Python Seminar PPT
- 1. PYTHON Submitted by: Shivam Gupta(1318710097) Shashendra Singh(1318710094)
- 2. What We Give you? âĒ What is PythonâĶ? âĒ Differences between program and scripting language âĒ History of Python âĒ Scope of Python âĒ What can I do with python âĒ Who uses python today âĒ Why do people use Python? âĒ Installing Python IDE âĒ A Sample Code âĒ Python code execution âĒ Running Python âĒ Python Basic(Variable, Strings, Data types etc.) 2
- 3. What is PythonâĶ? âĒ Python is a general purpose programming language that is often applied in scripting roles. âĒ So, Python is programming language as well as scripting language. âĒ Python is also called as Interpreted language 3
- 4. Differences between program and scripting language Program Scripting âĒ a program is executed (i.e. the source is first compiled, and the result of that compilation is expected) âĒ A "program" in general, is a sequence of instructions written so that a computer can perform certain task. âĒ a script is interpreted âĒ A "script" is code written in a scripting language. A scripting language is nothing but a type of programming language in which we can write code to control another software application. 4
- 5. History âĒ Invented in the Netherlands, early 90s by Guido van Rossum âĒ Python was conceived in the late 1980s and its implementation was started in December 1989 âĒ Guido Van Rossum is fan of âMonty Pythonâs Flying Circusâ, this is a famous TV show in Netherlands âĒ Named after Monty Python âĒ Open sourced from the beginning 5
- 6. Pythonâs Benevolent Dictator For Life âPython is an experiment in how much freedom programmers need. Too much freedom and nobody can read another's code; too little and expressiveness is endangered.â - Guido van Rossum 6
- 7. Why was python created? "My original motivation for creating Python was the perceived need for a higher level language in the Amoeba [Operating Systems] project. I realized that the development of system administration utilities in C was taking too long. Moreover, doing these things in the Bourne shell wouldn't work for a variety of reasons. ... So, there was a need for a language that would bridge the gap between C and the shellâ - Guido Van Rossum 7
- 8. Scope of Python âĒ Science - Bioinformatics âĒ System Administration -Unix -Web logic -Web sphere âĒ Web Application Development -CGI -Jython â Servlets âĒ Testing scripts 8
- 9. What can I do with PythonâĶ? âĒ System programming âĒ Graphical User Interface Programming âĒ Internet Scripting âĒ Component Integration âĒ Database Programming âĒ Gaming, Images, XML , Robot and more 9
- 10. Who uses python todayâĶ âĒ Python is being applied in real revenue-generating products by real companies. For instance: âĒ Google makes extensive use of Python in its web search system, and employs Pythonâs creator. âĒ Intel, Cisco, Hewlett-Packard, Seagate, Qualcomm, and IBM use Python for hardware testing. âĒ ESRI uses Python as an end-user customization tool for its popular GIS mapping products. âĒ The YouTube video sharing service is largely written in Python 10
- 11. Why do people use PythonâĶ? The following primary factors cited by Python users seem to be these: âĒ Python is object-oriented Structure supports such concepts as polymorphism, operation overloading, and multiple inheritance. . âĒ It's free (open source) Downloading and installing Python is free and easy Source code is easily accessible 11
- 12. âĒ It's powerful - Dynamic typing - Built-in types and tools - Library utilities - Third party utilities (e.g. Numeric, NumPy, SciPy) - Automatic memory management âĒ It's portable - Python runs virtually every major platform used today - As long as you have a compatible Python interpreter installed, Python programs will run in exactly the same manner, irrespective of platform. 12
- 13. Installing Python âĒ Python is pre-installed on most Unix systems, including Linux and MAC OS X âĒ But for in Windows Operating Systems , user can download from the https://www.python.org/downloads/ - from the above link download latest version of python IDE and install, recent version is 3.4.1 but most of them uses version 2.7.7 only 13
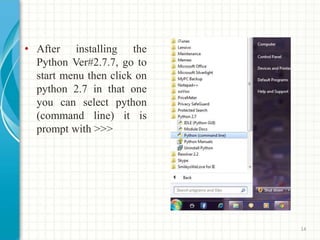
- 14. âĒ After installing the Python Ver#2.7.7, go to start menu then click on python 2.7 in that one you can select python (command line) it is prompt with >>> 14
- 15. 15
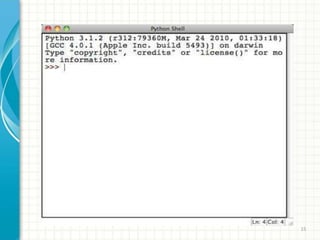
- 16. Running Python Once you're inside the Python interpreter, type in commands at will. âĒ Examples: >>> print 'Hello world' Hello world 16
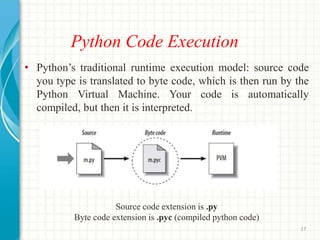
- 17. Python Code Execution âĒ Pythonâs traditional runtime execution model: source code you type is translated to byte code, which is then run by the Python Virtual Machine. Your code is automatically compiled, but then it is interpreted. Source code extension is .py Byte code extension is .pyc (compiled python code) 17
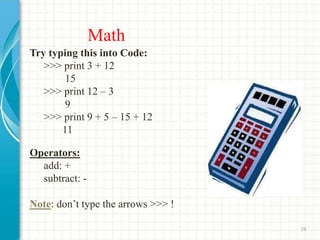
- 19. Math Try typing this into Code: >>> print 3 + 12 15 >>> print 12 â 3 9 >>> print 9 + 5 â 15 + 12 11 Operators: add: + subtract: - Note: donât type the arrows >>> ! 19
- 20. Math Rule: If you want Python to answer in floats, you have to talk to it in floats. More operators: divide: / multiply: * >>> print 3 * 12 36 >>> print 12 / 3 4 >>> print 11 / 3 3 >>> print 12.0 / 3.0 4.0 >>> print 11.0 / 3.0 3.66 20
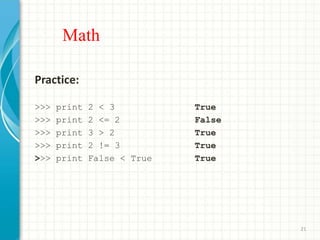
- 21. Math Practice: >>> print 2 < 3 True >>> print 2 <= 2 False >>> print 3 > 2 True >>> print 2 != 3 True >>> print False < True True 21
- 23. Strings Examples: Try typing one without quotes: Whatâs the result? >>> âItâs a beautiful day!â >>> âGoodbye, cruel world.â >>> Aggies >>> âAggiesâ >>> âRice fight, never die!â >>> â3 + 2â 23
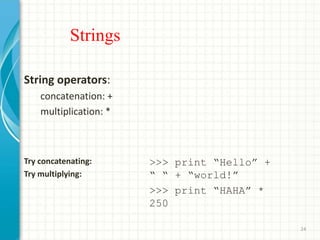
- 24. Strings String operators: concatenation: + multiplication: * Try concatenating: Try multiplying: >>> print âHelloâ + â â + âworld!â >>> print âHAHAâ * 250 24
- 26. Variable >>>headmaster=âDumbledoreâ >>>print headmaster âDumbledoreâ Create a Variable: Assigning a New Value: >>>headmaster=âHardcastleâ >>>print headmaster âHardcastleâ 26
- 27. DATA TYPES IN PYTHON
- 28. 28 Data Type: Python has many native data types. Here are the important ones: Booleans are either True or False. Numbers can be integers (1 and 2), floats (1.1 and 1.2), fractions (1/2 and 2/3), or even complex numbers. Strings are sequences of Unicode characters, e.g. an HTML document. Bytes and byte arrays, e.g. a JPEG image file. Lists are ordered sequences of values. Tuples are ordered, immutable sequences of values. Sets are unordered bags of values.
- 29. Example: 29 String âWhoop!â Integer 42 Float 3.14159 List [âJohnâ, âPaulâ, âGeorgeâ, âRingoâ] Python can tell us about types using the type() function: >>> print type(âWhoop!â) <type âstrâ>
- 31. 31 List: The list is a most versatile Data type available in Python which can be written as a list of comma-separated values (items) between square brackets. Important thing about a list is that items in a list need not be of the same type. Example: list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000]; list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
- 32. 32 SN Function with Description 1 cmp(list1, list2) Compares elements of both lists. 2 len(list) Gives the total length of the list. 3 max(list) Returns item from the list with max value. 4 min(list) Returns item from the list with min value. 5 list(seq) Converts a tuple into list.
- 33. List: a sequence of objects >>> Beatles = [âJohnâ, âPaulâ, âGeorgeâ, âRingoâ] >>> grades = [82, 93, 67, 99, 100] Guess what this will output: >>> type(Beatles) >>> type(grades) 33
- 34. Lists Index: Where an item is in the list >>> Beatles = [âJohnâ, âPaulâ, âGeorgeâ, âRingoâ] >>> Beatles[0] âJohnâ [âJohnâ, âPaulâ, âGeorgeâ, âRingoâ] 0 1 2 3 Python always starts at zero! 34
- 35. TUPLE: DATA TYPE
- 36. 36 Tuples: A tuple is a sequence of immutable Python objects. Tuples are sequences, just like lists. The differences between tuples and lists are, the tuples cannot be changed unlike lists and tuples use parentheses, whereas lists use square brackets. Example: tup2 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ); tup3 = ("a", "b", "c", "dâ); Accessing Values: print "tup2[1:5]: â Output: tup2[1:5]: [2, 3, 4, 5]
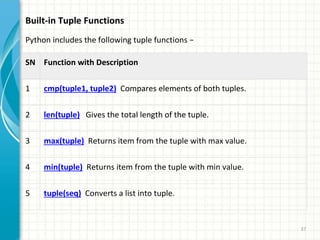
- 37. 37 Built-in Tuple Functions Python includes the following tuple functions â SN Function with Description 1 cmp(tuple1, tuple2) Compares elements of both tuples. 2 len(tuple) Gives the total length of the tuple. 3 max(tuple) Returns item from the tuple with max value. 4 min(tuple) Returns item from the tuple with min value. 5 tuple(seq) Converts a list into tuple.
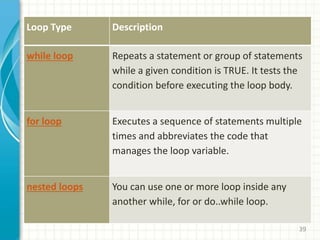
- 39. 39 Loop Type Description while loop Repeats a statement or group of statements while a given condition is TRUE. It tests the condition before executing the loop body. for loop Executes a sequence of statements multiple times and abbreviates the code that manages the loop variable. nested loops You can use one or more loop inside any another while, for or do..while loop.
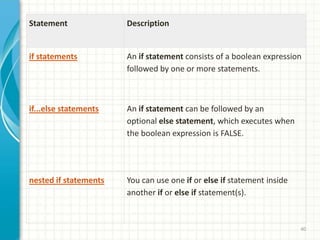
- 40. 40 Statement Description if statements An if statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements. if...else statements An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the boolean expression is FALSE. nested if statements You can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement(s).
- 41. 41 I believe the trial has shown conclusively that it is both possible and desirable to use Python as the principal teaching language: o It is Free (as in both cost and source code). o It is trivial to install on a Windows PC allowing students to take their interest further. For many the hurdle of installing a Pascal or C compiler on a Windows machine is either too expensive or too complicated; o It is a flexible tool that allows both the teaching of traditional procedural programming and modern OOP; It can be used to teach a large number of transferable skills; o It is a real-world programming language that can be and is used in academia and the commercial world; o It appears to be quicker to learn and, in combination with its many libraries, this offers the possibility of more rapid student development allowing the course to be made more challenging and varied; o and most importantly, its clean syntax offers increased understanding and enjoyment for students;
- 42. 42







![Why was python created?
"My original motivation for creating Python was the
perceived need for a higher level language in the
Amoeba [Operating Systems] project.
I realized that the development of system
administration utilities in C was taking too long.
Moreover, doing these things in the Bourne shell
wouldn't work for a variety of reasons. ...
So, there was a need for a language that
would bridge the gap between C and the shellâ
- Guido Van Rossum
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160403194316/85/Python-Seminar-PPT-7-320.jpg)














![Example:
29
String âWhoop!â
Integer 42
Float 3.14159
List [âJohnâ, âPaulâ, âGeorgeâ, âRingoâ]
Python can tell us about types using the type()
function:
>>> print type(âWhoop!â)
<type âstrâ>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160403194316/85/Python-Seminar-PPT-29-320.jpg)

![31
List:
The list is a most versatile Data type available in Python
which can be written as a list of comma-separated values
(items) between square brackets. Important thing about a
list is that items in a list need not be of the same type.
Example:
list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000];
list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160403194316/85/Python-Seminar-PPT-31-320.jpg)

![List: a sequence of objects
>>> Beatles = [âJohnâ, âPaulâ, âGeorgeâ,
âRingoâ]
>>> grades = [82, 93, 67, 99, 100]
Guess what this will output:
>>> type(Beatles)
>>> type(grades)
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160403194316/85/Python-Seminar-PPT-33-320.jpg)
![Lists
Index: Where an item is in the list
>>> Beatles = [âJohnâ, âPaulâ, âGeorgeâ,
âRingoâ]
>>> Beatles[0]
âJohnâ
[âJohnâ, âPaulâ, âGeorgeâ, âRingoâ]
0 1 2 3
Python always starts at zero!
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160403194316/85/Python-Seminar-PPT-34-320.jpg)

![36
Tuples:
A tuple is a sequence of immutable Python objects. Tuples are
sequences, just like lists. The differences between tuples and
lists are, the tuples cannot be changed unlike lists and tuples
use parentheses, whereas lists use square brackets.
Example:
tup2 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 );
tup3 = ("a", "b", "c", "dâ);
Accessing Values:
print "tup2[1:5]: â
Output:
tup2[1:5]: [2, 3, 4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160403194316/85/Python-Seminar-PPT-36-320.jpg)