Python for beginners
- 1. Python For Beginners aliahuseyn[at]gmail[dot]com Telegram Link (click me)
- 2. What is data type ? Data type classification of data which tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data.
- 3. What is compiler/interpreter ? Just Translator, all have to know about it.
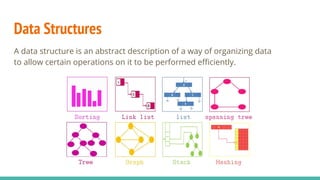
- 5. Data Structures A data structure is an abstract description of a way of organizing data to allow certain operations on it to be performed efficiently.
- 6. Data Structure vs Data Type A data type stores certain information without any semantics. A data type can be an integer, a floating point, a string (basic data types). In a data structure information is, well, structured, and there are certain ways you can access the information stored. For example in a First In First Out (FIFO) queue you can add information to the back and retrieve information from the front.
- 8. Guido van Rossum Now, it's my belief that Python is a lot easier than to teach to students programming and teach them C or C++ or Java at the same time because all the details of the languages are so much harder. Other scripting languages really don't work very well there either.
- 9. Data Types in Python Built-in Data types Sticking to the hierarchy scheme used in the official Python documentation these are numeric types, sequences, sets and mappings (and a few more not discussed further here).
- 10. Number Types int long float complex 10 51924361L 0.0 3.14j 100 -0x19323L 15.20 45.j -786 0122L -21.9 9.322e-36j 080 0xDEFABCECBDAECBFBAEL 32.3+e18 .876j -0490 535633629843L -90. -.6545+0J
- 11. Variable & Variable Assignment A variable is a location in memory used to store some data (value). We use the assignment operator (=) to assign values to a variable. Any type of value can be assigned to any valid variable.
- 13. Holberton s1 s2 del(s2) Holberton s1 s2 Reference Memory in Python
- 14. Control Flow
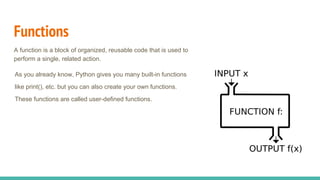
- 15. Functions A function is a block of organized, reusable code that is used to perform a single, related action. As you already know, Python gives you many built-in functions like print(), etc. but you can also create your own functions. These functions are called user-defined functions.
- 16. Data Structures They are structures which can hold some data together. In other words, they are used to store a collection of related data.
- 17. Sequence Types list, dict, tuples, sets, strings In computing, these types implement storage of data elements. Being templates, they can be used to store arbitrary elements, such as integers or custom classes. One common property of all sequential types is that the elements can be accessed sequentially.
- 18. Accessing Values in Strings var1 = 'Hello World!' var2 = "Python Programming" print(var1[0]) # H print(var2[1:5]) # ytho Updating Strings var1 = 'Hello World!' var2 = var1[:6] + 'Python' print(var2) # Hello Python String Formatting Operator print("My name is %s and weight is %d kg!" % ('Tofik', 120))
- 19. List Manipulation colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green'] print(colors[0]) # red print(colors[2]) # green print(len(colors)) # 3 b = colors # Does not copy the list
- 20. Update & Delete List Elements list = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000] # Update print(list[2]) # 1997 list[2] = 2001 print(list[2]) # 2001 # Delete print(list) # ['physics', 'chemistry', 2001, 2000] del(list[2]) print(list) # ['physics', 'chemistry', 2000]
- 21. Control Flow #2 - For Loop Statement Lists as an iterable: list = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000] for x in list: ˇ.print(x) Strings as an iterable: string = 'chemistry' for x in string: print(x)
- 22. Flat Sequences Elements which has that subtype are more compact, but they are limited to holding primitive values like characters, bytes and numbers. Container Sequences Hold references to the object they contain, which may be of any type. While flat sequences physically store that value of each item within its own memory space. list, tuple, collections.deque ... str, bytes, array.array, ....
- 23. Mutable and Immutable Objects in Python
- 24. Simple put, a mutable object can be changed after it is created, and an immutable object canˇŻt. Objects of built-in types like (int, float, bool, str, tuple) are immutable. Objects of built-in types like (list, set, dict) are mutable.
- 25. Immutable Objects ItˇŻs no big surprise that it fails since we just learnt immutable objects cannot change their state.
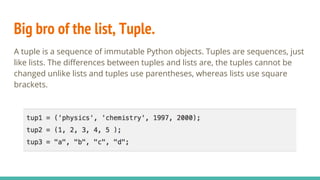
- 27. Big bro of the list, Tuple. A tuple is a sequence of immutable Python objects. Tuples are sequences, just like lists. The differences between tuples and lists are, the tuples cannot be changed unlike lists and tuples use parentheses, whereas lists use square brackets.

![Python For Beginners
aliahuseyn[at]gmail[dot]com
Telegram Link (click me)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonforbeginnersdatatypes-180922191753/85/Python-for-beginners-1-320.jpg)













![Accessing Values in
Strings
var1 = 'Hello World!'
var2 = "Python Programming"
print(var1[0]) # H
print(var2[1:5]) # ytho
Updating Strings
var1 = 'Hello World!'
var2 = var1[:6] + 'Python'
print(var2) # Hello Python
String Formatting Operator
print("My name is %s and weight is %d kg!" % ('Tofik', 120))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonforbeginnersdatatypes-180922191753/85/Python-for-beginners-18-320.jpg)
![List Manipulation
colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green']
print(colors[0]) # red
print(colors[2]) # green
print(len(colors)) # 3
b = colors # Does not copy the list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonforbeginnersdatatypes-180922191753/85/Python-for-beginners-19-320.jpg)
![Update & Delete List Elements
list = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000]
# Update
print(list[2]) # 1997
list[2] = 2001
print(list[2]) # 2001
# Delete
print(list) # ['physics', 'chemistry', 2001, 2000]
del(list[2])
print(list) # ['physics', 'chemistry', 2000]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonforbeginnersdatatypes-180922191753/85/Python-for-beginners-20-320.jpg)
![Control Flow #2 - For Loop Statement
Lists as an iterable:
list = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000]
for x in list:
ˇ.print(x)
Strings as an iterable:
string = 'chemistry'
for x in string:
print(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonforbeginnersdatatypes-180922191753/85/Python-for-beginners-21-320.jpg)