Project Management Tools & Techniques by Susan W. Carey
- 1. Project Management Tools & Techniques Susan W. Carey
- 2. Workshop Objectives ŌĆó Recognize project management terminology ŌĆó Explain roles and responsibilities for key players ŌĆó Develop a project proposal ŌĆó Construct a work breakdown structure ŌĆó Identify tools for tracking and controlling a project ŌĆó Recognize the importance of a formal closeout
- 4. Module Objectives ŌĆó Recite project management terminology ŌĆó Describe the characteristics of a project ŌĆó Distinguish between a project and sub projects ŌĆó Identify the benefits of project management ŌĆó Define the roles and responsibilities of the various stakeholders ŌĆó Determine what it takes for successful project management
- 5. BASICS OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT
- 6. Definition of a Project ŌĆó A series of inter-related and sequenced activities, managed by a single individual, designed and organized to accomplish a specific goal, within a limited timeframe, frequently with specific budgetary requirements
- 7. Remember:
- 8. Characteristics of Projects ŌĆó Undertaken at all levels ŌĆó Single person or thousands ŌĆó Duration could be weeks or years ŌĆó Single unit or entire organization Projects are critical to the realization of the performing organizationŌĆÖs business strategy because projects are a means by which strategy is implemented.
- 9. Characteristics of Projects ŌĆó Are unique ŌĆó Consume time ŌĆó Cost money ŌĆó Requires people ŌĆó Contain risks ŌĆó Sequence of tasks
- 10. Types of Projects ŌĆó Developing a new product or service ŌĆó Effecting a change in structure, staffing, or style of an organization ŌĆó Designing a new transportation vehicle ŌĆó Developing or acquiring a new or modified information system ŌĆó Constructing or renovating a building or facility ŌĆó Building a water system for a community in a developing country ŌĆó Running a campaign for political office ŌĆó Implementing a new or improved business process or procedure
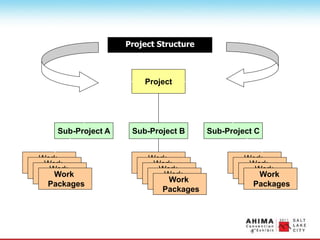
- 11. Subprojects ŌĆó Based on project process such as a single phase (e.g. design) ŌĆó According to human resource skill requirements (e.g. plumbing) ŌĆó By major deliverable (e.g. training)
- 12. Project Structure Project Sub-Project A Sub-Project B Sub-Project C Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages Work Packages
- 13. Definition of Project Management ŌĆó Taking knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques, applying those to project activities to satisfy the business need for which the project was undertaken
- 14. Benefits of Project Management ŌĆó Do more with less ŌĆó Flexible framework ŌĆó Clear expectations ŌĆó Progress is monitored ŌĆó Lessons learned ŌĆó Do it right the first time ŌĆó Less frustration
- 15. Project Phases / Project Life Cycle ŌĆó Involve a degree of uncertainty ŌĆó Divide the project into several phases ŌĆō Improve control ŌĆō Provide links to operation ŌĆó Phases are referred to as the ŌĆ£project life cycleŌĆØ
- 16. Characteristics of the Project Life Cycle ŌĆó Defines the beginning and end of a project ŌĆó Includes the following phases: ŌĆō Initiation ŌĆō Planning ŌĆō Execution ŌĆō Closeout
- 17. WhatŌĆÖs Your Organization Type? ŌĆó Functional? ŌĆó Matrix? ŌĆó Projectized?
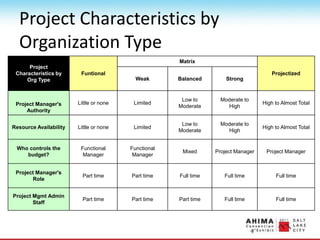
- 18. Project Characteristics by Organization Type Project Characteristics by Org Type Funtional Matrix Projectized Weak Balanced Strong Project Manager's Authority Little or none Limited Low to Moderate Moderate to High High to Almost Total Resource Availability Little or none Limited Low to Moderate Moderate to High High to Almost Total Who controls the budget? Functional Manager Functional Manager Mixed Project Manager Project Manager Project Manager's Role Part time Part time Full time Full time Full time Project Mgmt Admin Staff Part time Part time Part time Full time Full time
- 19. Challenges in a Matrix Environment ŌĆó Lack of PMŌĆÖs formal authority (biggest challenge) ŌĆó Resource management ŌĆó Dual reporting relationship ŌĆó Potential for duplication of effort ŌĆó Unclear roles and responsibilities ŌĆó Greater potential for conflict ŌĆó Lack of accountability
- 20. Types of Authority ŌĆó Formal ŌĆó Purse-string ŌĆó Bureaucratic ŌĆó Technical ŌĆó Charismatic
- 21. Key Players ŌĆó Project sponsor ŌĆō Ensures the project meets the business needs ŌĆō Provides funding ŌĆō Approves key deliverables ŌĆō Assists in issues resolution and change management
- 22. Project Sponsor Challenges ŌĆó Micro managing project sponsor ŌĆó The invisible project sponsor
- 23. Key Players ŌĆó Project manager ŌĆō Assembles the project team ŌĆō Assigns tasks and activities ŌĆō Monitors progress, risk, issues ŌĆō Manages the scope ŌĆō Delivers on time and within budget ŌĆō Ensures project documentation is prepared
- 24. Key Players ŌĆó Stakeholders ŌĆō Individuals or organizations that are actively involved in the project or whose interests may be positively or negatively affected as a result of the project ŌĆō May exert influence over the project and its results
- 25. Key Players ŌĆó Project leader ŌĆō Responsible for a subproject ŌĆō Ensures technical aspects are delivered ŌĆō Monitors progress, risk, issues ŌĆō Manages the scope and the change management process ŌĆō Delivers on time and within budget ŌĆō Communicates status to project manager
- 26. Key Players ŌĆó Project team members ŌĆō Complete assigned tasks on time ŌĆō Work with other team members ŌĆō Monitor progress on their tasks ŌĆō Resolve issues ŌĆō Monitor changes and risks ŌĆō Advise others of potential problems
- 27. Key Players ŌĆó Other ŌĆō Subject matter experts ŌĆō Business liaisons
- 28. Types of Teams ŌĆó Working group ŌĆó Pseudo team ŌĆó Potential team ŌĆó Real team ŌĆó High-performing team
- 29. Is PM a science or an art? ŌĆó Science ŌĆō Charts ŌĆō Graphs ŌĆō Calculations ŌĆō Tools ŌĆō Hard skills ŌĆó Art ŌĆō Politics ŌĆō Interpersonal ŌĆō Organization ŌĆō Communication ŌĆō Negotiation ŌĆō Conflict resolution ŌĆō Soft skills
- 31. Competing Demands ŌĆó Stakeholders with different needs ŌĆó Identified and unidentified requirements ŌĆó Triple constraints of scope/quality, time, and cost Differences between or among stakeholders should be resolved in favor of the customer.
- 32. Top Two Reasons Projects Fail ŌĆó Ineffective COMMUNICATION ŌĆó Lack of LEADERSHIP
- 33. Why is Communication Important? You are the chief airplane washer at the company hangar and you: ŌĆó Hook the high pressure hose up to the soap suds machine. ŌĆó Turn the machine ŌĆ£on.ŌĆØ ŌĆó Receive an important call and have to leave work to go home. ŌĆó As you depart for home, you yell to your assistant, ŌĆ£Don, turn it off.ŌĆØ ŌĆó Assistant Don thinks he hears, ŌĆ£DonŌĆÖt turn it off.ŌĆØ He shrugs and leaves the area right after you. ŌĆó The resultŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”
- 35. Project Manager - Tips for Success ŌĆó Remain calm, even under stress ŌĆó Motivate and reward the team ŌĆó Be proactive ŌĆó Organize, plan, and communicate ŌĆó Set priorities and deadlines ŌĆó Have a sense of humor
- 36. Project Manager - Tips for Success ŌĆó Show strong leadership skills ŌĆó Generate a shared commitment ŌĆó Show empathy ŌĆó Work smarter, not harder ŌĆó Set realistic goals ŌĆó Lead by example
- 39. Module Objectives ŌĆó Identify the objectives of the initiation phase ŌĆó Prepare a project proposal ŌĆó Determine next steps for entry into the planning phase
- 40. Which way should I go? That depends on which way you are going. I donŌĆÖt know where IŌĆÖm going. Then it doesnŌĆÖt matter which way you go.
- 41. Gather Data ŌĆó Interview the project sponsor ŌĆó Identify key project stakeholders ŌĆó Conduct additional interviews ŌĆó Read documentation ŌĆó Learn as much as you can ŌĆó Research on the internet
- 42. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Goal: ŌĆō General statement of intent ŌĆō Purpose toward which the effort is directed ŌĆō Answers the question ŌĆ£why?ŌĆØ ŌĆō Must be linked to an organizational strategic goal
- 43. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Goal examples: ŌĆō To improve our competitive position within the financial services industry ŌĆō To reduce operating costs and become a more cost- effective service provider ŌĆō To improve customer service and our image as the company that cares ŌĆō To improve the quality of clinical care and reduce mortality rate ŌĆō To provide quality services to our neighborhoods
- 44. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Objectives: ŌĆō Specific statements of the measurable results to be provided by the project
- 45. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Objective examples: ŌĆō To convert all data to release 3.6 of Acme Ledger System no later than March 31, 2008, at a cost not to exceed $2.5 million, according to all internal standards, policies, and procedures ŌĆō To renovate the youth shelter no later than May 1, 2008, at a cost not to exceed $500,000, according to all building codes in Jefferson County, using the design suggested by ABC Architectural firm
- 46. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Scope and major deliverables ŌĆō Sum total of the project ŌĆō What is included in the project ŌĆō Major deliverables ŌĆō Examples ŌĆó Training ŌĆó Construction ŌĆó Equipment
- 47. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Boundaries ŌĆō Opposite of scope ŌĆō What is not included ŌĆō Helps manage expectations ŌĆō Clarifies the scope ŌĆō Avoid unpleasant surprises
- 48. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Business considerations and requirements ŌĆō Helps to understand the business environment ŌĆō Special needs ŌĆō Written by the business owner ŌĆō Need to surface early for planning
- 49. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Technical considerations and requirements ŌĆō Helps to understand the technical environment ŌĆō Special needs ŌĆō Technology perspective ŌĆō Need to surface early
- 50. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Performance measurement criteria ŌĆō Measures of success ŌĆō Helps define when the project is over ŌĆō Used during closeout phase ŌĆō Ensures quality
- 51. Develop the Project Proposal ŌĆó Benefits ŌĆō Positive results expected from the project ŌĆō Purpose for which the project was undertaken ŌĆō May be ŌĆó Tangible ŌĆó Intangible
- 52. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Priorities ŌĆō Time driven? ŌĆō Cost driven? ŌĆō Scope/quality driven?
- 53. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Assumptions ŌĆō Factors that are considered to be true, real, or certain ŌĆō Must occur to be successful ŌĆō Must be documented and understood Resources are available Budget is approved
- 54. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Constraints ŌĆō Factors that may limit your options: ŌĆó Pre-defined budget (e.g. not to exceed) ŌĆó Pre-determined project team ŌĆó Time-driven project
- 55. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Risks ŌĆō Unplanned events ŌĆō Can have positive or negative consequences ŌĆō Uncertainty ŌĆō Document at a high level
- 56. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Open issues or pending decisions ŌĆō Items that must be resolved before proceeding ŌĆō May include resource or technical issues ŌĆō Outstanding questions
- 57. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Interdependencies to other projects ŌĆō Predecessor projects ŌĆō Successor projects ŌĆō Co-dependent projects
- 58. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó High-level costs ŌĆō Ballpark estimate of project cost ŌĆō Known costs and best guess at other costs Provide a range of estimates, if possible
- 59. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Major milestones and high-level target dates ŌĆō Ballpark estimate of project length ŌĆō Show major milestones ŌĆō Use ranges
- 60. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Alternative implementation strategies ŌĆō Ask subject matter experts ŌĆō Review other projects ŌĆō Include advantages and disadvantages
- 61. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Recommended approach ŌĆō Select best alternative ŌĆō Explain the reasoning ŌĆō Include any risks
- 62. Develop Project Proposal ŌĆó Resource needs ŌĆō Specific people ŌĆō Specific skill sets ŌĆō Equipment ŌĆō Training rooms
- 63. Gain Sponsor Approval ŌĆó Present the proposal ŌĆó Explain your approach ŌĆó Receive approval ŌĆó Ask for needed assistance ŌĆó Negotiate due date for next phase ŌĆó Agree on progress reporting ŌĆó Publish announcement memo
- 66. Module Objectives ŌĆó Identify the planning processes ŌĆó Describe a detailed work breakdown structure ŌĆó Build an activity list ŌĆó Estimate the duration of activities ŌĆó Document risks ŌĆó Finalize project plan development
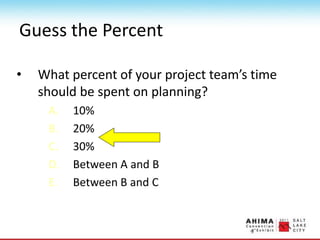
- 67. Guess the Percent ŌĆó What percent of your project teamŌĆÖs time should be spent on planning? A. 10% B. 20% C. 30% D. Between A and B E. Between B and C
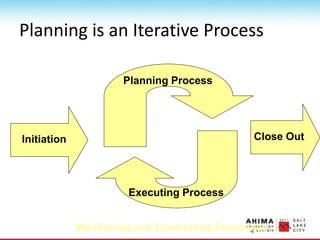
- 68. Planning Processes ŌĆó There are several planning processes ŌĆó Planning is an ongoing effort throughout the life of the project
- 69. Planning is an Iterative Process Initiation Close Out Planning Process Executing Process Monitoring and Controlling Processes
- 70. Planning Phase Deliverables ŌĆó Integrated project management plan ŌĆō Project definition (approved project proposal) ŌĆō Project structure ŌĆō Subsidiary management plans
- 71. Subsidiary Management Plans ŌĆó Integration ŌĆó Communications ŌĆó Risk ŌĆó Procurement ŌĆó Cost ŌĆó Quality ŌĆó Human Resources ŌĆó Scope ŌĆó Time
- 72. Creating the Work Breakdown Structure ŌĆó Deliverable-oriented, tree-like structure ŌĆó Graphically defines all the work in the project If itŌĆÖs not in the work breakdown structure, itŌĆÖs not in the project! Golden Rule of Project Management
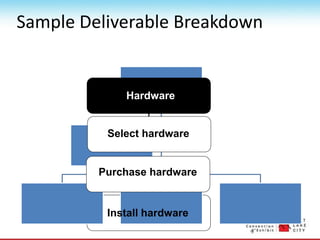
- 73. Sample Deliverable Breakdown Purchase hardware Install hardware Select hardware Hardware
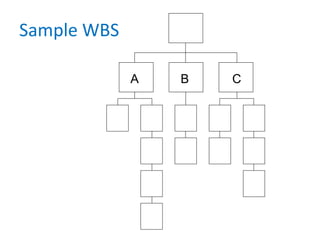
- 74. Sample WBS A B C
- 75. Roles and Responsibilities ŌĆó Start with the WBS ŌĆó Identify project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships ŌĆó Document primary and support responsibilities
- 76. Selecting Resources ŌĆó Work with functional managers ŌĆó Ensure right skill sets are available when needed ŌĆó Create your own resource pool
- 77. Defining the Work ŌĆó Identify your deliverables (work buckets) ŌĆō Usually a single word ŌĆō Must be a NOUN ŌĆó Break each deliverable down into tasks ŌĆō These require action ŌĆō Starts with a VERB ŌĆó Break each task down as far as necessary
- 78. Sequencing the Work ŌĆó Document interactivity dependencies ŌĆó Ensure a realistic schedule ŌĆó Identify constraints
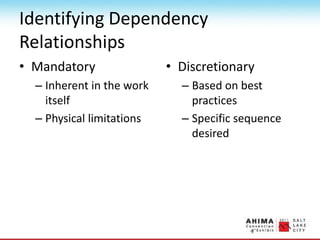
- 79. Identifying Dependency Relationships ŌĆó Mandatory ŌĆō Inherent in the work itself ŌĆō Physical limitations ŌĆó Discretionary ŌĆō Based on best practices ŌĆō Specific sequence desired
- 80. Estimating the Time Required ŌĆó Estimate the time needed to complete each activity ŌĆó Consider each resourcesŌĆÖ availability
- 81. Creating the Project Schedule ŌĆó Tasks and activities ŌĆó Start and finish dates ŌĆó Resources ŌĆó Dependencies
- 83. Estimating the Project Cost ŌĆó Base estimate: ŌĆō Start with the WBS ŌĆō Select an estimating method ŌĆō Estimate expected cost of project by cost category ŌĆō Estimate contingency (management) reserve for: ŌĆó Cost mitigation ŌĆó Scope changes ŌĆó Unexpected risk events
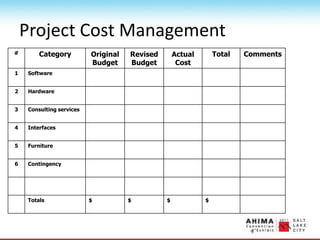
- 84. Project Cost Management # Category Original Budget Revised Budget Actual Cost Total Comments 1 Software 2 Hardware 3 Consulting services 4 Interfaces 5 Furniture 6 Contingency Totals $ $ $ $
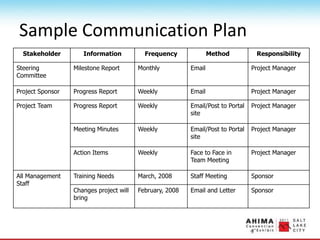
- 85. Project Communication Plan ŌĆó Identify key project stakeholders ŌĆó Determine the information needs ŌĆō Upwards communication ŌĆō Lateral communication ŌĆō Downward communication ŌĆó Document what, when, why and how information will be distributed ŌĆó Develop documentation standards
- 86. WBS EXERCISE
- 87. Sample Communication Plan Stakeholder Information Frequency Method Responsibility Steering Committee Milestone Report Monthly Email Project Manager Project Sponsor Progress Report Weekly Email Project Manager Project Team Progress Report Weekly Email/Post to Portal site Project Manager Meeting Minutes Weekly Email/Post to Portal site Project Manager Action Items Weekly Face to Face in Team Meeting Project Manager All Management Staff Training Needs March, 2008 Staff Meeting Sponsor Changes project will bring February, 2008 Email and Letter Sponsor
- 88. Scope Management Plan ŌĆó Spells out the process involved for making changes to the scope ŌĆó Defines who has the authority to approve changes
- 89. Change Control Process ŌĆó Can be different from project to project ŌĆó Simple projects ŌĆō simple solution ŌĆō PM and/or Sponsor signs off on any changes ŌĆó Complex projects ŌĆō ŌĆō May have different levels of change ŌĆō May have a Change Control Board in place to approve more detailed or complex changes
- 90. Integration Management Plan ŌĆó Document spelling out how each of the individual plans will work together
- 91. Project Management Plan ŌĆó Combination of subsidiary mgmt plans ŌĆó Assemble all planning deliverables ŌĆó Publish final plan to key project personnel and management ŌĆó Track and compare actual implementation to original baseline
- 93. Module Objectives ŌĆó Identify what needs to be monitored during the execution phase ŌĆó Describe the steps necessary for maintaining control of the project during execution ŌĆó Illustrate how variances should be managed ŌĆó Differentiate between various performance reports
- 94. MurphyŌĆÖs Law ŌĆó When things are going well, something will go wrong ŌĆó When things just canŌĆÖt get any worse, they will ŌĆó When things appear to be going better, you have obviously overlooked something
- 95. Ongoing Questions during Execution ŌĆó Are we on schedule? ŌĆó Are we on budget? ŌĆó Has the business need changed? ŌĆó What new issues do we have to address? ŌĆó Are any risk events materializing? ŌĆó Where are we in danger of not meeting our goal?
- 96. Ongoing Questions during Execution ŌĆó Are we delivering a quality product? ŌĆó Are our vendors delivering as promised? ŌĆó Do we have enough resources? ŌĆó Are unauthorized changes being allowed? ŌĆó Is the team working together productively?
- 97. Monitoring the Schedule ŌĆó Update the project schedule on a weekly basis ŌĆó Compare actual to plan ŌĆó Report and address variances quickly ŌĆó Hold the team accountable for delivering on time ŌĆó Replan as necessary
- 98. Monitoring the Budget ŌĆó Review financial information no less than monthly ŌĆó Compare actual to plan ŌĆó Report and address variances quickly ŌĆó Hold the team accountable for cost containment ŌĆó Re-project expenses as necessary
- 99. Monitoring Scope ŌĆó Compare work results to the plan daily ŌĆó Ensure results meet the need ŌĆó Ensure formal acceptance is received ŌĆó Reflect approved changes in the project plan
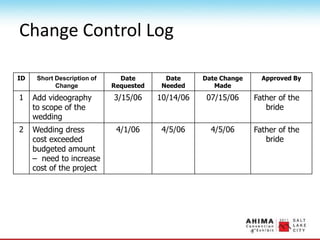
- 100. Change Management ŌĆó Any modification to the benefits, scope, time or cost ŌĆó Need an organized process for change ŌĆó Follow the process for change as outlined in the change management plan ŌĆó Source of changes: ŌĆō Sponsor ŌĆō Regulatory ŌĆō External ŌĆō Internal ŌĆó Keep a record!
- 101. Change Control Log ID Short Description of Change Date Requested Date Needed Date Change Made Approved By 1 Add videography to scope of the wedding 3/15/06 10/14/06 07/15/06 Father of the bride 2 Wedding dress cost exceeded budgeted amount ŌĆō need to increase cost of the project 4/1/06 4/5/06 4/5/06 Father of the bride
- 102. Scope Creep ŌĆó Changes through the ŌĆ£back doorŌĆØ ŌĆó Usually thought to be minor ŌĆó Enforce the change management process
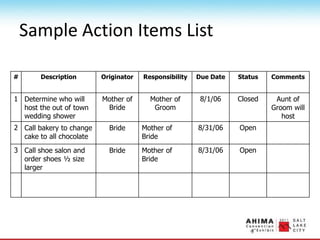
- 103. Monitoring Issues ŌĆó Use an ŌĆ£action items listŌĆØ to document issues ŌĆó Ensure ownership is clear ŌĆó Assign an due date ŌĆó Review progress at the weekly status meeting
- 104. Sample Action Items List # Description Originator Responsibility Due Date Status Comments 1 Determine who will host the out of town wedding shower Mother of Bride Mother of Groom 8/1/06 Closed Aunt of Groom will host 2 Call bakery to change cake to all chocolate Bride Mother of Bride 8/31/06 Open 3 Call shoe salon and order shoes ┬Į size larger Bride Mother of Bride 8/31/06 Open
- 105. Monitoring Risk ŌĆó Review the risk management plan regularly ŌĆó Monitor triggers and the watch list ŌĆó Implement mitigation plans ŌĆó Invoke contingency plans as necessary ŌĆó Repeat the ŌĆ£identify, assess, respondŌĆØ cycle as changes occur
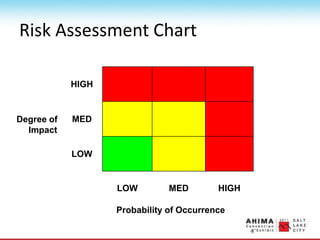
- 106. Risk Management Plan ŌĆó Identify the potential RISK EVENT ŌĆó Rate the risk for: ŌĆō Degree of impact ŌĆō Probability of occurrence ŌĆó Will you place the risk on the watch list? ŌĆó Assign a risk owner to watch for the triggers
- 107. Risk Assessment Chart HIGH Degree of Impact MED LOW LOW MED HIGH Probability of Occurrence
- 108. Risk Assessment ŌĆó Red area ŌĆō always ŌĆ£yesŌĆØ which means develop a risk management plan. ŌĆó Yellow area ŌĆō iffy, answer on a case-by-case basis. ŌĆó Green area ŌĆō always ŌĆ£noŌĆØ, donŌĆÖt develop a risk management plan. Just hope it doesnŌĆÖt happen and if it does deal with it then.
- 109. Monitoring Quality ŌĆó Review work products to ensure quality standards are met ŌĆó Use an independent reviewer ŌĆó Implement process improvements as necessary to eliminate unsatisfactory performance
- 110. Monitoring the Vendor ŌĆó Review the vendorŌĆÖs performance regularly ŌĆó Ensure performance meets the requirements as documented in the contract ŌĆó Insist on formal progress reports
- 111. Monitoring Human Resources ŌĆó Will the resources be available as originally planned? ŌĆó Are resources being utilized effectively? ŌĆó Are resources working together?
- 112. Team Building ŌĆó Develop a personal rapport ŌĆó Be supportive of the team ŌĆó Be clear on expectations ŌĆó Take a personal interest ŌĆó Celebrate special occasions ŌĆó Be accessible
- 113. Performance Reporting ŌĆó Provide project information to key stakeholders in a timely manner and method ŌĆó Execute the communications management plan ŌĆó Report progress and trends on all aspects of the project
- 114. Progress Reports ŌĆó Project progress ŌĆó Accomplishments this reporting period ŌĆó Plans for the next reporting period ŌĆó Comments (yellow flags) ŌĆó Issues or concerns (red flags)
- 115. Performance Reporting Guidelines ŌĆó Steering committee, or senior management ŌĆō Summary level information (monthly) ŌĆó Project sponsor ŌĆō As agreed upon (varies) ŌĆó Project manager ŌĆō Mid-level information (weekly) ŌĆó Team members ŌĆō Detailed information (weekly)
- 118. Module Objectives ŌĆó Outline key tasks in the closeout phase ŌĆó Recognize the importance of formally closing out the project ŌĆó Address special challenges in project closeout ŌĆó Conduct a project review meeting and document final results
- 119. Entry into the Closeout Phase ŌĆó Project was completed successfully ŌĆó Project was put on hold ŌĆó Project was terminated or canceled
- 120. Closeout Activities ŌĆó Recognition ŌĆó Closure ŌĆó Performance improvements ŌĆó Final approvals ŌĆó Contract closure
- 121. Closeout Activities ŌĆó Transfer responsibilities ŌĆó Release resources ŌĆó Documentation ŌĆó Close out project accounting (time and budget)
- 122. Special Challenges ŌĆó Uncertainty ŌĆó Post-project depression
- 123. Project Review Document ŌĆó Introduction ŌĆó Performance Criteria ŌĆó Lessons learned ŌĆó Open issues or action items ŌĆó Acknowledgements ŌĆó Chronology of major events ŌĆó Appendix
- 124. Why Projects DonŌĆÖt Live up to Expectations ŌĆó Failure to reach agreement on requirements ŌĆó Political battles, unresolved conflicts ŌĆó Skill set mismatch ŌĆó Plan was not doable
- 125. Why Projects DonŌĆÖt Live up to Expectations ŌĆó Plan was not followed ŌĆó Ineffective communication ŌĆó Lack of leadership ŌĆó Lack of project management skills
- 126. Celebrate!! ŌĆó Show appreciation! ŌĆó Recognize key individuals! ŌĆó Reinforce positive behavior!
- 127. LetŌĆÖs Review!
- 128. Basics ŌĆó Definition of a project ŌĆó Organizational and sponsor challenges ŌĆó Hard versus soft skills ŌĆó Triple constraints ŌĆó Communicate, communicate, communicate!
- 129. Initiation Input: ŌĆó Gathering data Output: ŌĆó Project proposal
- 130. Planning Input: ŌĆó Work breakdown structure ŌĆó Roles and responsibilities ŌĆó Activities Output: ŌĆó Project management plan
- 131. Execution Input: ŌĆó Integrated project management plan Output: ŌĆó Progress reports
- 132. Close Out Input: ŌĆó Lessons learned Output: ŌĆó Final documentation ŌĆó Party!
- 133. Questions?