PULMONARY CIRCULATION- Pulmonary artery and vein.pptx
- 1. PULMONARY CIRCULATION Ms. Saili Gaude Asst. Professor Shri Bhumika College of Nursing Parye Goa NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 3. Know pulmonary circulation LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the discussion, students should be able to: Know pulmonary blood pressure Know factors affecting pulmonary blood flow 1 2 3 NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 4. PULMONARY CIRCULATION Pulmonary artery brings deoxygenated blood from right ventricles to lungs Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from lungs to left atria NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 5. PROCESS Superior and inferior vena cava bring deoxygenated blood from all over body to the right atria Right atria send the blood to right ventricles Right ventricles sends it to pulmonary artery via pulmonic valve NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 6. Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood to lungs for oxygenation The pulmonary artery divides into smaller branches in the lungs These branches forms capillary plexus with the alveoli NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 7. Oxygen present in alveoli is exchanged with carbondioxide in blood capillary and the blood is oxygenated The oxygenated blood than enters the pulmonary veins Pulmonary veins carries the oxygenated veins to left atrium of heart NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 8. Left atrium of heart pumps the oxygenated blood to left ventricles Left ventricle pumps the blood to the whole body via aorta NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 9. SALIENT FEATURES OF PULMONARY BLOOD VESSELS NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
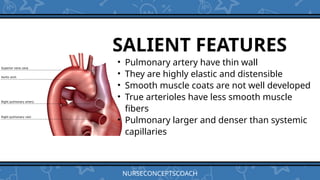
- 10. SALIENT FEATURES • Pulmonary artery have thin wall • They are highly elastic and distensible • Smooth muscle coats are not well developed • True arterioles have less smooth muscle fibers • Pulmonary larger and denser than systemic capillaries NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 11. SALIENT FEATURES • Vascular resistance is less in Pulmonary vessels • It is a low pressure system • Carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs • Pulmonary oxygenated blood from lungs to heart • physiological shunt is present NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 12. PULMONARY BLOOD FLOW Both lungs recieves the whole amount of blood that is pumped out from right ventricles Output per minute is same for both right and left side 5 L approx NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 13. PULMONARY BLOOD PRESSURE Systolic pressure - 25mmHg Diastolic pressure - 10mmHg Mean arterial pressure - 15mmHg Capillary pressure - 7mmHg Pulmonary vessels are very distensible thus their pressure is lower than systemic pressure NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 14. REGULATION OF PULMONARY BLOOD FLOW NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 15. 1.CARDIAC OUTPUT Pulmonary blood flow = Cardiac output Cardiac output Volume of blood pumped out per ventricle per minute. Cardiac output is influenced by • Venous return • Force of contraction • Rate of contraction • Peripheral resistance NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 16. 2. VASCULAR RESISTANCE Pulmonary blood flow = 1/ Pulmonary vascular resistance Inspiration Veins distend causing decrease in Vascular resistance and increase in blood flow Expiration Veins contracts increasing vascular resistance and decrease in blood flow Vascular resistance :the resistance that must be overcome for blood to flow through the circulatory system. NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 17. 3. NERVOUS FACTOR Sympathetic nervous system increases vascular resistance and decreases blood flow Parasympathetic nervous system decreases vascular resistance and increases blood flow NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
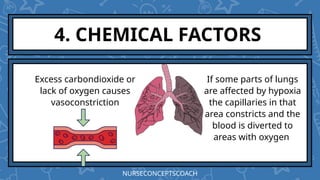
- 18. 4. CHEMICAL FACTORS Excess carbondioxide or lack of oxygen causes vasoconstriction If some parts of lungs are affected by hypoxia the capillaries in that area constricts and the blood is diverted to areas with oxygen NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 19. 5. GRAVITY & HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE Hydrostatic pressure The hydrostatic pressure difference between the top and bottom of the lungs causes blood to flow more at the bottom. This is because the pressure in the vessels at the top of the lungs may be lower than the alveolar pressure, causing the vessels to collapse NURSECONCEPTSCOACH
- 20. ZONES OF BLOOD FLOW Zone 1 Zone 2 Zone 3 Alveolar pressure > Pulmonary arterial pressure Alveolar pressure < Pulmonary arterial pressure but Alveolar pressure > venous pressure Venous pressure > alveolar pressure No blood flow Blood flow in pulsation Continous blood flow Zone 1 - not usually present in healthy lungs Zone 2 - part of lungs 3cm above heart Zone 3 - majority of lungs