pulse and digital circuits file dadadesd
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes10 views
/slideshow/low-pass-filters/50443558
1 of 19
Download to read offline







Recommended
Pulse & Linear Integrated Circuits



Pulse & Linear Integrated CircuitsSRAVANIP22
╠²
This document outlines a course on pulse and linear integrated circuits taught at Matrusri Engineering College. The course objectives are to analyze linear and non-linear wave shaping circuits, multivibrators, operational amplifiers, and various data converter circuits. The course is divided into units that will cover linear and non-linear wave shaping, attenuators, clipping circuits, clamping circuits, and applications of operational amplifiers and timers. Students will analyze circuit responses to different input signals and learn to design circuits using transistors and operational amplifiers.Pulse & Digital Circuits



Pulse & Digital CircuitsSRAVANIP22
╠²
The document provides information about the Pulse and Digital Circuits course at Matrusri Engineering College. It includes the course objectives, which are to analyze various pulse circuits and understand operational amplifiers. It also lists the course outcomes, such as being able to design multivibrators and analyze characteristics of operational amplifiers. The document then covers several topics that will be taught in the course, including linear wave shaping circuits, attenuators, and nonlinear wave shaping circuits like clippers and clampers.Pdc ppt



Pdc pptGirish Pechetti
╠²
This document provides an overview of linear and non-linear wave shaping. It discusses topics such as analog and digital signals, pulse definitions, periodic waveforms, linear wave shaping circuits including high pass RC circuits and low pass RC circuits. It also covers non-linear wave shaping including different types of clippers such as unbiased clippers, series positive clippers, and their working mechanisms. The document is intended to introduce fundamental concepts of signal processing.ADE UNIT-I.pptx



ADE UNIT-I.pptxKUMARS641064
╠²
This document contains a syllabus for a course on Analog and Digital Electronics. The syllabus covers 5 units: Diodes and Applications, Bipolar Junction Transistors, Combinational Logic Circuits, Field Effect Transistors and Digital Circuits, and Sequential Logic Circuits. Unit I focuses on diode characteristics such as I-V curves and applications like rectifiers. Diode types covered include PN junction diodes, Zener diodes, and photo diodes. Rectifier circuits such as half wave, full wave, and bridge rectifiers are also discussed along with capacitor filters.Oscillator



OscillatorSedhuMadhavan7
╠²
Oscillators convert DC to AC signals using a feedback loop that sustains oscillations. Common oscillator circuits include LC, RC, quartz, and relaxation oscillators. The Hartley oscillator uses a tapped coil and capacitor in a feedback loop to generate radio frequencies. The Colpitts oscillator also uses an LC tank circuit but with capacitors in the feedback path. The Franklin oscillator uses two transistors and an LC circuit, with each transistor inverting the phase to sustain oscillations. The Wein bridge oscillator is an RC circuit that produces sine waves with high quality resonance and tuning capabilities. Oscillators are used to generate signals for applications like radio transmission, testing equipment, and sensors.oscillator



oscillatorTaslima Yasmin Tarin
╠²
An oscillator is an electronic circuit that generates an alternating current signal through feedback and amplification. The oscillator contains a feedback path where part of the output signal is fed back to the input. For oscillation to be sustained, the feedback signal must be larger than and in phase with the input signal. Common waveforms produced by oscillators include sinusoidal and square waves. Oscillators are classified by the waveform type and frequency range. Sine wave oscillators use inductors and capacitors (LC oscillators) or crystals to control frequency, while relaxation oscillators produce square waves. Oscillators are essential components in electronic devices and are used as stable frequency sources in applications like timers, calculators, and oscilloscopes.Basic Electronics by The Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology



Basic Electronics by The Veer Surendra Sai University of TechnologyMounerSaleh1
╠²
This note explains the following topics: Signals, Linear Wave Shaping Circuits, Properties of Semiconductors, Diodes, Bipolar junction Transistor, Feedback Amplifiers and Oscillators, Field Effect Transistors, Operational Amplifiers, Digital Fundamentals, Electronic Instruments.
Full Wave Bridge Rectifier simulation (with/without filter capacitor)



Full Wave Bridge Rectifier simulation (with/without filter capacitor)Jaspreet Singh
╠²
1) The document describes a full wave bridge rectifier circuit with and without a filter capacitor.
2) It explains how the circuit works by using 4 diodes to convert an AC input voltage into a DC output voltage that only contains the positive half of the sinusoidal wave.
3) The summary compares the results with and without a filter capacitor, noting that the capacitor reduces the ripple in the output when used.Full Wave Bridge Rectifier simulation (with/without filter capacitor)



Full Wave Bridge Rectifier simulation (with/without filter capacitor)Jaspreet Singh
╠²
1) The document describes a full wave bridge rectifier circuit with and without a filter capacitor.
2) It explains how the circuit works by using 4 diodes to convert an AC input voltage into a DC output voltage that only contains the positive half of the sinusoidal wave.
3) The summary compares the results with and without a filter capacitor, noting that the capacitor reduces the ripple in the output when used.A new precision peak detector full wave rectifier



A new precision peak detector full wave rectifierVishal kakade
╠²
This document summarizes a research paper that proposes a new precision peak detector/full-wave rectifier circuit based on dual-output current conveyors. The key points are:
1) The proposed circuit uses MOS transistors, a phase shifter, and dual-output current conveyors to generate a DC output voltage equal to the peak amplitude of the input sinusoidal signal over a wide frequency range.
2) An all-pass filter is used to shift the phase of the input signal by 90 degrees. This allows the circuit to fully rectify both halves of the sinusoidal wave.
3) Simulation results show the circuit has very low ripple voltage and harmonic distortion compared to existing techniques, making itKTU -EET 203 Module 5 Transducers and Digital instruments including modern re...



KTU -EET 203 Module 5 Transducers and Digital instruments including modern re...sindhusudhir
╠²
Transducers and Digital Instruments: Overview
Transducers
A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy into another, typically transforming physical parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, or light) into electrical signals for measurement and analysis. Transducers are essential components in instrumentation and measurement systems.
Types of Transducers
Based on Energy Conversion:
Active Transducers: Generate electrical signals directly from the input (e.g., thermocouples, piezoelectric sensors).
Passive Transducers: Require an external power source to operate (e.g., resistive, capacitive, and inductive transducers).
Based on Application:
Temperature Sensors: Thermistors, RTDs, thermocouples.
Pressure Sensors: Strain gauges, piezoelectric pressure transducers.
Position Sensors: Potentiometers, LVDTs (Linear Variable Differential Transformers).
Optical Sensors: Photodiodes, phototransistors.
Characteristics of Transducers
Sensitivity: Output signal per unit of input.
Linearity: Proportionality of output to input.
Range: Maximum and minimum input limits.
Accuracy and Precision: Closeness to true value and reproducibility.
Frequency Response: Ability to follow input changes over time.
Digital Instruments
Digital instruments use electronic circuits to measure, process, and display physical quantities digitally. They have largely replaced analog instruments due to their higher accuracy, easier readability, and better data processing capabilities.
Features of Digital Instruments
High Accuracy: Minimized manual errors and noise sensitivity.
Direct Readout: Digital displays for clarity.
Data Storage and Transmission: Capability to store and communicate data electronically.
Automation: Integration with automated systems for monitoring and control.
Examples of Digital Instruments
Multimeters: Measure voltage, current, and resistance digitally.
Oscilloscopes: Display and analyze voltage waveforms in real time.
Digital Thermometers: Use digital displays to show temperature readings.
Digital Pressure Gauges: Provide accurate pressure readings with digital output.
Modern Recording and Display Instruments
Data Loggers:
Collect and store data over time.
Used in environmental monitoring, industrial processes, and research.
Digital Oscilloscopes:
Provide precise waveform analysis and digital storage capabilities.
Equipped with advanced signal processing features.
Electronic Chart Recorders:
Replace mechanical chart recorders by digitizing signals for storage and visualization.
Touchscreen Interfaces:
Widely used in medical devices, industrial panels, and laboratory equipment.
Smart Sensors and IoT Devices:
Include built-in processing and communication capabilities.
Often integrated with cloud-based systems for real-time monitoring and analytics.
Advantages of Modern Instruments
Enhanced data accuracy and precision.
Real-time monitoring and analytics.
Seamless integration with networks and automated systems.
Analog VLSI CIrcuits_beforeMID_merged.pdf



Analog VLSI CIrcuits_beforeMID_merged.pdfssuser822da11
╠²
This document discusses analog VLSI design and MOSFETs. It introduces analog VLSI design as the process of designing and fabricating integrated circuits that primarily involve analog electronic components and circuits on a single semiconductor chip. Analog circuits deal with continuous signals like voltages and currents, unlike digital circuits that work with discrete 0s and 1s. The document then discusses MOSFET device characteristics, explaining the key regions of operation and their corresponding I-V characteristics in common source configuration. It emphasizes that understanding MOSFET behavior is important for analog circuit design.Network analysis of rf and microwave circuits



Network analysis of rf and microwave circuitsShankar Gangaju
╠²
This document discusses microwave network analysis and two-port network analysis. It begins by defining a microwave network as consisting of microwave devices and components coupled by transmission lines. It then discusses that at microwave frequencies, circuit analysis techniques like KCL and KVL cannot be used and S-parameters provide an alternative. The document defines S-parameters as a way to characterize networks using normalized power waves rather than voltages and currents. It provides properties and definitions of S-parameters for two-port networks, including what S11, S12, S21, and S22 represent. It also discusses uses of S-parameters and scattering matrices for modeling networks.UNIT_5 PPT-MBM.pptx



UNIT_5 PPT-MBM.pptxMadhuriMulik1
╠²
The document discusses various solid state microwave devices including varactor diodes, PIN diodes, Gunn diodes, and IMPATT diodes. It provides details on their operating principles and applications. Varactor diodes exploit the voltage-variable capacitance of a reverse biased PN junction and are used in voltage controlled oscillators and filters. PIN diodes act as switches and attenuators in microwave systems. Gunn diodes rely on negative differential resistance and are commonly used to generate microwave signals from 1-100 GHz. IMPATT diodes use avalanche breakdown and transit time delay to achieve negative resistance for oscillation at microwave frequencies.ŌĆ£Microcontroller Based Substation Monitoring system with gsm modemŌĆØ.



ŌĆ£Microcontroller Based Substation Monitoring system with gsm modemŌĆØ.Priya Rachakonda
╠²
ŌĆó The system is used for transmitting the message to predefined number about the
status of electrical parameters such as voltage, current, temperature etc., to improve
the quality of power.
ŌĆó Studied about the protection, monitoring and control of a power system.Oscillators



OscillatorsPrasad Deshpande
╠²
An oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces repetitive waveforms without an external input signal. It uses positive feedback to sustain oscillations, with the frequency determined by circuit components like inductors and capacitors. Common types include sinusoidal oscillators that produce sine waves, and relaxation oscillators that produce non-sinusoidal waves like square waves. Oscillators are essential components in many electronic devices and systems to generate stable frequency signals.TLW_Unit I material pdf.ppt



TLW_Unit I material pdf.pptKanmaniRajamanickam
╠²
This document discusses transmission lines and their parameters. It begins by introducing common types of transmission lines including two-wire lines, coaxial cables, and waveguides. It then describes how a transmission line can be modeled as a series of lumped inductors and shunt capacitors, known as the transmission line parameters. These parameters include the series resistance R', inductance L', shunt conductance G', and capacitance C' per unit length. Using these parameters, expressions are derived for the characteristic impedance Z0 and propagation constant ╬│ of the transmission line.Electronic Components



Electronic ComponentsArnab Bhaumik
╠²
This document provides an overview of various electronic components presented by Arnab Bhaumik. It discusses both active components like transistors and integrated circuits that require external power as well as passive components like resistors, capacitors, and transformers that cannot supply their own power. For each component, the document outlines their basic functionality and symbol. Diodes are described as only allowing current to flow in one direction, with types including PN junction, Zener, and LEDs. Transistors are categorized as bipolar or field-effect and are used to amplify signals. Transformers transfer energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Integrated circuits can contain millions of components on a single semiconductor chip.Ece syllabus



Ece syllabusrakesh45_kumar
╠²
The document outlines the course details for several electronics courses, including Analog Electronics, Digital Electronics, Signal and Systems, Electromagnetic Field Theory, and Linear Control Systems. Some key topics covered across the courses include high frequency transistors, large signal amplifiers, multistage amplifiers, feedback in amplifiers, oscillators, regulated power supplies, number systems, combinational and sequential logic circuits, D/A and A/D converters, semiconductor memories, logic families, system and signal analysis, random signal theory, transmission through linear networks, guided waves, transmission lines, waveguides, modelling of linear systems, time and frequency domain analysis, root locus, compensation networks, and control components.Webinar ║▌║▌▀Żs: Measurements and Analysis for Switched-mode Power Designs



Webinar ║▌║▌▀Żs: Measurements and Analysis for Switched-mode Power Designsteledynelecroy
╠²
This webinar covers the measurements of interest for designers of switched-mode power conversion circuits and devices. With the goal of high efficient and reliable designs, we review the acquisition of voltage and current, their relationship in switched-mode power conversion circuits.
We review specific power circuit performance areas including the analysis of power device switching losses, conduction losses, dynamic on-resistance, control loop response, power quality, conducted emissions, best practices for probing power circuits, and power rail integrity measurements.Basic of Diode Rectifiers



Basic of Diode Rectifiersssuser4b487e1
╠²
This document provides an overview of rectifiers. It discusses the basics of half-wave and full-wave rectifiers. For half-wave rectifiers, it notes they produce more ripple, have lower efficiency around 40%, and utilize the transformer less efficiently. Full-wave rectifiers have higher efficiency of around 81% and produce less ripple by using both halves of the AC cycle. The document also discusses rectifier applications, components like diodes and transformers, and how to reduce ripple through the use of filters. The key learning objectives are to classify rectifier types, assemble and test rectifier circuits, and select the proper rectifier for different applications.Design and testing of Voltage Regulator using 723



Design and testing of Voltage Regulator using 723HaleshMREC
╠²
Design and testing of Voltage Regulator using 723Transistor applications



Transistor applicationsHarshitParkar6677
╠²
Electrical current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and inductance are a few of the basic elements of electronics and radio. Apart from current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and inductance, there are many other interesting elements to electronic technology. ... Use Electronics Notes to learn electronics online.Transistor applications (2)



Transistor applications (2)HarshitParkar6677
╠²
Electrical current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and inductance are a few of the basic elements of electronics and radio. Apart from current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and inductance, there are many other interesting elements to electronic technology. ... Use Electronics Notes to learn electronics online.Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdf



Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdfARENCOS
╠²
Biophilic design is emerging as a key approach to enhancing well-being by integrating natural elements into residential architecture. In Crete, where the landscape is rich with breathtaking sea views, lush olive groves, and dramatic mountains, biophilic design principles can be seamlessly incorporated to create healthier, more harmonious living environments.
More Related Content
Similar to pulse and digital circuits file dadadesd (20)
Full Wave Bridge Rectifier simulation (with/without filter capacitor)



Full Wave Bridge Rectifier simulation (with/without filter capacitor)Jaspreet Singh
╠²
1) The document describes a full wave bridge rectifier circuit with and without a filter capacitor.
2) It explains how the circuit works by using 4 diodes to convert an AC input voltage into a DC output voltage that only contains the positive half of the sinusoidal wave.
3) The summary compares the results with and without a filter capacitor, noting that the capacitor reduces the ripple in the output when used.A new precision peak detector full wave rectifier



A new precision peak detector full wave rectifierVishal kakade
╠²
This document summarizes a research paper that proposes a new precision peak detector/full-wave rectifier circuit based on dual-output current conveyors. The key points are:
1) The proposed circuit uses MOS transistors, a phase shifter, and dual-output current conveyors to generate a DC output voltage equal to the peak amplitude of the input sinusoidal signal over a wide frequency range.
2) An all-pass filter is used to shift the phase of the input signal by 90 degrees. This allows the circuit to fully rectify both halves of the sinusoidal wave.
3) Simulation results show the circuit has very low ripple voltage and harmonic distortion compared to existing techniques, making itKTU -EET 203 Module 5 Transducers and Digital instruments including modern re...



KTU -EET 203 Module 5 Transducers and Digital instruments including modern re...sindhusudhir
╠²
Transducers and Digital Instruments: Overview
Transducers
A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy into another, typically transforming physical parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, or light) into electrical signals for measurement and analysis. Transducers are essential components in instrumentation and measurement systems.
Types of Transducers
Based on Energy Conversion:
Active Transducers: Generate electrical signals directly from the input (e.g., thermocouples, piezoelectric sensors).
Passive Transducers: Require an external power source to operate (e.g., resistive, capacitive, and inductive transducers).
Based on Application:
Temperature Sensors: Thermistors, RTDs, thermocouples.
Pressure Sensors: Strain gauges, piezoelectric pressure transducers.
Position Sensors: Potentiometers, LVDTs (Linear Variable Differential Transformers).
Optical Sensors: Photodiodes, phototransistors.
Characteristics of Transducers
Sensitivity: Output signal per unit of input.
Linearity: Proportionality of output to input.
Range: Maximum and minimum input limits.
Accuracy and Precision: Closeness to true value and reproducibility.
Frequency Response: Ability to follow input changes over time.
Digital Instruments
Digital instruments use electronic circuits to measure, process, and display physical quantities digitally. They have largely replaced analog instruments due to their higher accuracy, easier readability, and better data processing capabilities.
Features of Digital Instruments
High Accuracy: Minimized manual errors and noise sensitivity.
Direct Readout: Digital displays for clarity.
Data Storage and Transmission: Capability to store and communicate data electronically.
Automation: Integration with automated systems for monitoring and control.
Examples of Digital Instruments
Multimeters: Measure voltage, current, and resistance digitally.
Oscilloscopes: Display and analyze voltage waveforms in real time.
Digital Thermometers: Use digital displays to show temperature readings.
Digital Pressure Gauges: Provide accurate pressure readings with digital output.
Modern Recording and Display Instruments
Data Loggers:
Collect and store data over time.
Used in environmental monitoring, industrial processes, and research.
Digital Oscilloscopes:
Provide precise waveform analysis and digital storage capabilities.
Equipped with advanced signal processing features.
Electronic Chart Recorders:
Replace mechanical chart recorders by digitizing signals for storage and visualization.
Touchscreen Interfaces:
Widely used in medical devices, industrial panels, and laboratory equipment.
Smart Sensors and IoT Devices:
Include built-in processing and communication capabilities.
Often integrated with cloud-based systems for real-time monitoring and analytics.
Advantages of Modern Instruments
Enhanced data accuracy and precision.
Real-time monitoring and analytics.
Seamless integration with networks and automated systems.
Analog VLSI CIrcuits_beforeMID_merged.pdf



Analog VLSI CIrcuits_beforeMID_merged.pdfssuser822da11
╠²
This document discusses analog VLSI design and MOSFETs. It introduces analog VLSI design as the process of designing and fabricating integrated circuits that primarily involve analog electronic components and circuits on a single semiconductor chip. Analog circuits deal with continuous signals like voltages and currents, unlike digital circuits that work with discrete 0s and 1s. The document then discusses MOSFET device characteristics, explaining the key regions of operation and their corresponding I-V characteristics in common source configuration. It emphasizes that understanding MOSFET behavior is important for analog circuit design.Network analysis of rf and microwave circuits



Network analysis of rf and microwave circuitsShankar Gangaju
╠²
This document discusses microwave network analysis and two-port network analysis. It begins by defining a microwave network as consisting of microwave devices and components coupled by transmission lines. It then discusses that at microwave frequencies, circuit analysis techniques like KCL and KVL cannot be used and S-parameters provide an alternative. The document defines S-parameters as a way to characterize networks using normalized power waves rather than voltages and currents. It provides properties and definitions of S-parameters for two-port networks, including what S11, S12, S21, and S22 represent. It also discusses uses of S-parameters and scattering matrices for modeling networks.UNIT_5 PPT-MBM.pptx



UNIT_5 PPT-MBM.pptxMadhuriMulik1
╠²
The document discusses various solid state microwave devices including varactor diodes, PIN diodes, Gunn diodes, and IMPATT diodes. It provides details on their operating principles and applications. Varactor diodes exploit the voltage-variable capacitance of a reverse biased PN junction and are used in voltage controlled oscillators and filters. PIN diodes act as switches and attenuators in microwave systems. Gunn diodes rely on negative differential resistance and are commonly used to generate microwave signals from 1-100 GHz. IMPATT diodes use avalanche breakdown and transit time delay to achieve negative resistance for oscillation at microwave frequencies.ŌĆ£Microcontroller Based Substation Monitoring system with gsm modemŌĆØ.



ŌĆ£Microcontroller Based Substation Monitoring system with gsm modemŌĆØ.Priya Rachakonda
╠²
ŌĆó The system is used for transmitting the message to predefined number about the
status of electrical parameters such as voltage, current, temperature etc., to improve
the quality of power.
ŌĆó Studied about the protection, monitoring and control of a power system.Oscillators



OscillatorsPrasad Deshpande
╠²
An oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces repetitive waveforms without an external input signal. It uses positive feedback to sustain oscillations, with the frequency determined by circuit components like inductors and capacitors. Common types include sinusoidal oscillators that produce sine waves, and relaxation oscillators that produce non-sinusoidal waves like square waves. Oscillators are essential components in many electronic devices and systems to generate stable frequency signals.TLW_Unit I material pdf.ppt



TLW_Unit I material pdf.pptKanmaniRajamanickam
╠²
This document discusses transmission lines and their parameters. It begins by introducing common types of transmission lines including two-wire lines, coaxial cables, and waveguides. It then describes how a transmission line can be modeled as a series of lumped inductors and shunt capacitors, known as the transmission line parameters. These parameters include the series resistance R', inductance L', shunt conductance G', and capacitance C' per unit length. Using these parameters, expressions are derived for the characteristic impedance Z0 and propagation constant ╬│ of the transmission line.Electronic Components



Electronic ComponentsArnab Bhaumik
╠²
This document provides an overview of various electronic components presented by Arnab Bhaumik. It discusses both active components like transistors and integrated circuits that require external power as well as passive components like resistors, capacitors, and transformers that cannot supply their own power. For each component, the document outlines their basic functionality and symbol. Diodes are described as only allowing current to flow in one direction, with types including PN junction, Zener, and LEDs. Transistors are categorized as bipolar or field-effect and are used to amplify signals. Transformers transfer energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Integrated circuits can contain millions of components on a single semiconductor chip.Ece syllabus



Ece syllabusrakesh45_kumar
╠²
The document outlines the course details for several electronics courses, including Analog Electronics, Digital Electronics, Signal and Systems, Electromagnetic Field Theory, and Linear Control Systems. Some key topics covered across the courses include high frequency transistors, large signal amplifiers, multistage amplifiers, feedback in amplifiers, oscillators, regulated power supplies, number systems, combinational and sequential logic circuits, D/A and A/D converters, semiconductor memories, logic families, system and signal analysis, random signal theory, transmission through linear networks, guided waves, transmission lines, waveguides, modelling of linear systems, time and frequency domain analysis, root locus, compensation networks, and control components.Webinar ║▌║▌▀Żs: Measurements and Analysis for Switched-mode Power Designs



Webinar ║▌║▌▀Żs: Measurements and Analysis for Switched-mode Power Designsteledynelecroy
╠²
This webinar covers the measurements of interest for designers of switched-mode power conversion circuits and devices. With the goal of high efficient and reliable designs, we review the acquisition of voltage and current, their relationship in switched-mode power conversion circuits.
We review specific power circuit performance areas including the analysis of power device switching losses, conduction losses, dynamic on-resistance, control loop response, power quality, conducted emissions, best practices for probing power circuits, and power rail integrity measurements.Basic of Diode Rectifiers



Basic of Diode Rectifiersssuser4b487e1
╠²
This document provides an overview of rectifiers. It discusses the basics of half-wave and full-wave rectifiers. For half-wave rectifiers, it notes they produce more ripple, have lower efficiency around 40%, and utilize the transformer less efficiently. Full-wave rectifiers have higher efficiency of around 81% and produce less ripple by using both halves of the AC cycle. The document also discusses rectifier applications, components like diodes and transformers, and how to reduce ripple through the use of filters. The key learning objectives are to classify rectifier types, assemble and test rectifier circuits, and select the proper rectifier for different applications.Design and testing of Voltage Regulator using 723



Design and testing of Voltage Regulator using 723HaleshMREC
╠²
Design and testing of Voltage Regulator using 723Transistor applications



Transistor applicationsHarshitParkar6677
╠²
Electrical current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and inductance are a few of the basic elements of electronics and radio. Apart from current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and inductance, there are many other interesting elements to electronic technology. ... Use Electronics Notes to learn electronics online.Transistor applications (2)



Transistor applications (2)HarshitParkar6677
╠²
Electrical current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and inductance are a few of the basic elements of electronics and radio. Apart from current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and inductance, there are many other interesting elements to electronic technology. ... Use Electronics Notes to learn electronics online.Recently uploaded (20)
Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdf



Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdfARENCOS
╠²
Biophilic design is emerging as a key approach to enhancing well-being by integrating natural elements into residential architecture. In Crete, where the landscape is rich with breathtaking sea views, lush olive groves, and dramatic mountains, biophilic design principles can be seamlessly incorporated to create healthier, more harmonious living environments.
Renewable-Energy-Powering-Mozambiques-Economic-Growth.pptx



Renewable-Energy-Powering-Mozambiques-Economic-Growth.pptxRofino Licuco
╠²
Mozambique, a country with vast natural resources and immense potential, nevertheless faces several economic challenges, including high unemployment, limited access to energy, and an unstable power supply. Underdeveloped infrastructure has slowed the growth of industry and hampered peopleŌĆÖs entrepreneurial ambitions, leaving many regions in the darkŌĆöliterally and figuratively.
https://www.rofinolicuco.net/blog/how-renewable-energy-can-help-mozambique-grow-its-economyCloud Cost Optimization for GCP, AWS, Azure



Cloud Cost Optimization for GCP, AWS, Azurevinothsk19
╠²
Reduce Cloud Waste across AWS, GCP, Azure and Optimize Cloud Cost with a structured approach and improve your bottomline or profitability. Decide whether you want to outsource or manage it in house. Soil Properties and Methods of Determination



Soil Properties and Methods of DeterminationRajani Vyawahare
╠²
This PPT covers the index and engineering properties of soil. It includes details on index properties, along with their methods of determination. Various important terms related to soil behavior are explained in detail. The presentation also outlines the experimental procedures for determining soil properties such as water content, specific gravity, plastic limit, and liquid limit, along with the necessary calculations and graph plotting. Additionally, it provides insights to understand the importance of these properties in geotechnical engineering applications.AIR FILTER system in internal combustion engine system.ppt



AIR FILTER system in internal combustion engine system.pptthisisparthipan1
╠²
air filter system in ic engine Environmental Product Declaration - Uni Bell



Environmental Product Declaration - Uni BellManishPatel169454
╠²
The Uni-Bell PVC Pipe Association (PVCPA) has published the first North American industry-wide environmental product declaration (EPD) for water and sewer piping, and it has been verified by NSF Sustainability, a division of global public health organization NSF International.Failover System in Cloud Computing System



Failover System in Cloud Computing SystemHitesh Mohapatra
╠²
Uses established clustering technologies for redundancy
Boosts availability and reliability of IT resources
Automatically transitions to standby instances when active resources become unavailable
Protects mission-critical software and reusable services from single points of failure
Can cover multiple geographical areas
Hosts redundant implementations of the same IT resource at each location
Relies on resource replication for monitoring defects and unavailability conditionsTaykon-Kalite belgeleri



Taykon-Kalite belgeleriTAYKON
╠²
Kalite Politikam─▒z
Taykon ├ćelik i├¦in kalite, hayallerinizi bizlerle payla┼¤t─▒─¤─▒n─▒z an ba┼¤lar. Proje ├¦iziminden detaylar─▒n ├¦├Čz├╝m├╝ne, detaylar─▒n ├¦├Čz├╝m├╝nden ├╝retime, ├╝retimden montaja, montajdan teslime hayallerinizin ger├¦ekle┼¤ti─¤ini g├Črd├╝─¤├╝n├╝z ana kadar ge├¦en t├╝m a┼¤amalar─▒, ├¦al─▒┼¤anlar─▒, t├╝m teknik donan─▒m ve ├¦evreyi i├¦ine al─▒r KAL─░TE.Biases, our brain and software development



Biases, our brain and software developmentMatias Iacono
╠²
Quick presentation about cognitive biases, classic psychological researches and quite new papers that displays how those biases might be impacting software developers.Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in digital frensics.pdf



Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in digital frensics.pdfAbhijit Bodhe
╠²
This topic contain information about Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in cyber and digital awarenessINVESTIGATION OF PUEA IN COGNITIVE RADIO NETWORKS USING ENERGY DETECTION IN D...



INVESTIGATION OF PUEA IN COGNITIVE RADIO NETWORKS USING ENERGY DETECTION IN D...csijjournal
╠²
Primary User Emulation Attack (PUEA) is one of the major threats to the spectrum sensing in cognitive
radio networks. This paper studies the PUEA using energy detection that is based on the energy of the
received signal. It discusses the impact of increasing the number of attackers on the performance of
secondary user. Moreover, studying how the malicious user can emulate the Primary User (PU) signal is
made. This is the first analytical method to study PUEA under a different number of attackers. The
detection of the PUEA increases with increasing the number of attackers and decreases when changing the
channel from lognormal to Rayleigh fading.Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdf



Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdfAbhinandanMishra30
╠²
Wireless technology used in chargerIoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptx



IoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptxatharvapardeshi03
╠²
IoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptxTurbocor Product and Technology Review.pdf



Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdfTotok Sulistiyanto
╠²
High Efficiency Chiller System in HVACCommon Network Architecture:X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): fram...



Common Network Architecture:X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): fram...SnehPrasad2
╠²
X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): frame format and specifications, Wireless LANŌĆÖs ŌĆō 802.11x, 802.3 Bluetooth etc.
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-1 and Unit-2



ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-1 and Unit-2prasadmutkule1
╠²
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-1 and Unit-2ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-2 and Unit-3



ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-2 and Unit-3prasadmutkule1
╠²
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-2 and Unit-3pulse and digital circuits file dadadesd
- 1. East Africa University DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME: PULSE & DIGITAL CIRCUITS LECTURER NAME: Abdulkadir. M . Daar
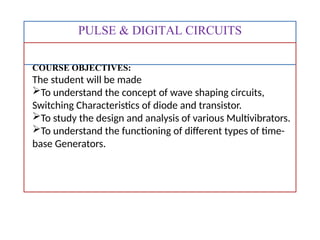
- 2. PULSE & DIGITAL CIRCUITS COURSE OBJECTIVES: The student will be made ’āśTo understand the concept of wave shaping circuits, Switching Characteristics of diode and transistor. ’āśTo study the design and analysis of various Multivibrators. ’āśTo understand the functioning of different types of time- base Generators.
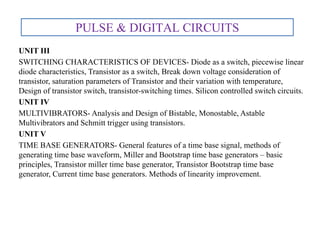
- 3. UNIT I LINEAR WAVESHAPING- High pass, low pass RC circuits, their response for sinusoidal, step, pulse, square and ramp inputs. RC network as differentiator and integrator, attenuators, its applications in CRO probe, RL and RLC circuits and their response for step input, Ringing circuit. UNIT II NON-LINEAR WAVE SHAPING- Diode clippers, Transistor clippers, clipping at two independent levels, Comparators, applications of voltage comparators, clamping operation, clamping circuits taking source and diode resistances into account clamping circuit theorem , practical clamping circuits, effect of diode characteristics on clamping voltage, Synchronized clamping PULSE & DIGITAL CIRCUITS
- 4. UNIT III SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS OF DEVICES- Diode as a switch, piecewise linear diode characteristics, Transistor as a switch, Break down voltage consideration of transistor, saturation parameters of Transistor and their variation with temperature, Design of transistor switch, transistor-switching times. Silicon controlled switch circuits. UNIT IV MULTIVIBRATORS- Analysis and Design of Bistable, Monostable, Astable Multivibrators and Schmitt trigger using transistors. UNIT V TIME BASE GENERATORS- General features of a time base signal, methods of generating time base waveform, Miller and Bootstrap time base generators ŌĆō basic principles, Transistor miller time base generator, Transistor Bootstrap time base generator, Current time base generators. Methods of linearity improvement. PULSE & DIGITAL CIRCUITS
- 5. MODULE-I: Linear wave shaping CONTENTS: ’āś High pass RC circuits with Step, Pulse, Square wave and Ramp inputs ’āś Low pass RC circuits with Step, Pulse, Square wave and Ramp inputs ’āś High pass RC circuit as Differentiator ’āś Low pass RC circuit as Integrator OUTCOMES: ’āśTo derive the response of high-pass and low-pass RC circuits to different types of inputs like Sinusoidal, pulse, step, square, ramp signals. ’āśTo describe the application of high pass and low pass circuit as Differentiator and integrator respectively.
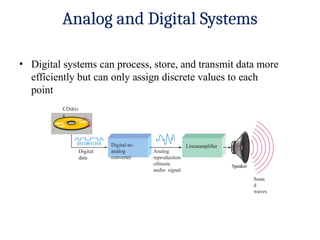
- 6. Analog and Digital Systems ŌĆó Digital systems can process, store, and transmit data more efficiently but can only assign discrete values to each point CDdriv e 10110011101 Digital data Analog reproduction ofmusic audio signal Speaker Soun d waves Digital-to- analog converter Linearamplifier
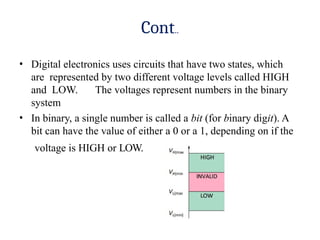
- 7. Cont.. ŌĆó Digital electronics uses circuits that have two states, which are represented by two different voltage levels called HIGH and LOW. The voltages represent numbers in the binary system ŌĆó In binary, a single number is called a bit (for binary digit). A bit can have the value of either a 0 or a 1, depending on if the voltage is HIGH or LOW.
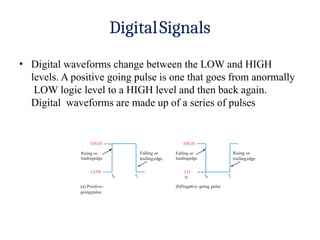
- 8. DigitalSignals ŌĆó Digital waveforms change between the LOW and HIGH levels. A positive going pulse is one that goes from anormally LOW logic level to a HIGH level and then back again. Digital waveforms are made up of a series of pulses Falling or leadingedge (b)NegativeŌĆōgoing pulse HIGH Rising or trailingedge LO W (a) PositiveŌĆō goingpulse HIGH Rising or leadingedge Falling or trailingedge LOW t0 t1 t0 t1
- 10. Periodic Pulse Waveforms ŌĆó Periodic pulse waveforms are composed of pulses that repeats in a fixed interval called the period. ŌĆó The frequency is the rate it repeats and is measured in hertz. The clock is a basic timing signal that is an example of a periodic wave. What is the period of a repetitive wave if f = 3.2 GHz?
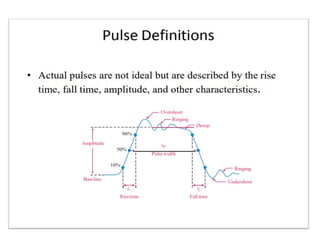
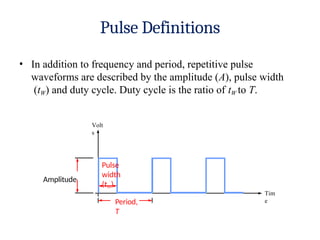
- 11. Pulse Definitions ŌĆó In addition to frequency and period, repetitive pulse waveforms are described by the amplitude (A), pulse width (tW) and duty cycle. Duty cycle is the ratio of tW to T. Volt s Pulse width (tW) Tim e Period, T Amplitude
- 12. LINEAR WAVESHAPING Linear elements such as resistors, capacitors and inductors are employed to shape a signal in this linear wave shaping. A Sine wave input has a sine wave output and hence the non-sinusoidal inputs are more prominently used to understand the linear wave shaping.
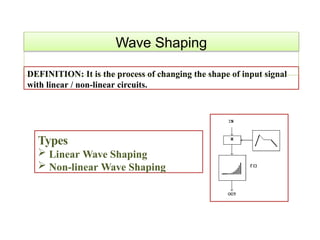
- 13. DEFINITION: It is the process of changing the shape of input signal with linear / non-linear circuits. Wave Shaping Types ’āś Linear Wave Shaping ’āś Non-linear Wave Shaping
- 14. DEFINITION: The process where by the form of a non- sinusoidal signal is changed by transmission through a linear network is called linear wave shaping. Linear Wave Shaping Types ’āś High Pass RC Circuit. ’āś Low Pass RC Circuit.
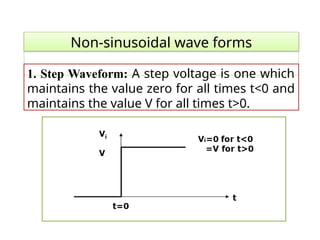
- 15. Non-sinusoidal wave forms 1. Step Waveform: A step voltage is one which maintains the value zero for all times t<0 and maintains the value V for all times t>0.
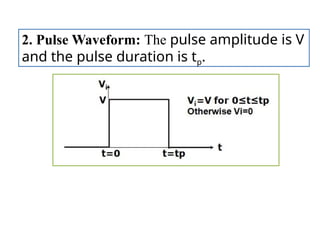
- 16. 2. Pulse Waveform: The pulse amplitude is V and the pulse duration is tp.
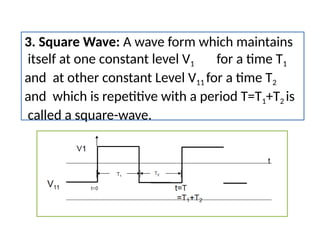
- 17. 3. Square Wave: A wave form which maintains itself at one constant level V1 for a time T1 and at other constant Level V11 for a time T2 and which is repetitive with a period T=T1+T2 is called a square-wave.
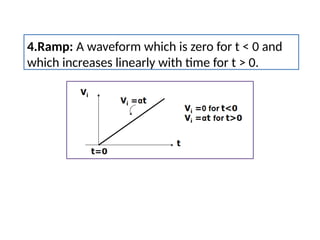
- 18. 4.Ramp: A waveform which is zero for t < 0 and which increases linearly with time for t > 0.
- 19. 5. Exponential 0 t ŌĆó The exponential waveform input is given by where T is the time constant of the exponential input Vi V






