QC Circle
- 1. QC CircleâĶâĶâĶ? Presented By: Md. Mahamudul Hassan Date: 06.03.18
- 2. â We all are know about âKAIZENâ right? âKaizenâ is Japanese word Means âContinuous Improvementâ
- 3. â Now some question for you if yes please raise your hand âĒ Who Wants âKAIZENâ? âĒ Who Wants to âKAIZENâ? âĒ Who Wants to Lead the âKAIZENâ? âĒ Those Who Wants to KAIZEN lets start âQCCâ activitiesâĶ.
- 4. WHAT IS QC CIRCLE? âĒ QC Circle is a group of employees who meet regularly to discuss their Work related problems, Investigate causes, Recommend solutions, and take corrective actions. âĒ Generally , QC Circle is a small group of employees (4-5 person)belonging to the same similar work area. OTHER NAME OF QUALITY CIRCLES âĒ Small Group âĒ Action Circles âĒ Excellence Circles âĒ Productivity Circles
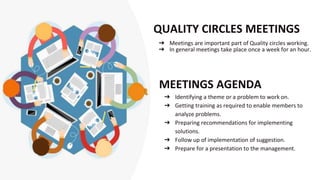
- 5. QUALITY CIRCLES MEETINGS â Meetings are important part of Quality circles working. â In general meetings take place once a week for an hour. MEETINGS AGENDA â Identifying a theme or a problem to work on. â Getting training as required to enable members to analyze problems. â Preparing recommendations for implementing solutions. â Follow up of implementation of suggestion. â Prepare for a presentation to the management.
- 6. Background of QC Circle W. Edwards Deming had noticed that, managers and engineers belongs about 85% of the responsibility for quality control and line workers only about 15%, Deming argued that these shares should be reversed. After WW II, W Edwards Deming invited by Japan for the improvement of Poor Quality and economic condition in Japan. Then W. Edwards Deming had shared that concept in the 1950s. The idea was later formalized across Japan in 1962 by Kaoru Ishikawa in the form of QC Circle. Now it has been recognized that QC Circle played vital role for sudden quality revolution in Japan after WWII. Now rest of the world have benchmarked the concept from Japan.
- 7. âA Quality Circle will not last long unless the nature of its activities is voluntary and independent.â - Kaoru Ishikawa âĒFather QC Circle
- 8. THE OBJECTIVES OF QUALITY CIRCLE I.To improve Quality, Productivity, safety and cost reduction. II.To give chance to the employees to use their wisdom and creativity. III.To encourage team spirit, cohesive culture among different levels and sections of the employees. IV.To promote self and mutual development including leadership quality. V.To fulfill the self-esteem and motivational needs of employees. VI.To improve the quality of work-life of employees.
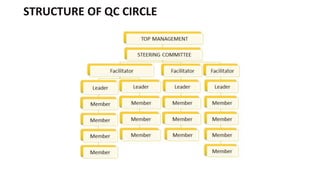
- 9. STRUCTURE OF QC CIRCLE
- 10. The success of the quality circles depends solely on the attitude of the Top management and plays an important role to ensure the success of implementation of quality circles in the organization. STEERING COMMITTEE Roles of Steering Committee (Management) âĒ Formally announce the launching of quality circle initiative. âĒ Provide full support and encouragement to QCC movement. âĒ Provide leadership and guidance to develop the QCC activities. âĒ Arranging competition, Performing Quality Day. âĒ Facilitate the approval and implementation of the QCC solutions. âĒ Sanction the necessary monetary budgets. âĒ Provide the logistic support as needed. âĒ Give due recognition to quality circles. âĒ Develop guidelines for measuring the effectiveness of QCC. âĒ Review the performance and progress of quality circles periodically.
- 11. Steering committee will appoint a facilitator to facilitate the Quality Control Circles Depending on capability one facilitator may help to more than one circle. FACILITATOR Roles of Facilitator âĒ Support and advice the QCC as a facilitator. âĒ Arranging training program & providing training âĒ Monitoring the problems of QCC âĒ Act as a coordinator between the QCC & organization âĒ Reporting the improvement of QCC in the steering committee âĒ Support & inspire QCC to make presentation âĒ Ensure to have supporting stationaries when needed âĒ Primarily act as an observer in the meeting âĒ Cordially communicate with the QCC leader & members
- 12. QCC member will select one as a leader among them. Team leadership may be rotated among the members. LEADER Roles of Leader âĒ Acquire the necessary skills in various quality circle tools and techniques. âĒ Don't criticize, show respect others opinion. âĒ Motivate the members for their full participation in the proceedings of quality circle meetings and related activities. âĒ Maintain the records of quality circles meetings and other related activities. âĒ Interact with the quality circle facilitator frequently. âĒ Make presentations of solutions to the management. Involve the members in making the presentations. âĒ Ensure implementation of the approved solutions with the active involvement of the members.
- 13. A team will be formed by 4 to 5 members MEMBERS Roles of Members âĒ Regularly & Timely attending meeting, âĒ Acquire the necessary skills in various quality circle tools and techniques. âĒ Participate in the meeting diligently âĒ Listening when other member speak âĒ Don't criticize, show respect others opinion. âĒ Participate in the management presentation âĒ Help the leader in all respect âĒ Positive mind-set and act cordially with members âĒ Maintain discipline âĒ Participate in implementing the finalized solutions.
- 14. âYou can't manage, what you canât measure.â -W.Edwards Deming âIf I had an hour to solve any problem Iâd spend 55 minutes thinking about problem and 5 minutes thinking about solution.â -Albert Einstein
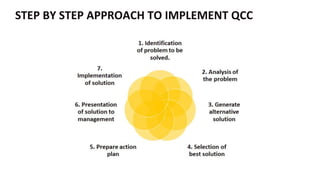
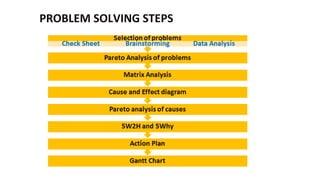
- 15. STEP BY STEP APPROACH TO IMPLEMENT QCC
- 18. QUALITY CIRCLES ARE NOTâĶ.. â Quality Circles do not tackle just quality problems. â Quality Circles do not change the existing organizational structure or the chain of command. â Quality Circles are not a forum for grievances or a springboard for demands. â Quality Circles are not a means for the management to unload all their problems. â Quality Circles are not just another techniques. â Quality Circles are not a remedy for all ills.
- 19. AREAS OF INTEREST TO QUALITY CIRCLE âĒ Quality Improvement. âĒ Efficiency Improvement. âĒ Process and working environment improvement. âĒ Safety in materials handling and equipment operations. âĒ Reduction in work in progress (WIP). âĒ Reduction in human errors. âĒ Equipment and manpower utilization. âĒ Cost Reduction
- 20. iFiix âZero Defect,Zero Delay & Zero Contaminationâ Now it's our turn to make it happenâĶ!!!
- 21. THANK YOU