Public Revenue
- 1. PUBLIC REVENUE PUBLIC FINANCE Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No:
- 2. TABLE OF CONTENTS Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: 18  INTRODUCTION  CLASSIFICATION  TAX REVENUE  CANONS OF TAXATION  DIRECT TAXES  MERITS AND DEMERITS  INDIRECT TAXES  MERTIS AND DEMERITS  NON TAX REVENUE  TAX COLLECTION  GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION  BIBLIOGRAPHY
- 3. INTRODUCTION Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: ÔÉò Government needs to perform political, social and economic duties so as to maximize social and economic welfare. In order to perform these duties and functions government requires large amount of resources . ÔÉò These sources of revenue to the governments, viz. Central, State and Local Governments, are called Public Revenues. ÔÉò Development of agriculture, industries & infrastructure, defense, maintenance of law & order, conducting elections, serving public debt & any unforeseen expenses.
- 4. CLASSIFICATION Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll Public Revenue Tax Revenue Direct Taxes Income Tax, Wealth Tax, Corporate Tax, Capital Gains Tax, Gift Tax, Securities Transaction Tax, Estate Duty, Perquisite Tax, Etc Indirect Taxes Sales Tax, Service Tax, VAT, Customs & Octroi Duty, Excise Duty, Professional Tax, Municipal Tax, Entertainment Tax, Education Cess, Etc Non Tax Revenue Profits from PSU, Administrative Fees, Fines & Forfeitures, Hidden Resources, Escheats, Financial Aid, Public Debt, Capital Gains Fund
- 5. TAX REVENUE Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: 18 ÔÉò Tax is a compulsory contribution of the wealth of a person that is to say, it involves a sacrifice on the part of the contributor. ÔÉò Tax Revenue is the income gained by governments through taxation. ÔÉò Who is required to pay tax? Ans: There is a saying that only two things in life are certain: Death and Taxes. Every individual pays tax, either directly or indirectly. This implies that the burden of taxation is on anyone and everyone.
- 6. CANONS OF TAXATION Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: 18 ÔÉò Canon of Equity ÔÉò Canon of Certainty ÔÉò Canon of Convenience ÔÉò Canon of Economy ÔÉò Canon of Productivity ÔÉò Canon of Simplicity ÔÉò Canon of Elasticity ÔÉò Canon of Diversity
- 7. DIRECT TAX Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: ÔÉò Direct tax is a tax imposed and collected directly from person on whom it is legally imposed. ÔÉò The burden of it falls on one person and cannot be shifted to another person. ÔÉò Income Tax, Wealth Tax, Corporate Tax, Capital Gains Tax, Gift Tax, Securities Transaction Tax, Perquisite Tax, Estate Duty are Direct Taxes.
- 8. MERITS V/S DEMERITS OF DIRECT TAXES Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll MERITS DEMERITS Just and Equitable Progressive Elastic Productive Anti-Inflationary Effective Certain Arbitrary Unpopular Inconvenient Evasion Uneconomical Narrow Base Tax on Honesty
- 9. INDIRECT TAXES Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: ÔÉò Indirect Tax is collected by an intermediary from the person who bears the ultimate burden. ÔÉò An indirect tax is one that can be shifted by the taxpayer to someone else. ÔÉò Sales Tax, Service Tax, Value Added Tax (VAT), Customs and Octroi Duties, Excise Duty, Professional Tax, Municipal Tax, Entertainment Tax, Education Cess, Etc. are Indirect Taxes.
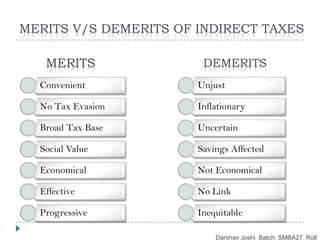
- 10. MERITS V/S DEMERITS OF INDIRECT TAXES Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll MERITS DEMERITS Convenient No Tax Evasion Broad Tax Base Social Value Economical Effective Progressive Unjust Inflationary Uncertain Savings Affected Not Economical No Link Inequitable
- 11. NON TAX REVENUE Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: ÔÉò Non Tax Revenue includes all revenues other than taxes, accruing to the Government. ÔÉò Revenues mobilized from sources other than taxes are called Non-Tax revenue. ÔÉò Profits from PSU, Administrative Fees, Fines & Forfeitures, Hidden Resources, Escheats, Financial Aid - Gifts, Indemnities, Public Debt, Capital Gain Fund are Non Tax Revenues.
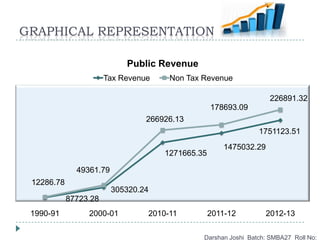
- 12. TAX COLLECTION Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: Particulars 1990-91 2000-01 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 A) Tax Revenue 87723.28 305320.24 1271665.35 1475032.29 1751123.51 1) Direct Taxes 12260.11 71763.57 450822.09 507888.09 578364.02 2) Indirect Taxes 75463.17 233556.67 820843.26 967144.20 1172759.49 B) Non Tax Revenue 12286.78 49361.79 266926.13 178693.09 226891.32 Rs. In Crores In Crores
- 13. GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: 87723.28 305320.24 1271665.35 1475032.29 1751123.51 12286.78 49361.79 266926.13 178693.09 226891.32 1990-91 2000-01 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 Public Revenue Tax Revenue Non Tax Revenue
- 14. CONCLUSION Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No:  Revenue earned by the government is used to incure developmental and non-developmental expenses.  Government should design ways to develop multiple sources of revenue to reduce dependence on any one.  A just and fair tax system should be designed keeping in mind both Smith’s as well as Modern Canons of Taxation.  A good tax system is required for the over all development of any economy.
- 15. BIBLIOGRAPHY Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll No: WEB BASED  Ministry of Finance, Govt. of India: www.finmin.nic.in  Income Tax Dept. : www.incometaxindia.gov.in BOOK BASED  Public Revenue – By Prof. S.N.Chand  Macro Economics – By Prof. Michael Vaz
- 16. THANK YOU Darshan Joshi Batch: SMBA27 Roll