Quality Management - Cafeteria Analysis UGR
- 1. Cafeteria Analysis Quality Management ŌĆō Master in Economics Cristina Alcaide Mu├▒oz Carmen Olea Villoslada Federica Qualizza Desir├®e Su├Īrez Santana
- 2. Index ’éŚ Introduction ’éŚ Stratification ’éŚ General frequency ’éŚ Pareto Chart ’éŚ Frequent users ’éŚ Type service frequency ’éŚ Correlations ’éŚ Why-Why Diagram ’éŚ Ideas for improvements
- 3. Introduction ’éŚ The purpose of this study is to know customer satisfaction and provide some ideas to improve the cafeteria service. ’éŚ The questionnaire
- 4. Introduction ’éŚ Likert scale ’āś 1 Strongly disagree ’āś 2 Disagree ’āś 3 Neither disagree nor agree ’āś 4 Agree ’āś 5 Strongly agree ’éŚ Customers are satisfied with the cafeteria service. ’éŚ The cafeteria receives few complaints.
- 5. Stratification ŌĆóThe cafeteria receives few complaints. Type of service Years in the 14% Breakfast universty 11% Lunch 21% 50% 1 to 2 years 15% 34% 55% Afternoon 3 to 4 years snack 5 to 10 years Others Working 15% Yes 85% No
- 7. Pareto Chart
- 9. Type service frequency OTRO MIERENDA ALMUERZO DESAYUNO 0 20 40 60 DESAYUN ALMUERZ MIEREND OTRO O O A Bad quality/price rate 15 2 7 1 no good comunication between workers 9 2 3 1 Not clean 8 0 5 0 People are not treated well 6 0 4 1 Service is not fast 4 0 2 1
- 10. Correlations (I): table Commu- variables Speed Customer Quality/ Cleanli- nication Treatment Price ness between Ratio workers Correlation 1,000 ,639** ,518** ,465** ,603** Coefficient Speed Sig. (bilateral) . ,000 ,000 ,000 ,000 N 232 231 232 231 231 Correlation ,639** 1,000 ,479** ,548** ,625** Customer Coefficient treatment Sig. (bilateral) ,000 . ,000 ,000 ,000 N 231 233 233 232 232 Correlation ,518** ,479** 1,000 ,541** ,506** Quality/Price Coefficient Rho de Spearman ratio Sig. (bilateral) ,000 ,000 . ,000 ,000 N 232 233 234 233 233 Correlation ,465** ,548** ,541** 1,000 ,626** Coefficient Cleanliness Sig. (bilateral) ,000 ,000 ,000 . ,000 N 231 232 233 233 232 Correlation Communication Coefficient ,603** ,625** ,506** ,626** 1,000 between workers Sig. (bilateral) ,000 ,000 ,000 ,000 . N 231 232 233 232 233 **. The correlation is significant at 0.01 (bilateral)
- 11. University Correlations (I): table Years Correlation Coefficient 1,000 University Years Sig. (bilateral) . N 247 Correlation Coefficient ,150* Speed Sig. (bilateral) ,024 N 226 Correlation Coefficient ,101 Customer Treatment Sig. (bilateral) ,129 N 227 SpearmanŌĆÖs Ratio Correlation Coefficient ,107 Quality/Price Rate Sig. (bilateral) ,106 N 228 Correlation Coefficient ,202** Cleanliness Sig. (bilateral) ,002 N 227 Correlation Coefficient ,123 Sig. (bilateral) ,065 Communication between Workers N 227
- 12. INTERACTIONS RELATIONSHIP Correlations X Negative relationship ŌŚÅ Perfect Correlation XX Positive relationship ŌŚŗ Very Strong Correlation (II): matrix Ō¢Ī Strong Correlation ╬© Moderate Correlation ╬┤ Weak Correlation ŌŚŖ Not Correlation xx xx xx xx xx xx Customer Quality/Price Cleanli- Communication between University VARIABLES Speed treatment Rate ness workers Years Speed . Ō¢Ī ╬© ╬© Ō¢Ī ╬┤ Customer treatment Ō¢Ī . ╬© ╬© Ō¢Ī ŌŚŖ Quality/Price Rate ╬© ╬© . ╬© ╬© ŌŚŖ Cleanliness ╬© ╬© ╬© . Ō¢Ī ╬┤ Communication between workers Ō¢Ī Ō¢Ī ╬© Ō¢Ī . ŌŚŖ University Years ╬┤ ŌŚŖ ŌŚŖ ╬┤ ŌŚŖ .
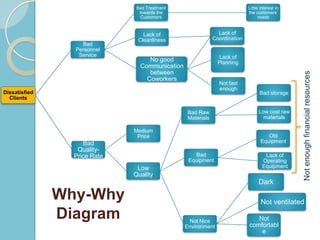
- 13. Bad Treatment Little interest in towards the the customersŌĆÖ Customers needs Lack of Lack of Lack of Cleanliness Coordination Coordination Bad Personnel Service Lack of No good Planning Communication between Not enough financial resources Coworkers Not fast enough Dissatisfied Bad storage Clients Bad Raw Low cost raw Materials materials Medium Price Old Bad Equipment Quality- Price Rate Bad Lack of Equipment Operating Low Equipment Quality Dark Why-Why Not ventilated Diagram Not Nice Not Environment comfortabl e
- 14. Ideas for improvements ’éŚ Cleaning right after the customer has left the table ’éŚ Better relationships with suppliers/new suppliers ’éŚ Investment in new equipment ’éŚ More flexibility ’éŚ Better communication ’éŚ More interest in customersŌĆÖ needs and opinions ’éŚ Another spatial distribution ’éŚ Customer service courses
- 15. Thank you for your attention!