Prolonged pregnancy and abnormal uterine contractions (4) (1).pdf
- 1. Prolonged pregnancy and abnormal uterine action Post term or prolonged pregnancy is defined as one that exceeds 294 days of pregnancy from the first day of the last menses Post maturity or post mature are terms used for the neonate and refer to fetuses or the condition of the baby.
- 2. Incidence and date ŌĆó The incidence of post term pregnancy is 10% ŌĆó Primigravids have mean duration of 288 days ŌĆó Multigravidas have mean duration of 283 days ŌĆó Pregnancy cannot be said is prolonged without accurate date ŌĆó Abdominal exam and fundal height is not certain ŌĆó Quickening can be felt at different weeks ŌĆó Ultrasound scan in early pregnancy is used to assess the duration of pregnancy and the fetal age.
- 3. Risks of post term pregnancy ŌĆó Increased perinatal mortality and morbidity rates ŌĆó Fetal malnutrition ŌĆó Absence of vernix and lanugo ŌĆó Meconium staining ŌĆó Macrosomia ŌĆó Oligohydramnios ŌĆó Fetal distress
- 4. Management of post term pregnancy ŌĆó Antenatal ŌĆó CTG ŌĆó Amniotic fluid measurement
- 5. Induction of labor ŌĆó It is the stimulation of uterine contractions before the onset of spontaneous labor. It should be associated with ripe cervix and adequate contractions which will bring progressive dilatation of the cervix.
- 6. Maternal indications for induction ŌĆó Prolonged or post term pregnancy ŌĆó Hypertension and preeclampsia ŌĆó Medical problems ŌĆó Placental abruption ŌĆó Previous still birth ŌĆó Unstable lie ŌĆó PROM & SROM ŌĆó Maternal request
- 7. Fetal indication ŌĆó IUGR ŌĆó Decreased fetal movements ŌĆó Rh isoimmunization
- 8. Contraindication of induction of labor ŌĆó Placenta previa ŌĆó Transverse and compound presentations ŌĆó Cord presentation and cord prolapse ŌĆó CPD ŌĆó Severe fetal compromise
- 9. Methods of induction ŌĆó 1) prostaglandins ŌĆó An objective method of assessing whether the cx. Is favorable for induction is Bishop's score ŌĆó Prostaglandins is administered by intravaginal route. Prostaglandin E2 ŌĆó Is available in gel or pessary form ŌĆó They are inserted in the posterior cervical fornix ŌĆó Labor starts 30%- 50% of mothers ŌĆó 2) sweeping or striping of the membranes ŌĆó Prostaglandins in the fetal membrane stimulate the cx to start labor
- 10. BISHOP SCORE
- 11. How to calculate bishop score
- 12. Methods of induction ŌĆó 3) Amniotomy ŌĆó ARM is performed to induce labor only when ŌĆó The cervix is favorable ŌĆó There is well fitting presenting part ŌĆó ARM allows the presenting part to descend pressure on the os increases the level of prostaglandins ŌĆó 4) Oxytocin ŌĆó It is a hormone released from the posterior pituitary gland the receptors of the uterus start to respond to its production at term ŌĆó Side effects of oxytocin ŌĆó Hyperstimulation ŌĆó Postpartum atony ŌĆó Water retention ŌĆó Transient vasodilatation and hypotension
- 13. ŌĆó Maternal well being ŌĆó Observation of vital signs and plotting of partogram ŌĆó Uterine contractions ŌĆó Observe for their frequency duration and strength ŌĆó Continuous CTG assessment ŌĆó Appropriate pain relief ŌĆó Assess progress of labour ŌĆó Fetal well being ŌĆó Watch for signs of fetal distress
- 14. prolonged labour ŌĆó It is defined as labour which exceeds 24 hours or it exceeds 12 hours when labour is established or actively managed ŌĆó Prolonged labour is common among primi and may be caused by a) Inactive uterine action b) CPD c) OP positions Prolonged latent phase The average duration of latent phase of primi is 8.6 hours but if lasted more than 20 hours it is considered prolonged Prolonged active phase When the cervix doesn't dilate at a fixed rate that is 1cm per hour it causes prolonged active phase Factors which contribute are The cervix and the uterus The fetus and mother's pelvis Slow progress of labour is attributed to inefficient uterine action which is usually because of ketoacidosis and the positioning of the mother
- 15. augmentation of labour ŌĆó It is done to correct slow progress of labour ŌĆó It includes amniotomy and administration of oxytocin
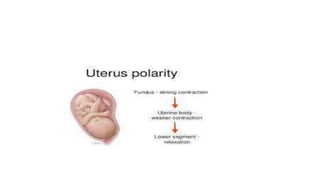
- 16. incoordinate uterine activity ŌĆó This called colicky uterus and it is due to hypertonic inefficient uterine action lacking fundal dominance the contraction begins and lasts longer in the lower uterine segment ŌĆó The coordination of the contraction is completely lacking different areas of the uterus which it contracts independently causing severe pain. ŌĆó Incoordination causes fetal distress and diminished placental perfusion.
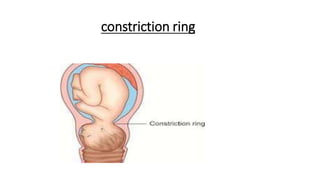
- 21. constriction ring dystocia ŌĆó It is localized spasm of a ring of muscles fibers which occur at the junction of the upper and lower uterine segment ŌĆó It is commonly seen in late first stage and early second stage of labour and it is due to oxytocin.
- 25. management of prolonged labour 1) Give information to the mother and family 2) Comfort and analgesia 3) Observation of the partogram and vital signs 4) Fluid balance intake and output 5) Assessment of progress 6) Fetal well being
- 27. What is the partograph according to WHO? ŌĆó Partograph is a paper-based tool developed by the W.H.O. to monitor labour during pregnancy. The use of the partograph is recommended as an important indicator for monitoring intrapartum care. Partograph includes several labour vitals including cervix dilatation of the mother.
- 28. How do you interpret the partogram? ŌĆó The WHO partograph has two diagonal lines: an alert line and an action line. The alert line goes from 4 to 10 cm and corresponds to an average dilation rate of 1 cm per hour. ŌĆó If the labour curve crosses to the right of this alert line, this means that the dilation is less than 1 cm per hour.
- 29. management of prolonged second stage ŌĆó Vaginal exam should be carried out to confirm ŌĆó Position ŌĆó Attitude ŌĆó Station ŌĆó Presenting part and assessment of fetal heart ŌĆó In the presence of inefficient uterine contractions oxytocin should be started
- 30. cervical dystocia ŌĆó It is due to cervical scaring or congenital structural anomaly where despite good contractions the cervix fails to dilate although it may efface but C/S is necessary to deliver the baby.
- 31. Overt efficient uterine activity or precipitate labour ŌĆó It is due to frequent and strong contractions from the onset of labour resulting in rapid completion of the first and second stage of labour ŌĆó Complications ŌĆó Retained pieces or PPH ŌĆó Fetal hypoxia ŌĆó Precipitate labour can repeat itself in the coming pregnancies
- 32. What is the diagnosis for labor? ŌĆó The diagnosis of labor is simple if the woman has contractions less than 10 minutes apart, a fully effaced cervix, and a few centimeters' dilatation.
- 33. ŌĆó The exact cause of precipitous labor is unknown. It can happen to anyone, but certain factors may increase your chances of a quick birth: ŌĆó Being in your teens or early 20s at the time of delivery ŌĆó Having a previous vaginal birth ŌĆó Preeclampsia, a disorder of high blood pressure and other signs that occur after 20 weeks of pregnancy ŌĆó A baby with a low birth, which refers to any newborn weighing less than 2.5kg ŌĆó Placental abruption, when the placenta
- 34. trial of labour ŌĆó A trial of labour is offered when the mother has a minor degree of CPD. ŌĆó The outcome of labour depends on 1) The effectiveness of the uterine contractions 2) The give of the pelvic joints 3) Flexion of the head 4) The degree of moulding of the head 5) Trial is done when the fetus is cephalic and the progress is assessed by the partogram and the fetal well being
- 35. obstructed labour ŌĆó Labour is said to be obstructed when there is no advancement of the presenting part despite strong uterine contractions ŌĆó Causes of obstructed labour 1) CPD 2) Deep transverse arrest 3) Malpresentations 4) Pelvic masses 5) Fetal abnormalities
- 36. signs and symptom of obstructed labour 1) The presenting part doesn't enter the brim despite good contractions 2) Inefficient cervical dilatation 3) Empty sleeve cervix 4) Elongated ac of fore water 5) Dehydration and ketosis 6) Pyrexia and rapid pulse 7) Decreased urine output 8) Fetal distress 9) Moulding of the uterus around the fetus 10) Formation of retraction ring or BundleŌĆÖs ring 11) On vag. Exam is hot and dry presenting part is high with excessive moulding and formation of caput succedaneum
- 37. Management of obstructed labour ŌĆó Antenatal ŌĆó ABDOMINAL EXAM ŌĆó Labour ŌĆó DECENT VAGINAL EXAM AND CONTRACTIONS
- 38. COMPLICATIONS OF OBSTRUCTED LABOUR ŌĆó Maternal 1) Trauma to the bladder 2) Vesicovaginal fistula 3) Intrauterine infection 4) Urine incontinence 5) Rupture uterus 6) Death of the mother and the fetus
- 39. fetal complication ŌĆó Intrauterine asphyxia ŌĆó Stillbirth ŌĆó Alive but with brain damage ŌĆó Meconium aspiration causing pneumonia ŌĆó Ascending infection due to ruptured membranes