Qb D Akhilesh Dwivedi
- 1. Presentation on Quality by DesignÔÇÿPharmaceutical GMPs for the 21st CenturyÔÇÖ By: Akhilesh Kumar DwivediDr. ReddyÔÇÖs Labs. F.T.O-IIIDate: 18 Jan 2011QUALITY BY DESIGN
- 3. HISTORY: Quality by Design (QbD) is a concept first outlined by well-known quality expert Joseph M. Juran in various publications, most notably Juran on Quality by Design. Juran believed that quality could be planned, and that most quality crises and problems relate to the way in which quality was planned in the first place.QUALITY BY DESIGN
- 4. What is Quality?QualityRequirements= need or expectationsTarget ProductQuality Profile Patient(or surrogate)ÔÇ£Good pharmaceutical quality represents an acceptably low risk of failing to achieve the desired clinical attributes.ÔÇØ
- 5. The quality mantra ÔÇ£Quality can not be tested into products; it has to be built in by designÔÇØÔÇ£Quality is never an accident; it is always the result of high intention, sincere effort, intelligent direction and skillful execution; it represents the wise choice of many alternatives.ÔÇØ
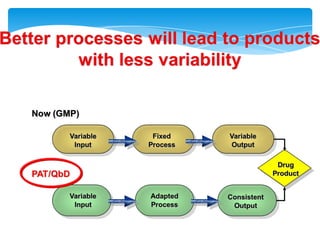
- 6. How can we modernize our industry?More knowledge of our products and processes, allowing better design and more controlBetter management:- introduction of quality risk management- expansion of GMP to more extensive pharmaceutical quality system
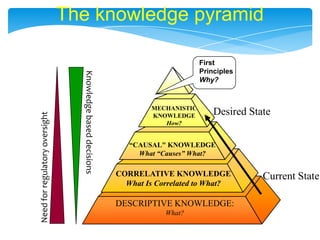
- 7. The knowledge pyramidDesired StateKnowledge based decisionsFirstPrinciples Why?MECHANISTICKNOWLEDGEHow?ÔÇ£CAUSAL" KNOWLEDGEWhat ÔÇ£CausesÔÇØ What?Need for regulatory oversightCORRELATIVE KNOWLEDGEWhat Is Correlated to What?Current StateDESCRIPTIVE KNOWLEDGE: What?
- 8. The New Quality Paradigm ÔÇô The Evolving Regulatory FrameworkProduct Life CycleProductDesign Process DesignScale-up &Transfer Commercial ManufactureProductICH Q8/Q8(R) - Pharmaceutical DevelopmentPAT GuidanceICH Q9 ÔÇô Quality Risk ManagementICH Q10 ÔÇô Pharmaceutical Quality Systems
- 9. Definition: Quality by DesignQuality by Design isa systematic approach to developmentthat begins with predefined objectivesand emphasizes - product and process understanding - and process control,based on sound science and quality risk management.
- 10. Quality by Design approach can be used forSimple dosage forms
- 11. Advanced drug delivery systems
- 12. Devices
- 16. AnalyticsImpact of QbDCompanies re-organize their science
- 17. Universities change their curriculum
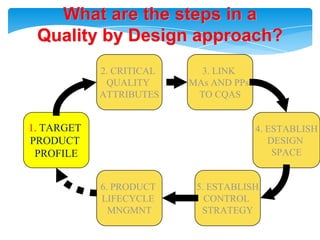
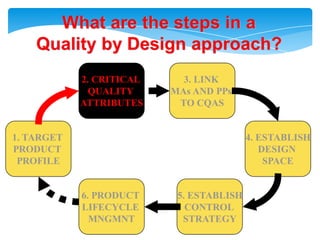
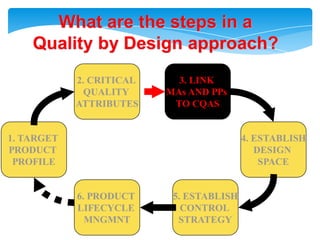
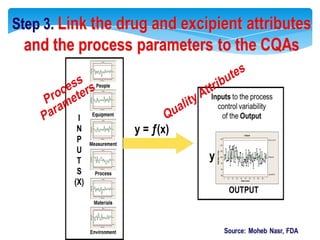
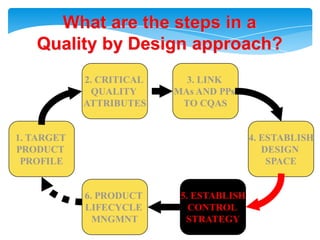
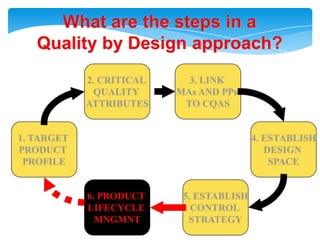
- 18. Health authorities change their assessment and inspectionQUALITY BY DESIGNStep 1. Agree on the Target Product ProfileStep 2. Determine the Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)Step 3. Link the drug and excipient attributes and the process parameters to the CQAsStep 4. Define the Design SpaceStep 5. Define the Control StrategyStep 6. Prepare QbD registration fileStep 7. Product lifecycle management and continual improvement
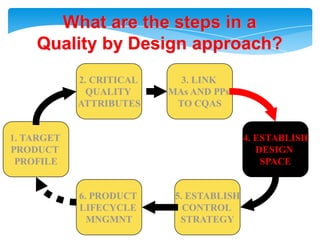
- 19. What are the steps in aQuality by Design approach?2. CRITICAL QUALITY ATTRIBUTES3. LINK MAs AND PPs TO CQAS1. TARGETPRODUCT PROFILE4. ESTABLISHDESIGN SPACE6. PRODUCT LIFECYCLE MNGMNT5. ESTABLISHCONTROL STRATEGY
- 20. Step 1. Agree on the Target Product ProfileConsider:dosage formroute of administrationstrengthrelease / delivery of the drugpharmacokinetic characteristics(e.g., dissolution; aerodynamic performance)drug product quality criteria(e.g., sterility, purity).Target Product Profile:- a prospective and dynamic summary of the quality characteristics of a drug product - that ideally will be achieved to ensure that the desired quality, and hence the safety and efficacy, of a drug product is realized. The TPP forms the basis of design of the product.
- 22. CRITICAL QUALITY ATTRIBUTES - definitionA critical quality attribute (CQA) is a - physical, chemical, biological, or microbiological property or characteristic - that should be within an appropriate limit, range, or distribution - to ensure the desired product quality.
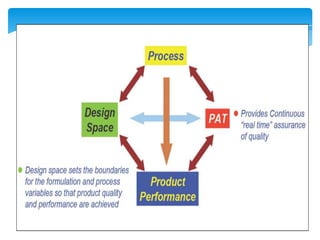
- 29. Step 4. Define the Design SpaceThe linkage between - the process inputs (input variables and process parameters) and - the critical quality attributes
- 30. can be described in the design space.
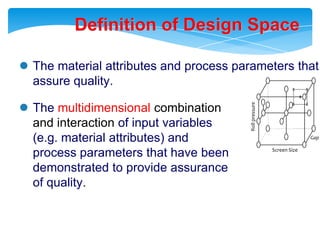
- 31. Definition of Design SpaceRoll pressureGap widthScreen SizeThe material attributes and process parameters that assure quality.
- 32. The multidimensionalcombination and interaction of input variables (e.g. material attributes) and process parameters that have beendemonstrated to provide assurance of quality.
- 34. Step 5. Define the Control StrategyThe control strategy should describe and justify howin-process controls and
- 35. the controls of - input materials (drug substance and excipients), - container closure system, - intermediates and
- 36. the controls of end products contribute to the final product quality
- 37. 5. CONTROL STRATEGYElements of a control strategy can include, but are not limited to, the following:ÔÇó Control of input material attributes (e.g., drug substance, adhesive polymer, primary packaging materials) based on an understanding of their impact on processability or product qualityÔÇó Product specification(s)ÔÇó Controls for unit operations that have an impact on downstream processing or end-product quality (e.g., the impact of solvent on degradation)ÔÇó In-process or real-time release in lieu of end-product testingÔÇó A monitoring program (e.g., full product testing at regular intervals) for verifying multivariate prediction models.