Project Management Institute 02 18 10
- 1. The Project Management Institute Project Management in a Healthcare Environment Mark Kresse, PT, FACHE February 18, 2010 SAINT VINCENT Project Management Institute - Erie 02_18_10
- 2. Rule #1: Know your audience Current work environments? Manufacturing Healthcare Government Other Services Interest in the health care environment?
- 3. Begin with the end in mindŌĆ” What types of projects are managed within hospitals and health care organizations? Who are the key stakeholders and how are their relationships managed? In what other ways is project management in a health care environment unique? Tools?
- 4. Project Types Facilities Campus-building New construction Renovation From design through construction, outfitting and inauguration
- 5. Project Types Information systems & technology Network infrastructure Electronic medical records Long-term record archiving Disaster recovery Telemedicine
- 6. Project Types Information systems & technology Network infrastructure Electronic medical records Long-term record archiving Disaster recovery Telemedicine
- 7. Project Types Health care services New medical services (e.g. urgent care center, cardiac CT)
- 8. Project Types Health care services New medical services (e.g. urgent care center, cardiac CT) Provider recruitment (physicians, mid-level providers, etc.)
- 9. Project Types Health care services New medical services (e.g. urgent care center, cardiac CT) Provider recruitment (physicians, mid-level providers, etc.) New equipment and/or procedures (e.g. hip resurfacing, least invasive valve surgery)
- 10. Project Types Administrative projects Patient safety projects (e.g. medication reconciliation)
- 11. Project Types Administrative projects Patient safety projects (e.g. medication reconciliation) Evidence-based practice implementation ŌĆ£ comparative-effectiveness analysisŌĆØ
- 12. Project Types
- 13. Project Types Mixed projects New services that involve facilities, information systems, medical services and administrative aspects
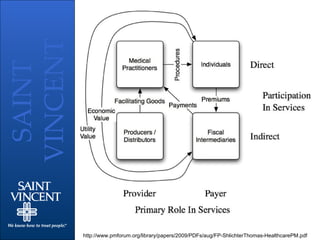
- 14. Stakeholder Relationships Macro - Payers - Government, businesses and individuals Fiscal intermediaries - Insurers, HMOs, pharmacy benefits managers Providers ŌĆō hospitals, integrated delivery networks, and individual clinics and physician practices
- 15. Stakeholder Relationships Macro - Purchasers ŌĆō groups which aggregate healthcare products and services for distribution Producers ŌĆō providers of drugs and devices used in health care services
- 17. Stakeholder Relationships Micro - Board and executive administration Medical staff leadership and key physicians Nursing and other patient services Facilities management/construction Information technology/services Finance/patient accounting Purchasing/supply chain Legal/corporate compliance Community ŌĆ£constituentsŌĆØ External providers ŌĆō physicians, other hospitals Department of Health (C.O.N. state?)
- 18. Compare & Contrast Legal and Regulatory Issues PA Department of Health The Joint Commission HIPAA Third party payer contracts
- 19. Compare & Contrast Legal and Regulatory Issues PA Department of Health The Joint Commission HIPAA Third party payer contracts Public reporting (hospitalcompare.com)
- 20. Compare & Contrast Legal and Regulatory Issues PA Department of Health The Joint Commission HIPAA Third party payer contracts Public reporting (hospitalcompare.com) Competitive landscape ŌĆō like politics, health care is local
- 21. Compare & Contrast Legal and Regulatory Issues Public reporting Competitive landscape Who does project management? Strategic plan alignment? Organization-wide or department/ function specific? Health care providers do not receive training in project management during professional training
- 22. Provider Relationships One of the most daunting problems facing healthcare projects is the management of stakeholders and their competing interests. Key constituents are often highly educated, with deeply embedded opinions about how processes should work.
- 23. Provider Relationships One of the most daunting problems facing healthcare projects is the management of stakeholders and their competing interests. Key constituents are often highly educated, with deeply embedded opinions about how processes should work. Physician motivators * Pride Professionalism Profit *Peter Lund, MD ŌĆō Erie Urologist, former President of PA Medical Society
- 25. Critical Success Factors A well-defined strategic plan and top-down leadership help set priorities
- 26. Critical Success Factors A well-defined strategic plan and top-down leadership help set priorities Strong executive champion for overall project management or specific projects
- 27. Critical Success Factors A well-defined strategic plan and top-down leadership help set priorities Strong executive champion for overall project management or specific projects Key medical staff/physician support
- 28. Critical Success Factors A well-defined strategic plan and top-down leadership help set priorities Strong executive champion for overall project management or specific projects Key medical staff/physician support Strong cooperation between departments supporting project implementation
- 29. Current project management communication tool? MS Project MS Excel Other
- 30. References http://www.pmforum.org/library/papers/2009/PDFs/aug/FP-ShlichterThomas-HealthcarePM.pdf http://www.pmforum.org/library/editorials/2009/PDFs/may/Editorial-Pells-PM-for-Hospitals.pdf http://www.rinergroup.com/default.aspx
- 31. If you build it, they will comeŌĆ”
- 32. ╠²
- 33. ╠²
- 34. ╠²
- 35. Mark Kresse, PT, FACHE [email_address] 814/452-7888 SAINT VINCENT

































![Mark Kresse, PT, FACHE [email_address] 814/452-7888 SAINT VINCENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanagementinstituteerie021810-12665803860471-phpapp01/85/Project-Management-Institute-02-18-10-35-320.jpg)