Prokinetics.pptx
- 1. Prokinetics By: Ms. Priya Shukla Assistant Professor SSR College of Pharmacy, Sayli
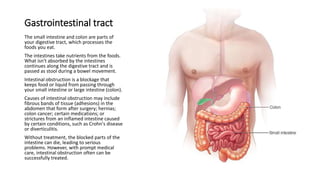
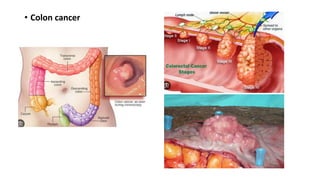
- 2. Gastrointestinal tract The small intestine and colon are parts of your digestive tract, which processes the foods you eat. The intestines take nutrients from the foods. What isn't absorbed by the intestines continues along the digestive tract and is passed as stool during a bowel movement. Intestinal obstruction is a blockage that keeps food or liquid from passing through your small intestine or large intestine (colon). Causes of intestinal obstruction may include fibrous bands of tissue (adhesions) in the abdomen that form after surgery; hernias; colon cancer; certain medications; or strictures from an inflamed intestine caused by certain conditions, such as Crohn's disease or diverticulitis. Without treatment, the blocked parts of the intestine can die, leading to serious problems. However, with prompt medical care, intestinal obstruction often can be successfully treated.
- 3. Symptoms Signs and symptoms of intestinal obstruction include: • Crampy abdominal pain that comes and goes • Loss of appetite • Constipation • Vomiting • Inability to have a bowel movement or pass gas • Swelling of the abdomen
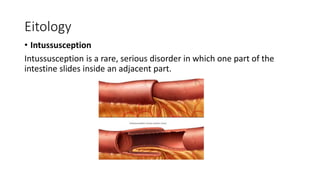
- 4. Eitology • Intussusception Intussusception is a rare, serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides inside an adjacent part.
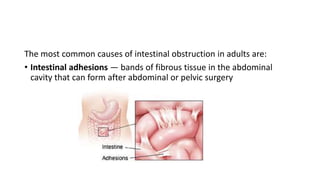
- 5. The most common causes of intestinal obstruction in adults are: • Intestinal adhesions — bands of fibrous tissue in the abdominal cavity that can form after abdominal or pelvic surgery
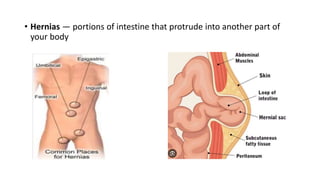
- 6. • Hernias — portions of intestine that protrude into another part of your body
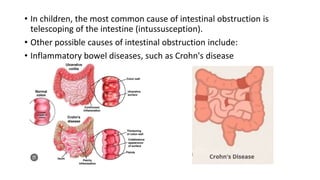
- 8. • In children, the most common cause of intestinal obstruction is telescoping of the intestine (intussusception). • Other possible causes of intestinal obstruction include: • Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn's disease
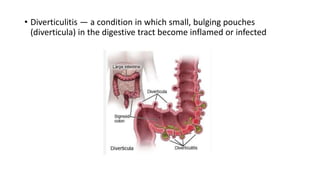
- 9. • Diverticulitis — a condition in which small, bulging pouches (diverticula) in the digestive tract become inflamed or infected
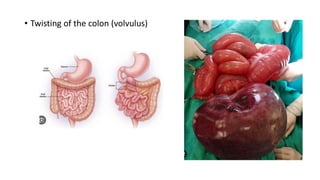
- 10. • Twisting of the colon (volvulus)
- 13. Nausea, vomiting, diarrheoa, and bradycardiac