Quantum Computing - Basic Concept .
- 1. Quantu m Comput ing Presented By - Mr. Prathamesh Devkar Mr. Suraj Bhujbal Mr. Ganesh Pasnurwar
- 2. Agenda ⢠What is Quantum Computer ⢠Basic Quantum Information ⢠Superposition & Entanglement ⢠Quantum Gates
- 3. What is Quantum Computer ? ⢠A quantum computer is a machine that performs calculations based on the laws of quantum mechanics, which is the behavior of particles at the sub-atomic level.
- 4. Why Quantum Computing ? Process massive amount of complex data in very less time than classical computer. It has ability to solve scientific and commercial problems, which never have even solved. Process data in a much faster speed than classical Computer. It has Capability to convey more accurate answers.
- 5. How Quantum Bit is different than Classical Bit ⢠In existing computers, all information is expressed in terms of 0's and 1's, and the entity that carries such information is called a "bit." ⢠A bit can be in either a 0 or 1 state at any one moment in time. ⢠A quantum computer, on the other hand, uses a "quantum bit" or "qubit" instead of a bit. ⢠A qubit also makes use of two states (0 and 1) to hold information, but in contrast to a bit, In this state, a qubit can take on the properties of 0 and 1 simultaneously at any one moment. ⢠Accordingly, two qubits in this state can express the four values of 00, 01, 10, and 11 all at one time.
- 7. Qubit Representation <Ï| is a row vector known as bra |Ï> is a column vector known as ket Ket : |a> = a1 Bra : <b| = ( b1,b2 ) a2 <b| = |b>+ = b1 + b2 Bra-Ket : <b|a> = a1b1 * + a2b2 * = <a|b>* Ket-Bra : |a><b| = a1b1 * a1b2 * a2b1 * a2b2 *
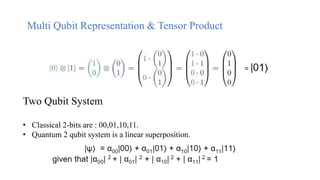
- 8. Multi Qubit Representation & Tensor Product Two Qubit System ⢠Classical 2-bits are : 00,01,10,11. ⢠Quantum 2 qubit system is a linear superposition.
- 9. Superposition ⢠Classical bits can only be found in the states 0 and 1 ⢠Qubit can represent the values 0 and 1, or linear combinations of both. ⢠These linear combinations are known as superpositions. ⢠|Ï> = α|0> + β|1> ,where |α|2 +|β|2 =1
- 10. Quantum Entanglement ⢠Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon wherein the quantum properties of two (or more) particles become codependent, with the properties of one being instantaneously affected by measurements conducted on the other. ⢠Example : A pair of electrons having opposite spins, with the actual spin of each particle remaining in a state of quantum uncertainty .On the separation of the pair of particles, even by a huge distance, and on measuring one particle's spin the other particle's spin will automatically resolve itself in the other direction. On the separation of the pair of This Photo by Unknown author is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND.
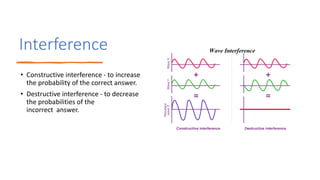
- 11. Interference ⢠Constructive interference - to increase the probability of the correct answer. ⢠Destructive interference - to decrease the probabilities of the incorrect answer.
- 12. Bloch Sphere The Bloch Sphere is a representation of a qubit, the fundamental building block of quantum computers. The most general state vector of a qubit can be expressed as where θ is the polar angle and Φ is the az-imuthal angle of the unit vector in 3-d real vector space.
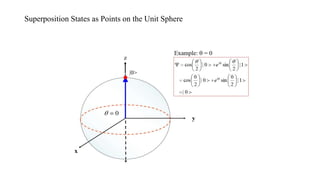
- 13. Superposition States as Points on the Unit Sphere
- 14. Superposition States as Points on the Unit Sphere
- 15. Superposition States as Points on the Unit Sphere
- 16. Superposition States as Points on the Unit Sphere
- 18. Quantum Gates Quantum gates and circuits are the quantum computing counterparts to classical logic gates and circuits, but with a dash of quantum weirdness. In classical computing, you manipulate bits using logical gates like AND, OR, and NOT. Quantum computing, being the quantum rebel it is, uses quantum gates to perform operations on qubits
- 22. Thank You