PVC
- 1. Prepared by : Muhammed Faiq Muhammed Lateef Abdulqadr Pshtiwan 3rd stage Supervised by : M. Bushra Mahmoodi Soran University Faculty Of Engineering Chemical Engineering Department
- 2. OUTLINE • Introduction • Production • Physical Properties • Application • Disadvantage • How is PVC made? • References
- 3. INTRODUCTION • Also known as poly vinyl or vinyl, commonly abbreviated PVC, is the world's third- most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer, after polyethylene and polypropylene. • PVC comes in two basic forms: __ rigid and flexible .
- 4. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES • Fire retarding properties • Durability • Chemical resistance • Mechanical stability • Processability and mouldability
- 5. PRODUCTION • Polyvinyl chloride is produced by polymerization of the vinyl chloride monomer (VCM). PVC is a petrochemical product : Although PVC can be produced from a range of hydrocarbons including coal, and derivatives of plants such as sugar cane, the bulk of world production is currently manufactured using the chemical compound ethylene. Ethylene (or ethane) which has the chemical formula C2H4, is a product of the oil & gas industry.
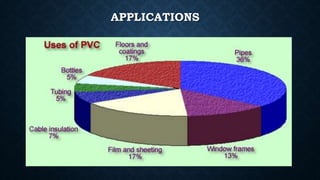
- 7. APPLICATIONS
- 9. DISADVANTAGES • Recycling difficulty • it is not recommended for use above 70 degrees Celsius. • Sensitive to UV and oxidative degradation. • Thermal decomposition evolves HCl. • It is less flame resistance. • PVC contains the volatile compound which are harmful to the environmental. • They do not have the same strength as cast-iron or galvanized irons pipes.
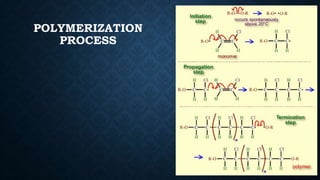
- 10. HOW IS PVC MADE? • The chemical process for making PVC involves taking the simplest unit, called the monomer, and linking these monomer molecules together in the polymerisation process. • Long molecular chains are formed called polymers (which are also called macromolecules).
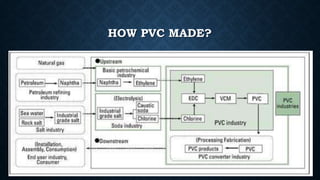
- 11. HOW PVC MADE?
- 13. ANY QUESTION!!! FELL FREE TO ASK