Pure culture techniques
- 1. Pure culture technique Mrs. V. A. Warad Assistant Professor Pharmaceutical Microbiology PES, Modern College of Pharmacy, (for Ladies), Moshi, Pune 1 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 2. Introduction Natural microbial populations are mixed cultures. Contain large number of organisms – single sneeze – 104 – 105 bacteria, 1gm feces – 1011 bacteria, 1gm fertile soil – billions of organisms. To study properties and to prepare products from microorganisms, they should be in pure culture. Definition: Mass of growth of cells containing only one type of cells is called pure culture. 2 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 3. Selective methods ÔÇ¥Desired microorganism may be less in number in mixed population or it may be slow growing. ÔÇ¥By using selective methods number of desired microorganism is increased relatively. ÔÇ¥This increases chance of isolation of Desired microorganism. 3 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 4. Selective methods 1. Chemical methods of selection. 2. Physical methods of selection. 3. Biological methods of selection. 4 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 5. Chemical methods of selection 1) Use of special carbon or nitrogen source - enrichment selection - Use of enrichment medium containing single source of carbon – α conidendrin – isolation of bacteria which can degrade α conidendrin Use of enrichment medium containing single source of nitrogen- N2 gas - Isolation of nitrogen fixing bacteria. 2)Use of dilute media – Caulobacter spp. (0.01% peptone) 5 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 6. 3)Use of inhibitory or toxic chemicals Isolation of Gram negative bacteria - addition of bile salts or crystal violate – MacConkys agar Campylobacter jejuni – vancomycin, polymyxin, trimethoprim added to medium to inhibit other interfering intestinal bacteria Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 6
- 7. Physical methods of selection 1) Heat treatment – endospore producing bacteria – 80oC – 10 min 2)Incubation temperature – Thermophiles: 55oC Psychrophiles isolation: 0-5oC 3)pH of medium – Isolation of lactobacilli – pH - 5.35 with acetate buffer to maintain pH  Isolation of V. cholera – pH – 8.5 7 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 8. 4) Cell size and motility – Isolation of Treponema spp. from oral cavity Membrane filter with pore size – 0.15 µm sample from oral cavity is placed on surface of agar. Treponema as small in size pass through filter on underlying agar medium. They have ability to move swim through solid surface of agar and grow within the agar. Other bacteria from oral cavity – neither pass through filter nor swim trough agar Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 8
- 9. Biological methods of selection ÔÇ¥Use of susceptible laboratory animals. ÔÇ¥Isolation of S. pneumoniae from sputum sample - by injecting sputum sample of patient in mice. After mice suffers from pneumonia, S. pneumoniae can be isolated from blood of mice. 9 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 10. Methods of isolating pure culture 1) The streak plate technique 2)Pour plate technique 3) Spread plate technique 4) Micromanipulator technique 10 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 11. 1) The streak plate technique Dilution of bacteria on solid nutrient media. It is done by streaking the culture over agar surface Pattern of streaking - Four quadrant method. Bacteria get separated from each other by sufficient distance. One organism produces one colony and is considered as pure culture. Colonies developed after streak plate method may require repeated streaking for isolation of bacteria from mixed culture Roll tube technique – for isolation of anaerobic bacteria - diagram, description 11 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 12. ÔÇ¥Advantages of streak plate technique: 1. Less material required 2. Less laborious 3. Surface colonies Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 12
- 13. Streak plate technique - Four quadrant method Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 13
- 14. Roll tube technique ÔÇ¥Modification of streak plate technique for isolation of anaerobic bacteria. ÔÇ¥Stoppered anaerobic culture tubes whose inner walls are coated with pre-reduced media are used. Tubes are filled with oxygen free nitrogen. ÔÇ¥Stopper is removed to keep them, anaerobic are flushed oxygen free CO2 from gas cannula. ÔÇ¥Inoculation done with transfer loop, held against agar surface as tube being rotated by a motor. ÔÇ¥Inoculation is started at bottom and drawing the loop gradually upward, the inoculum becomes thinned and well isolated colonies are can be obtained ÔÇ¥Tube is re-stoppered and incubated Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 14
- 15. 2)Pour plate technique ÔÇ¥Serial dilutions of mixed culture of sample are made. ÔÇ¥Diluted sample is added to tube of sterile sufficiently cooled agar medium and mixed. --- diagram ÔÇ¥Mixture is poured in Petri plate. ÔÇ¥After incubation plates are observed for isolated colonies. ÔÇ¥Advantage - Method can be used to determine number of bacteria in sample - Quantitative method. 15 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 16. Pour plate technique Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 16
- 17. Disadvantage – 1. Laborious 2. Time consuming 3. More material required 4. Some of the colonies are submerged, difficult to pickup and study. 5. Exposure of organism to 450C - can not be used to isolate psychrophiles Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 17
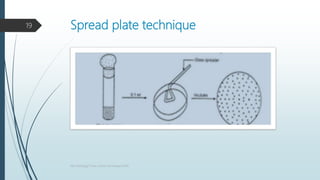
- 18. 3) Spread plate technique Serial dilutions of mixed culture of sample are made. Sample of dilution is added onto surface of agar plate. Sample is evenly spread on surface by sterile glass spreader. Advantage – 1. Surface colonies 2. No exposure to higher temperature of agar 3. Quantitative method. 18 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 19. Spread plate technique Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 19
- 20. 4) Micromanipulator technique Uses instrument – micromanipulator. Uses microscope in conjunction with micromanipulator. Micromanipulator allows controlled movement of micropipette Single cell is picked up with micropipette while observing cells through microscope. Single cell is added to nutrient medium. After incubation pure culture is developed from single cell. This culture is a clone. 20 Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW
- 21. Microbiology/ Pure culture technique/VAW 21