100 BC: Sutra texts ï 600â400 BC: Buddhist Jatakas- hypocritical manner ï usurerâ (kusidin) ï Vasishtha-Hindu Law Maker forbade interest 2623/11/2015
- 27. Adverse effects of usury on the civilizations: ï Babylon loaned much money at interest (usury) to Persia (Iran) ï Persia conquered Babylon to eliminate its debt and acquire Babylon's gold ï Persia loaned Greece much money at interest (usury) and Greece conquered Persia. ï Greece loaned Rome much money at interest (usury). Rome conquered Greece ï After the fall of Imperial Rome, the various nations of Europe were kept in bondage and poverty by the AB's (Anti-God Banksters) for many centuries, known as the "Dark Ages" 2723/11/2015
- 28. Inadequate distribution of wealth: an impact of usury Collapse of civilization Concentration of Total wealth to Babylonian 3% of the people Persia 2% of the people Greece 0.5% of the people Roman Empire 2,000 people America 2% of the people control 90% of the wealth 2823/11/2015
- 29. 2923/11/2015