Quality by deign
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes61 views
The document provides information about the preparer of the document. Sujitha Mary, an Assistant Professor at KVM College of Pharmacy, prepared the document.
1 of 16
Download to read offline





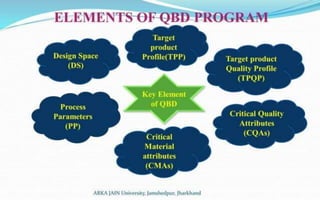










Recommended
POWDERS.pptx
POWDERS.pptxSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses solid dosage forms, primarily focusing on powders, tablets, and capsules for both internal and external use. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of powders, describing methods for mixing and dispensing them, as well as their usage in various pharmaceutical applications. Additionally, it details specific formulations and considerations when preparing and administering powdered medications.LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS.pptx
LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS.pptxSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses liquid dosage forms, highlighting their importance for patients with swallowing difficulties and the need for rapid therapeutic responses. It covers types such as solutions and dispersed systems, advantages like ease of swallowing, and disadvantages including potential for microbial contamination and dosing inaccuracies. Additionally, it details the role of various excipients, vehicles, and methods to enhance drug solubility in these formulations.DOSAGE FORM.pptx
DOSAGE FORM.pptxSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses a pharmaceutical dosage form. It was prepared by Sujitha Mary, an Assistant Professor at KVM College of Pharmacy. The document focuses on dosage form design for pharmaceutical products.COMPLAINTS. UNIT IV
COMPLAINTS. UNIT IVSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document outlines the procedures and protocols for handling complaints related to pharmaceutical products, including types of complaints, investigation steps, and product recall strategies. It details the management of returned goods and waste disposal in compliance with environmental regulations and quality assurance standards. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of thorough documentation and corrective actions in managing product quality and safety.Good laboratoty practise
Good laboratoty practise SUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document outlines the Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) standards for nonclinical laboratory studies, detailing the quality systems, organizational processes, and regulations necessary to ensure the integrity and reliability of safety data submitted for FDA approval. It covers aspects such as study protocols, testing facility responsibilities, equipment maintenance, and compliance monitoring by the quality assurance unit. GLP is essential for validating the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals and other products intended for human use.calibration-and-validation
calibration-and-validationSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses concepts related to validation in the pharmaceutical industry. It begins by defining validation as proving that a process consistently produces the expected results. There are three phases of validation: pre-validation to establish the design; process qualification to evaluate the design; and continued process verification. Validation is important for quality assurance and regulatory compliance. The key types of validation discussed are process validation, cleaning validation, and analytical method validation.warehousing
warehousingSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses warehousing and material management practices. It provides details on the importance of good warehousing practices for optimizing storage and preserving product quality and integrity. Key aspects of warehousing covered include receiving, identifying, storing, and distributing products according to written procedures. Material management aims to efficiently plan and control the flow of materials from purchase to production. Key functions involve materials planning, purchasing, inventory control, and coordination between departments. Stages of material management outlined are general controls, receipt and quarantine of incoming materials, sampling and testing, and proper storage and issue of materials.Nanoparticle for drug delivery system
Nanoparticle for drug delivery systemSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses nanoparticles, which are solid colloidal particles between 1-100 nm in size that can be used for drug delivery. Some key points discussed include:
- Nanoparticles offer advantages over microparticles for drug delivery due to their small size and ability to cross biological barriers.
- Common preparation methods include solvent evaporation, salting out, and nanoprecipitation.
- Particle size, surface charge, drug entrapment efficiency, and release kinetics are important characteristics to evaluate.
- Applications include cancer therapy, vaccines, and treatments requiring sustained or targeted drug delivery.Drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tract
Drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tractSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). It describes the key mechanisms of drug absorption including passive diffusion, carrier-mediated transport, pore transport, ionic diffusion, and vesicular transport. Factors that affect drug absorption are also covered, such as physicochemical properties like drug solubility and dissolution rate, particle size, polymorphism/amorphism, salt form, and lipophilicity. Pharmaceutical factors and patient-related factors that influence absorption are also outlined. The document provides detailed explanations of the various mechanisms and factors involved in drug absorption from the GIT.Pharmacokinetics&pharmacodynamics of biotechnological pdts
Pharmacokinetics&pharmacodynamics of biotechnological pdtsSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of biotechnological drugs including peptides, proteins, monoclonal antibodies, oligonucleotides, and gene therapy vectors. It covers topics such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of these drugs. For peptides and proteins, it describes various administration routes and challenges. For monoclonal antibodies, it discusses effector functions, modes of action, and characteristics. For oligonucleotides, it explains mechanisms of action and pharmacokinetics such as tissue distribution and excretion. Gene therapy methods using viral and non-viral vectors are also summarized.Modified release drug products
Modified release drug productsSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses modified release drug products, specifically extended release dosage forms. It defines extended release as releasing the drug over a longer period, usually twice as long as immediate release, to reduce dosing frequency and control blood concentrations. The document discusses the advantages of extended release including reduced dosing frequency and side effects. It also discusses factors that influence extended release kinetics like variable gastrointestinal conditions and the need to release the drug before it reaches the colon. Finally, it briefly outlines different types of extended release dosage forms.Biopharmaceutic considerations in drug product design and in
Biopharmaceutic considerations in drug product design and inSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses biopharmaceutic considerations in drug product design, focusing on various methods of dissolution testing and their significance for quality control and product performance. It outlines alternative dissolution testing methods, the necessity of calibration, and the importance of addressing variables that can affect dissolution results. Additionally, it highlights the challenges of meeting dissolution requirements and the relevance of different testing methods for various dosage forms.Computational modeling in drug disposition
Computational modeling in drug dispositionSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses computational modeling techniques for predicting drug disposition properties. It covers modeling approaches for drug absorption, distribution, and excretion. For absorption, it describes models for predicting solubility, intestinal permeability, and transporters. For distribution, it discusses models for volume of distribution, plasma protein binding, and blood-brain barrier permeability. For excretion, it summarizes models for hepatic and renal clearance. Current challenges include incorporating active transporters and generating predictive models from physiological understanding rather than empirical correlations.Ethics of computing in pharmaceutical research
Ethics of computing in pharmaceutical researchSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses the ethics of computing in pharmaceutical research. It addresses key issues like privacy, liability, ownership, and power. It outlines relevant codes of conduct for computer use, including those from the Association for Computing Machinery. The document also discusses how computers can be used for market analysis in the pharmaceutical industry, including facilitating information sharing, increasing competition, and potentially leading to higher prices for growers. It describes research conducted through surveys to understand industry acceptance of computer-aided marketing systems.Computers in pharmaceutical research and development
Computers in pharmaceutical research and developmentSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document provides an overview of the evolution of computers in pharmaceutical research and development from the 1940s to the 1990s, highlighting key milestones in computational chemistry and the integration of models in drug discovery processes. It discusses the transition from academic to industrial applications of computing in chemistry, the importance of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR), and the role of new technologies in enhancing drug development efficiency. It concludes by addressing the challenges and advancements related to statistical modeling in pharmaceutical research.Computational modelling of drug disposition active transport
Computational modelling of drug disposition active transportSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses computational modeling of active transport mechanisms that influence drug disposition. It summarizes modeling efforts for several major drug transporters, including P-glycoprotein (P-gp), Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP), nucleoside transporters, peptide transporter 1 (hPEPT1), Apical Sodium-dependent Bile Acid Transporter (ASBT), Organic Cation Transporters (OCTs), Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptides (OATPs), and the Blood Brain Barrier choline transporter. While transporter modeling has advanced, fully incorporating active transport into predictive models remains an ongoing challenge.Surfactants classification and application in cosmetics
Surfactants classification and application in cosmetics SUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses surfactants, their classification and applications in cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. Surfactants are amphipathic molecules with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail that lower surface tension. They are classified as anionic, cationic, non-ionic or amphoteric based on the nature of the hydrophilic group. Common applications include use as emulsifying agents, for foaming and cleansing purposes like in shampoos, and as wetting agents. Anionic, cationic, non-ionic and amphoteric surfactants are used for different purposes depending on their properties like detergency and foaming ability or mildness.Transport models biopharamaceutics
Transport models biopharamaceuticsSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses several key concepts related to drug transport and absorption:
1) The pH partition hypothesis states that acidic drugs are absorbed from acidic solutions and basic drugs from alkaline solutions, though some exceptions exist due to the microclimate pH near the membrane surface.
2) Tight junctions form a virtually impermeable barrier between cells, composed of sealing strands that prevent fluid passage.
3) According to Fick's first law, passive diffusion of solutes is determined by concentration gradients and membrane permeability. For ionizable drugs, the uncharged form is more permeable. The pH partition hypothesis relates permeability to pH and the fraction of uncharged molecules. targeted drug delivery slide
targeted drug delivery slideSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses Targeted Drug Delivery Systems (TDDS), which deliver pharmacologically active agents exclusively to their intended sites while minimizing toxicity. It outlines the objectives, concepts, ideal characteristics, various carrier systems, and targeting methods involved in TDDS. Additionally, it highlights the biological processes such as cellular uptake, transport across epithelial barriers, and extravasation essential for effective drug targeting.Emulsions and microemulsions- computer in pharmaceutical formulatation
Emulsions and microemulsions- computer in pharmaceutical formulatationSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses the role of computers in optimizing pharmaceutical formulations, focusing on emulsions and microemulsions as drug carriers. It outlines the definitions, types, stability issues, and preparation methods for emulsions and microemulsions, highlighting their applications and evaluation techniques. The content emphasizes the significance of emulsifying agents and theories of emulsification in enhancing stability and effectiveness in pharmaceutical applications.Viral and non viral gene transfer
Viral and non viral gene transferSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses gene transfer techniques, including viral and non-viral delivery systems. It describes gene therapy as using genes to treat disease by inserting a gene into a patient's cells instead of using drugs or surgery. It outlines various non-viral physical methods like gene guns, ultrasound, electroporation, and magnetofection and chemical methods like cationic liposomes and polymers to facilitate gene transfer. Viral vectors discussed include retroviruses, adenoviruses, and adeno-associated viruses. In conclusion, while progress has been made, developing safe and effective non-viral delivery systems for in vivo gene therapy remains a challenge.Monoclonal antibodies preparatation and applicatation
Monoclonal antibodies preparatation and applicatationSUJITHA MARY
╠²
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are identical antibodies produced by one type of immune cell that are directed against a specific antigen. They are produced through the fusion of B cells with myeloma cells to form hybridoma cells that can produce identical mAbs. mAbs have various applications including diagnostic uses in assays and imaging, therapeutic uses in cancer treatment and organ transplants, and research uses in protein purification. Their production involves immunizing mice with antigens, fusing spleen cells with myeloma cells, selecting antibody-producing hybridomas, and propagating the selected hybridoma cell lines to produce mAbs.Pulmonary drug delivery system
Pulmonary drug delivery systemSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses pulmonary drug delivery systems focusing on their benefits, technologies, and challenges. Pulmonary delivery is advantageous in targeted treatment of respiratory diseases, offering rapid effects and minimizing systemic side effects, but faces issues like low efficiency and formulation stability. Various aerosol types, inhalation devices, and methods for evaluating drug delivery effectiveness are also reviewed.Liposomsl gene delivery SYSTEM
Liposomsl gene delivery SYSTEMSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses liposomal gene delivery systems. It begins by defining liposomes and their use in encapsulating molecules for transport into cells. It then discusses gene therapy and the need for gene delivery systems. Liposomal gene delivery systems are introduced, with their principle being the use of cationic liposomes to condense and protect nucleic acids for delivery. The document covers the characteristics of liposomal systems, classifications of lipids used including cationic, neutral and anionic varieties, advantages and disadvantages of the approach, examples of uses, and conclusions about the variability and improvements in liposomal gene delivery formulations.Gene therapy types advantags disadvantages
Gene therapy types advantags disadvantagesSUJITHA MARY
╠²
Gene therapy involves inserting normal genes into patients to replace abnormal genes responsible for disease. There are two main types of gene therapy: ex vivo involves removing cells, modifying them, and reinserting them; in vivo delivers genes directly into target tissues. Viral and non-viral vectors are used to deliver genes. While gene therapy has potential to treat many diseases, it also has disadvantages like short-term effects and safety risks that must still be addressed.Microspheres types preparation evaluation and application
Microspheres types preparation evaluation and applicationSUJITHA MARY
╠²
Microspheres can be used to deliver drugs in a controlled manner. They are small spherical structures made of synthetic or natural polymers. Common preparation methods include single/double emulsion techniques, polymerization, coacervation, and solvent extraction. Drugs can be loaded during or after preparation. Release depends on degradation or diffusion properties. Microspheres find applications in taste masking, converting liquids to solids, sustained release, and targeted delivery. They allow controlled and targeted drug administration.INTRA NASEL ROUTE OF DRUG DELIVERY
INTRA NASEL ROUTE OF DRUG DELIVERYSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses various drug delivery systems for nasal administration including liquid nasal formulations, powder dosage forms, nasal gels and others. It describes the composition, preparation and evaluation of these nasal formulations. Some key delivery systems discussed are nasal drops, sprays, dry powder inhalers and metered dose inhalers. The document also outlines animal models and in vitro methods used to evaluate nasal absorption and permeation of drugs. Currently marketed nasal formulations containing xylometazoline and azelastine are also mentioned.Cosmetics regulations
Cosmetics regulationsSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document outlines the regulatory framework governing cosmetics in India under the Drug and Cosmetic Act of 1940, detailing definitions, import prohibitions, labeling requirements, and manufacturing guidelines. It highlights the penalties for offenses related to spurious and misbranded cosmetics, emphasizing the need for registration and quality standards as dictated by the Bureau of Indian Standards. Additionally, it covers the requirements for factory premises and equipment used in the manufacturing of cosmetics.ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdf
ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdfTechSoup
╠²
Accounting can be hard enough if you havenŌĆÖt studied it in school. Nonprofit accounting is actually very different and more challenging still.
Need help? Join Nonprofit CPA and QuickBooks expert Gregg Bossen in this first-time webinar and learn the ABCs of keeping books for a nonprofit organization.
Key takeaways
* What accounting is and how it works
* How to read a financial statement
* What financial statements should be given to the board each month
* What three things nonprofits are required to track
What features to use in QuickBooks to track programs and grants2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection.pptx
2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection.pptxmansk2
╠²
2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selectionMore Related Content
More from SUJITHA MARY (20)
Drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tract
Drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tractSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). It describes the key mechanisms of drug absorption including passive diffusion, carrier-mediated transport, pore transport, ionic diffusion, and vesicular transport. Factors that affect drug absorption are also covered, such as physicochemical properties like drug solubility and dissolution rate, particle size, polymorphism/amorphism, salt form, and lipophilicity. Pharmaceutical factors and patient-related factors that influence absorption are also outlined. The document provides detailed explanations of the various mechanisms and factors involved in drug absorption from the GIT.Pharmacokinetics&pharmacodynamics of biotechnological pdts
Pharmacokinetics&pharmacodynamics of biotechnological pdtsSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of biotechnological drugs including peptides, proteins, monoclonal antibodies, oligonucleotides, and gene therapy vectors. It covers topics such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of these drugs. For peptides and proteins, it describes various administration routes and challenges. For monoclonal antibodies, it discusses effector functions, modes of action, and characteristics. For oligonucleotides, it explains mechanisms of action and pharmacokinetics such as tissue distribution and excretion. Gene therapy methods using viral and non-viral vectors are also summarized.Modified release drug products
Modified release drug productsSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses modified release drug products, specifically extended release dosage forms. It defines extended release as releasing the drug over a longer period, usually twice as long as immediate release, to reduce dosing frequency and control blood concentrations. The document discusses the advantages of extended release including reduced dosing frequency and side effects. It also discusses factors that influence extended release kinetics like variable gastrointestinal conditions and the need to release the drug before it reaches the colon. Finally, it briefly outlines different types of extended release dosage forms.Biopharmaceutic considerations in drug product design and in
Biopharmaceutic considerations in drug product design and inSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses biopharmaceutic considerations in drug product design, focusing on various methods of dissolution testing and their significance for quality control and product performance. It outlines alternative dissolution testing methods, the necessity of calibration, and the importance of addressing variables that can affect dissolution results. Additionally, it highlights the challenges of meeting dissolution requirements and the relevance of different testing methods for various dosage forms.Computational modeling in drug disposition
Computational modeling in drug dispositionSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses computational modeling techniques for predicting drug disposition properties. It covers modeling approaches for drug absorption, distribution, and excretion. For absorption, it describes models for predicting solubility, intestinal permeability, and transporters. For distribution, it discusses models for volume of distribution, plasma protein binding, and blood-brain barrier permeability. For excretion, it summarizes models for hepatic and renal clearance. Current challenges include incorporating active transporters and generating predictive models from physiological understanding rather than empirical correlations.Ethics of computing in pharmaceutical research
Ethics of computing in pharmaceutical researchSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses the ethics of computing in pharmaceutical research. It addresses key issues like privacy, liability, ownership, and power. It outlines relevant codes of conduct for computer use, including those from the Association for Computing Machinery. The document also discusses how computers can be used for market analysis in the pharmaceutical industry, including facilitating information sharing, increasing competition, and potentially leading to higher prices for growers. It describes research conducted through surveys to understand industry acceptance of computer-aided marketing systems.Computers in pharmaceutical research and development
Computers in pharmaceutical research and developmentSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document provides an overview of the evolution of computers in pharmaceutical research and development from the 1940s to the 1990s, highlighting key milestones in computational chemistry and the integration of models in drug discovery processes. It discusses the transition from academic to industrial applications of computing in chemistry, the importance of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR), and the role of new technologies in enhancing drug development efficiency. It concludes by addressing the challenges and advancements related to statistical modeling in pharmaceutical research.Computational modelling of drug disposition active transport
Computational modelling of drug disposition active transportSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses computational modeling of active transport mechanisms that influence drug disposition. It summarizes modeling efforts for several major drug transporters, including P-glycoprotein (P-gp), Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP), nucleoside transporters, peptide transporter 1 (hPEPT1), Apical Sodium-dependent Bile Acid Transporter (ASBT), Organic Cation Transporters (OCTs), Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptides (OATPs), and the Blood Brain Barrier choline transporter. While transporter modeling has advanced, fully incorporating active transport into predictive models remains an ongoing challenge.Surfactants classification and application in cosmetics
Surfactants classification and application in cosmetics SUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses surfactants, their classification and applications in cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. Surfactants are amphipathic molecules with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail that lower surface tension. They are classified as anionic, cationic, non-ionic or amphoteric based on the nature of the hydrophilic group. Common applications include use as emulsifying agents, for foaming and cleansing purposes like in shampoos, and as wetting agents. Anionic, cationic, non-ionic and amphoteric surfactants are used for different purposes depending on their properties like detergency and foaming ability or mildness.Transport models biopharamaceutics
Transport models biopharamaceuticsSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses several key concepts related to drug transport and absorption:
1) The pH partition hypothesis states that acidic drugs are absorbed from acidic solutions and basic drugs from alkaline solutions, though some exceptions exist due to the microclimate pH near the membrane surface.
2) Tight junctions form a virtually impermeable barrier between cells, composed of sealing strands that prevent fluid passage.
3) According to Fick's first law, passive diffusion of solutes is determined by concentration gradients and membrane permeability. For ionizable drugs, the uncharged form is more permeable. The pH partition hypothesis relates permeability to pH and the fraction of uncharged molecules. targeted drug delivery slide
targeted drug delivery slideSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses Targeted Drug Delivery Systems (TDDS), which deliver pharmacologically active agents exclusively to their intended sites while minimizing toxicity. It outlines the objectives, concepts, ideal characteristics, various carrier systems, and targeting methods involved in TDDS. Additionally, it highlights the biological processes such as cellular uptake, transport across epithelial barriers, and extravasation essential for effective drug targeting.Emulsions and microemulsions- computer in pharmaceutical formulatation
Emulsions and microemulsions- computer in pharmaceutical formulatationSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses the role of computers in optimizing pharmaceutical formulations, focusing on emulsions and microemulsions as drug carriers. It outlines the definitions, types, stability issues, and preparation methods for emulsions and microemulsions, highlighting their applications and evaluation techniques. The content emphasizes the significance of emulsifying agents and theories of emulsification in enhancing stability and effectiveness in pharmaceutical applications.Viral and non viral gene transfer
Viral and non viral gene transferSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses gene transfer techniques, including viral and non-viral delivery systems. It describes gene therapy as using genes to treat disease by inserting a gene into a patient's cells instead of using drugs or surgery. It outlines various non-viral physical methods like gene guns, ultrasound, electroporation, and magnetofection and chemical methods like cationic liposomes and polymers to facilitate gene transfer. Viral vectors discussed include retroviruses, adenoviruses, and adeno-associated viruses. In conclusion, while progress has been made, developing safe and effective non-viral delivery systems for in vivo gene therapy remains a challenge.Monoclonal antibodies preparatation and applicatation
Monoclonal antibodies preparatation and applicatationSUJITHA MARY
╠²
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are identical antibodies produced by one type of immune cell that are directed against a specific antigen. They are produced through the fusion of B cells with myeloma cells to form hybridoma cells that can produce identical mAbs. mAbs have various applications including diagnostic uses in assays and imaging, therapeutic uses in cancer treatment and organ transplants, and research uses in protein purification. Their production involves immunizing mice with antigens, fusing spleen cells with myeloma cells, selecting antibody-producing hybridomas, and propagating the selected hybridoma cell lines to produce mAbs.Pulmonary drug delivery system
Pulmonary drug delivery systemSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses pulmonary drug delivery systems focusing on their benefits, technologies, and challenges. Pulmonary delivery is advantageous in targeted treatment of respiratory diseases, offering rapid effects and minimizing systemic side effects, but faces issues like low efficiency and formulation stability. Various aerosol types, inhalation devices, and methods for evaluating drug delivery effectiveness are also reviewed.Liposomsl gene delivery SYSTEM
Liposomsl gene delivery SYSTEMSUJITHA MARY
╠²
This document discusses liposomal gene delivery systems. It begins by defining liposomes and their use in encapsulating molecules for transport into cells. It then discusses gene therapy and the need for gene delivery systems. Liposomal gene delivery systems are introduced, with their principle being the use of cationic liposomes to condense and protect nucleic acids for delivery. The document covers the characteristics of liposomal systems, classifications of lipids used including cationic, neutral and anionic varieties, advantages and disadvantages of the approach, examples of uses, and conclusions about the variability and improvements in liposomal gene delivery formulations.Gene therapy types advantags disadvantages
Gene therapy types advantags disadvantagesSUJITHA MARY
╠²
Gene therapy involves inserting normal genes into patients to replace abnormal genes responsible for disease. There are two main types of gene therapy: ex vivo involves removing cells, modifying them, and reinserting them; in vivo delivers genes directly into target tissues. Viral and non-viral vectors are used to deliver genes. While gene therapy has potential to treat many diseases, it also has disadvantages like short-term effects and safety risks that must still be addressed.Microspheres types preparation evaluation and application
Microspheres types preparation evaluation and applicationSUJITHA MARY
╠²
Microspheres can be used to deliver drugs in a controlled manner. They are small spherical structures made of synthetic or natural polymers. Common preparation methods include single/double emulsion techniques, polymerization, coacervation, and solvent extraction. Drugs can be loaded during or after preparation. Release depends on degradation or diffusion properties. Microspheres find applications in taste masking, converting liquids to solids, sustained release, and targeted delivery. They allow controlled and targeted drug administration.INTRA NASEL ROUTE OF DRUG DELIVERY
INTRA NASEL ROUTE OF DRUG DELIVERYSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document discusses various drug delivery systems for nasal administration including liquid nasal formulations, powder dosage forms, nasal gels and others. It describes the composition, preparation and evaluation of these nasal formulations. Some key delivery systems discussed are nasal drops, sprays, dry powder inhalers and metered dose inhalers. The document also outlines animal models and in vitro methods used to evaluate nasal absorption and permeation of drugs. Currently marketed nasal formulations containing xylometazoline and azelastine are also mentioned.Cosmetics regulations
Cosmetics regulationsSUJITHA MARY
╠²
The document outlines the regulatory framework governing cosmetics in India under the Drug and Cosmetic Act of 1940, detailing definitions, import prohibitions, labeling requirements, and manufacturing guidelines. It highlights the penalties for offenses related to spurious and misbranded cosmetics, emphasizing the need for registration and quality standards as dictated by the Bureau of Indian Standards. Additionally, it covers the requirements for factory premises and equipment used in the manufacturing of cosmetics.Recently uploaded (20)
ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdf
ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdfTechSoup
╠²
Accounting can be hard enough if you havenŌĆÖt studied it in school. Nonprofit accounting is actually very different and more challenging still.
Need help? Join Nonprofit CPA and QuickBooks expert Gregg Bossen in this first-time webinar and learn the ABCs of keeping books for a nonprofit organization.
Key takeaways
* What accounting is and how it works
* How to read a financial statement
* What financial statements should be given to the board each month
* What three things nonprofits are required to track
What features to use in QuickBooks to track programs and grants2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection.pptx
2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection.pptxmansk2
╠²
2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selectionROLE PLAY: FIRST AID -CPR & RECOVERY POSITION.pptx
ROLE PLAY: FIRST AID -CPR & RECOVERY POSITION.pptxBelicia R.S
╠²
Role play : First Aid- CPR, Recovery position and Hand hygiene.
Scene 1: Three friends are shopping in a mall
Scene 2: One of the friend becomes victim to electric shock.
Scene 3: Arrival of a first aider
Steps:
Safety First
Evaluate the victimŌĆśs condition
Call for help
Perform CPR- Secure an open airway, Chest compression, Recuse breaths.
Put the victim in Recovery position if unconscious and breathing normally.
GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdf
GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdfSHERAZ AHMAD LONE
╠²
"Geography Study Material for Class 10th" provides a comprehensive and easy-to-understand resource for key topics like Resources & Development, Water Resources, Agriculture, Minerals & Energy, Manufacturing Industries, and Lifelines of the National Economy. Designed as per the latest NCERT/JKBOSE syllabus, it includes notes, maps, diagrams, and MODEL question Paper to help students excel in exams. Whether revising for exams or strengthening conceptual clarity, this material ensures effective learning and high scores. Perfect for last-minute revisions and structured study sessions.Paper 109 | Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes...
Paper 109 | Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes...Rajdeep Bavaliya
╠²
Get ready to embark on a cosmic quest as we unpack the archetypal power behind Christopher NolanŌĆÖs ŌĆśInterstellar.ŌĆÖ Discover how heroŌĆÖs journey tropes, mythic symbols like wormholes and tesseracts, and themes of love, sacrifice, and environmental urgency shape this epic odyssey. Whether youŌĆÖre a film theory buff or a casual viewer, youŌĆÖll learn why CooperŌĆÖs journey resonates with timeless mythsŌĆöand what it means for our own future. Smash that like button, and follow for more deep dives into cinemaŌĆÖs greatest stories!
M.A. Sem - 2 | Presentation
Presentation Season - 2
Paper - 109: Literary Theory & Criticism and Indian Aesthetics
Submitted Date: April 5, 2025
Paper Name: Literary Theory & Criticism and Indian Aesthetics
Topic: Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes in NolanŌĆÖs Cosmic Odyssey
[Please copy the link and paste it into any web browser to access the content.]
Video Link: https://youtu.be/vHLaLZPHumk
For a more in-depth discussion of this presentation, please visit the full blog post at the following link: https://rajdeepbavaliya2.blogspot.com/2025/04/archetypal-journeys-in-interstellar-exploring-universal-themes-in-nolan-s-cosmic-odyssey.html
Please visit this blog to explore additional presentations from this season:
Hashtags:
#ChristopherNolan #Interstellar #NolanFilms #HeroJourney #CosmicOdyssey #FilmTheory #ArchetypalCriticism #SciFiCinema #TimeDilation #EnvironmentalCinema #MythicStorytelling
Keyword Tags:
Interstellar analysis, Christopher Nolan archetypes, heroŌĆÖs journey explained, wormhole symbolism, tesseract meaning, myth in sci-fi, cinematic archetypes, environmental themes film, love across time, Nolan film breakdownHow to Manage Inventory Movement in Odoo 18 POS
How to Manage Inventory Movement in Odoo 18 POSCeline George
╠²
Inventory management in the Odoo 18 Point of Sale system is tightly integrated with the inventory module, offering a solution to businesses to manage sales and stock in one united system.Pests of Maize: An comprehensive overview.pptx
Pests of Maize: An comprehensive overview.pptxArshad Shaikh
╠²
Maize is susceptible to various pests that can significantly impact yields. Key pests include the fall armyworm, stem borers, cob earworms, shoot fly. These pests can cause extensive damage, from leaf feeding and stalk tunneling to grain destruction. Effective management strategies, such as integrated pest management (IPM), resistant varieties, biological control, and judicious use of chemicals, are essential to mitigate losses and ensure sustainable maize production.Introduction to Generative AI and Copilot.pdf
Introduction to Generative AI and Copilot.pdfTechSoup
╠²
In this engaging and insightful two-part webinar series, where we will dive into the essentials of generative AI, address key AI concerns, and demonstrate how nonprofits can benefit from using MicrosoftŌĆÖs AI assistant, Copilot, to achieve their goals.
This event series to help nonprofits obtain Copilot skills is made possible by generous support from Microsoft.Paper 108 | ThoreauŌĆÖs Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil Disobedience
Paper 108 | ThoreauŌĆÖs Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil DisobedienceRajdeep Bavaliya
╠²
Dive into the powerful journey from ThoreauŌĆÖs 19thŌĆæcentury essay to GandhiŌĆÖs mass movement, and discover how one manŌĆÖs moral stand became the backbone of nonviolent resistance worldwide. Learn how conscience met strategy to spark revolutions, and why their legacy still inspires todayŌĆÖs social justice warriors. Uncover the evolution of civil disobedience. DonŌĆÖt forget to like, share, and follow for more deep dives into the ideas that changed the world.
M.A. Sem - 2 | Presentation
Presentation Season - 2
Paper - 108: The American Literature
Submitted Date: April 2, 2025
Paper Name: The American Literature
Topic: ThoreauŌĆÖs Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil Disobedience
[Please copy the link and paste it into any web browser to access the content.]
Video Link: https://youtu.be/HXeq6utg7iQ
For a more in-depth discussion of this presentation, please visit the full blog post at the following link: https://rajdeepbavaliya2.blogspot.com/2025/04/thoreau-s-influence-on-gandhi-the-evolution-of-civil-disobedience.html
Please visit this blog to explore additional presentations from this season:
Hashtags:
#CivilDisobedience #ThoreauToGandhi #NonviolentResistance #Satyagraha #Transcendentalism #SocialJustice #HistoryUncovered #GandhiLegacy #ThoreauInfluence #PeacefulProtest
Keyword Tags:
civil disobedience, Thoreau, Gandhi, Satyagraha, nonviolent protest, transcendentalism, moral resistance, Gandhi Thoreau connection, social change, political philosophyRay Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big Cycle
Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big CycleDadang Solihin
╠²
A complete and practical understanding of the Big Debt Cycle. A much more practical understanding of how supply and demand really work compared to the conventional economic thinking. A complete and practical understanding of the Overall Big Cycle, which is driven by the Big Debt Cycle and the other major cycles, including the big political cycle within countries that changes political orders and the big geopolitical cycle that changes world orders.Revista digital preescolar en transformaci├│n
Revista digital preescolar en transformaci├│nguerragallardo26
╠²
EVOLUCI├ōN DEL CONTENIDO DE LA EVALUACI├ōN DE LOS RECURSOS Y DE LA FORMACI├ōN DE LOS DOCENTESECONOMICS, DISASTER MANAGEMENT, ROAD SAFETY - STUDY MATERIAL [10TH]
ECONOMICS, DISASTER MANAGEMENT, ROAD SAFETY - STUDY MATERIAL [10TH]SHERAZ AHMAD LONE
╠²
This study material for Class 10th covers the core subjects of Economics, Disaster Management, and Road Safety Education, developed strictly in line with the JKBOSE textbook. It presents the content in a simplified, structured, and student-friendly format, ensuring clarity in concepts. The material includes reframed explanations, flowcharts, infographics, and key point summaries to support better understanding and retention. Designed for classroom teaching and exam preparation, it aims to enhance comprehension, critical thinking, and practical awareness among students.Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
This presentation has been made keeping in mind the students of undergraduate and postgraduate level. In this slide try to present the brief history of Chaulukyas of Gujrat up to Kumarpala To keep the facts in a natural form and to display the material in more detail, the help of various books, websites and online medium has been taken. Whatever medium the material or facts have been taken from, an attempt has been made by the presenter to give their reference at the end.
Chaulukya or Solanki was one of the Rajputs born from Agnikul. In the Vadnagar inscription, the origin of this dynasty is told from Brahma's Chauluk or Kamandalu. They ruled in Gujarat from the latter half of the tenth century to the beginning of the thirteenth century. Their capital was in Anahilwad. It is not certain whether it had any relation with the Chalukya dynasty of the south or not. It is worth mentioning that the name of the dynasty of the south was 'Chaluky' while the dynasty of Gujarat has been called 'Chaulukya'. The rulers of this dynasty were the supporters and patrons of Jainism.Battle of Bookworms 2025 - U25 Literature Quiz by Pragya
Battle of Bookworms 2025 - U25 Literature Quiz by Pragya Pragya - UEM Kolkata Quiz Club
╠²
Battle of Bookworms is a literature quiz organized by Pragya, UEM Kolkata, as part of their cultural fest Ecstasia. Curated by quizmasters Drisana Bhattacharyya, Argha Saha, and Aniket Adhikari, the quiz was a dynamic mix of classical literature, modern writing, mythology, regional texts, and experimental literary forms. It began with a 20-question prelim round where ŌĆśstar questionsŌĆÖ played a key tie-breaking role. The top 8 teams moved into advanced rounds, where they faced audio-visual challenges, pounce/bounce formats, immunity tokens, and theme-based risk-reward questions. From Orwell and Hemingway to Tagore and Sarala Das, the quiz traversed a global and Indian literary landscape. Unique rounds explored slipstream fiction, constrained writing, adaptations, and true crime literature. It included signature IDs, character identifications, and open-pounce selections. Questions were crafted to test contextual understanding, narrative knowledge, and authorial intent, making the quiz both intellectually rewarding and culturally rich. Battle of Bookworms proved literature quizzes can be insightful, creative, and deeply enjoyable for all.YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptx
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
╠²
BLUF:
The Texas outbreak has slowed down, but sporadic cases continue to emerge in Kansas, Oklahoma, and New Mexico.
Elsewhere in the US, we continue to see signs of acceleration due to outbreaks outside the Southwest (North Dakota, Montana, and Colorado) and travel-related cases. Measles exposures due to travel are expected to pose a significant challenge throughout the summer.
The U.S. is on track to exceed its 30-year high for measles cases (1,274) within the next two weeks.
Here is the latest update:
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 919
ŌĆóTexas: 744 (+2) (55% of cases are in Gaines County).
ŌĆóNew Mexico: 81 (83% of cases are from Lea County).
ŌĆóOklahoma: 20 (+2)
ŌĆóKansas: 74 (+5) (38.89% of the cases are from Gray County).
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 104
ŌĆó Texas: 96 (+2) ŌĆō This accounts for 13% of all cases in Texas.
ŌĆó New Mexico: 7 ŌĆō This accounts for 9.47% of all cases in New Mexico.
ŌĆó Kansas: 3 ŌĆō This accounts for 5.08% of all cases in the state of Kansas.
DEATHS: 3
ŌĆóTexas: 2 ŌĆō This is 0.27% of all cases in Texas.
ŌĆóNew Mexico: 1 ŌĆō This is 1.23% of all cases in New Mexico.
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 1,197
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD
ŌĆóMexico: 2337 (+257), 5 fatalities
ŌĆÆChihuahua, Mexico: 2,179 (+239) cases, 4 fatalities, 7 currently hospitalized.
ŌĆóCanada: 3,207 (+208), 1 fatality
ŌĆÆOntario Outbreak, Canada: 2,115 (+74) cases, 158 hospitalizations, 1 fatality.
ŌĆÆAlberta, Canada: 879(+118) cases, 5 currently hospitalized.How to Manage Multi Language for Invoice in Odoo 18
How to Manage Multi Language for Invoice in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
Odoo supports multi-language functionality for invoices, allowing you to generate invoices in your customersŌĆÖ preferred languages. Multi-language support for invoices is crucial for businesses operating in global markets or dealing with customers from different linguistic backgrounds. Paper 109 | Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes...
Paper 109 | Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes...Rajdeep Bavaliya
╠²
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptx
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
╠²
Quality by deign
- 1. PREPARED BY SUJITHA MARY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR KVM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
