Quick Start Tutorial of KH Coder 2: Quantitative Content Analysis or Text Mining of English Language Data
- 1. Quick Start Tutorial of KH Coder: Quantitative Content Analysis or Text Mining of English Language Data Koichi Higuchi 1
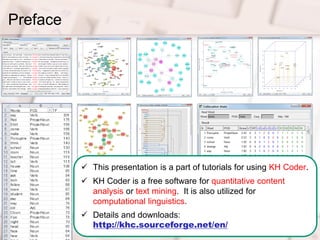
- 2. 2 Preface ? This presentation is a part of tutorials for using KH Coder. ? KH Coder is a free software for quantitative content analysis or text mining. It is also utilized for computational linguistics. ? Details and downloads: http://khc.sourceforge.net/en/
- 3. Table of Contents 3 Configure KH Coder for English speaking people / English data ? 1. Change the interface language to English ? 2. Settings for analyzing English text ? Notes on the stopwords Create a new project and prepare for analysis ? 3. Create a new project ? 4. Run pre-processing Frequently appeared words and co-occurrences ? 5. Word frequency list ? 6. KWIC and collocation stats ? 7. Co-occurrence network of words ? Methods for exploring co-occurrences of words Characteristics of each chapter ? 8. Distinctive words of each chapter ? 9. Correspondence analysis of words and chapters Coding Rules ? Use coding rules to count concepts ? 10. Search documents with coding rules ? 11. Cross tabulation of the codes
- 4. 1. Change the Interface Language to English 4 Choose ¡°English¡± here and restart KH Coder. If you prefer the Japanese interface, you may skip this step. You may also change the interface font. Go to [Project] [Settings] in the menubar.
- 5. 2. Settings for Analyzing English Text 5 (1) Go to [Project] [Settings] in the menubar. (2) Select ¡°Lemmatization.¡± (3) Click ¡°config.¡± (4) Open the ¡°tutorial_en¡± folder, then drag the file ¡°stopwords_sample_en.txt¡± and drop here. (Or just paste the content of the file here) (5) Click ¡°OK.¡±(6) Click ¡°OK.¡±
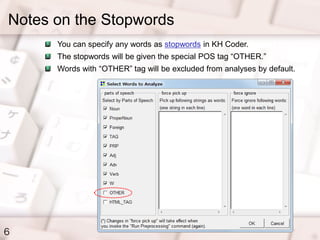
- 6. Notes on the Stopwords 6 You can specify any words as stopwords in KH Coder. The stopwords will be given the special POS tag ¡°OTHER.¡± Words with ¡°OTHER¡± tag will be excluded from analyses by default.
- 7. 3. Create a New Project 7 (1) Go to [Project] [New] in the menubar. (2) Click ¡°Browse¡± and open the file ¡°tutorial_en/botchan_en.txt¡± (3) fill in whatever memo you like (4) Click ¡°OK.¡± In this tutorial we analyze a novel ¡°Botchan¡± by Soseki. ¡°botchan_en.txt¡± contains all 11 chapters of the novel. Chapter headings are marked with h1 tag Next time you start KH Coder, go to [Project] [Open] in the menubar and open the project you have created here.
- 8. 4. Run Pre-Processing 8 Go to [Pre-Processing] [Run Pre-Processing] in the menubar. Then click ¡°OK.¡± Sentence splitting, tokenization, POS tagging and lemmatization are performed. The results are compiled into MySQL database for searching and statistical analysis. When processing data, KH Coder ¡°concentrates¡± on the job. So sometimes it looks frozen. But it is normal when CPU or disk is busy.
- 9. 5. Word Frequency List 9 Go to [Tools] [Words] [Frequency List] in the menubar. These are counts of base forms / lemmas
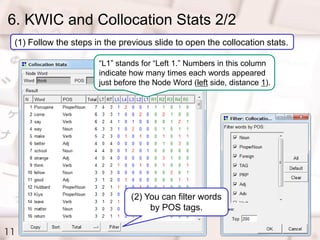
- 10. 6. KWIC and Collocation Stats 1/2 10 (1) Go to [Tools] [Words] [KWIC Concordance] in the menubar. (2) Input a base form of a word and hit ¡°Enter¡± on the keybord When you change sort options, click ¡°Search¡± button again. Double click any line to view wider contexts. You can change viewing Units below. (3) Click ¡°Stats¡± to open the collocation stats.
- 11. 6. KWIC and Collocation Stats 2/2 11 (1) Follow the steps in the previous slide to open the collocation stats. (2) You can filter words by POS tags. ¡°L1¡± stands for ¡°Left 1.¡± Numbers in this column indicate how many times each words appeared just before the Node Word (left side, distance 1).
- 12. 7. Co-Occurrence Network of Words 12 (3) Click ¡°Config¡± and check ¡°Larger nodes for higher frequency words¡±, then lick ¡°OK.¡± Now you can see a co-occurrence network of high frequency words in the text. The color change from blue (low) to pink (high). It indicates the centrality index. (1) Go to [Tools] [Words] [Co-Occurrence Network] in the menubar. (2) Select ¡°Paragraphs¡± as Unit, then click ¡°OK¡± (4) Click ¡°Config¡± and increase ¡°edges¡± (co- occurences) to ¡°top 100,¡± then lick ¡°OK.¡± (5) Select ¡°Community: modularity¡± as ¡°color.¡± Which version did you like?
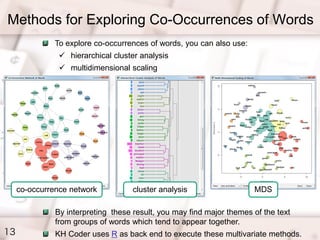
- 13. Methods for Exploring Co-Occurrences of Words 13 To explore co-occurrences of words, you can also use: ? hierarchical cluster analysis ? multidimensional scaling co-occurrence network cluster analysis MDS By interpreting these result, you may find major themes of the text from groups of words which tend to appear together. KH Coder uses R as back end to execute these multivariate methods.
- 14. 8. Distinctive Words of Each Chapter 14 (2) Click ¡°Heading 1.¡± Top 10 distinctive words of each chapter are tabulated. The ¡°distinctiveness¡± is calculated using Jaccard index. Basically, if a word shows larger probability of appearance in a specific chapter, It¡¯s considered distinctive. (1) Go to [Tools] [Variables & Headings] [List] in the menubar. (3) Select ¡°Sentences.¡± (4) Select ¡°catalogue: Excel.¡±
- 15. 9. Correspondence Analysis of Words and Chapters 15 (2) Click ¡°OK¡± Using correspondence analysis, you can visually interpret characteristics of each chapter. (1) Go to [Tools] [Words] [Correspondence Analysis] in the menubar. (3) Click ¡°Config¡±, then reduce words to ¡°Top 30,¡± check ¡°Bubble plot,¡± uncheck ¡°Size of variables...,¡± and click ¡°OK.¡± (This step is optional.)
- 16. Use Coding Rules to Count Concepts 16 In some cases, we have to count concepts, not words. To count concepts, you can compose ¡°cording rules¡± like this: *shopping store or shop or ( merchandise and not develop ) Indicates the name of this code. The conditions for attaching this code. Cases that contain words like store and shop are given the code ¡°shopping.¡± The parenthetical notation means that cases should contain the word ¡°merchandise¡± but should not contain the word ¡°develop.¡± If a case is acceptable under multiple coding rules, multiple codes will be given to the case. We use ¡°tutorial_en/themes.txt¡± as example coding rules in this tutorial. Please open this file and check the content.
- 17. 10. Search Documents with Coding Rules 17 (1) Go to [Tools] [Documents] [Search Documents] in the menubar. (2) Click ¡°Browse¡± and select ¡°tutorial_en/themes.txt¡± (3) Select ¡°Paragraphs¡± (4) Double click a code (5) Double click a result to view the whole paragraph. When you compose a coding rule, it is important to search and check the actual documents which are acceptable under the rule.
- 18. 11. Cross Tabulation of Codes 18 (1) Go to [Tools] [Coding] [Crosstab] in the menubar. (2) Click ¡°Browse¡± and select ¡°tutorial_en/themes.txt¡± (3) Select ¡°Sentences¡± (5) Click ¡°all¡± to make a graph. In the latter half of the novel, it looks like ¡°aggression¡± overwhelms ¡°positive affect¡± and forms the climax of the story at chapter X. (4) Click ¡°Run¡±
- 19. Acknowledgement I am grateful to students who attended the 2011 ¡°text mining¡± class at Doshisha University (Faculty of Culture and Information Science) for giving me some hints on composing coding rules for ¡°Botchan.¡± Questions or Comments? Please feel free to post questions or comments at web forum here: https://sourceforge.net/p/khc/discussion/


![1. Change the Interface Language to English
4
Choose ¡°English¡± here
and restart KH Coder.
If you prefer the Japanese interface, you may skip this step.
You may also change the interface font.
Go to [Project] [Settings] in the menubar.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-4-320.jpg)
![2. Settings for Analyzing English Text
5
(1) Go to [Project] [Settings] in the menubar.
(2) Select ¡°Lemmatization.¡±
(3) Click ¡°config.¡±
(4) Open the ¡°tutorial_en¡±
folder, then drag the file
¡°stopwords_sample_en.txt¡±
and drop here. (Or just paste
the content of the file here)
(5) Click ¡°OK.¡±(6) Click ¡°OK.¡±](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-5-320.jpg)
![3. Create a New Project
7
(1) Go to [Project] [New] in the menubar.
(2) Click ¡°Browse¡± and open the file
¡°tutorial_en/botchan_en.txt¡±
(3) fill in whatever
memo you like
(4) Click ¡°OK.¡±
In this tutorial we analyze a
novel ¡°Botchan¡± by Soseki.
¡°botchan_en.txt¡± contains all 11
chapters of the novel.
Chapter headings are marked
with h1 tag
Next time you start KH Coder,
go to [Project] [Open] in the
menubar and open the project
you have created here.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-7-320.jpg)
![4. Run Pre-Processing
8
Go to [Pre-Processing] [Run Pre-Processing]
in the menubar. Then click ¡°OK.¡±
Sentence splitting, tokenization, POS tagging
and lemmatization are performed.
The results are compiled into MySQL database
for searching and statistical analysis.
When processing data, KH Coder
¡°concentrates¡± on the job. So sometimes it
looks frozen. But it is normal when CPU or disk
is busy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-8-320.jpg)
![5. Word Frequency List
9
Go to [Tools] [Words] [Frequency List] in the menubar.
These are counts of base forms / lemmas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-9-320.jpg)
![6. KWIC and Collocation Stats 1/2
10
(1) Go to [Tools] [Words] [KWIC Concordance] in the menubar.
(2) Input a base form of a word
and hit ¡°Enter¡± on the keybord
When you change sort options,
click ¡°Search¡± button again.
Double click any line to view
wider contexts. You can
change viewing Units below.
(3) Click ¡°Stats¡± to open
the collocation stats.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-10-320.jpg)
![7. Co-Occurrence Network of Words
12
(3) Click ¡°Config¡± and check ¡°Larger nodes
for higher frequency words¡±, then lick ¡°OK.¡±
Now you can see a co-occurrence network of high frequency words in the text.
The color change from blue (low) to pink (high). It indicates the centrality index.
(1) Go to [Tools] [Words] [Co-Occurrence Network] in the menubar.
(2) Select ¡°Paragraphs¡± as Unit, then click ¡°OK¡±
(4) Click ¡°Config¡± and increase ¡°edges¡± (co-
occurences) to ¡°top 100,¡± then lick ¡°OK.¡±
(5) Select ¡°Community: modularity¡± as ¡°color.¡±
Which version did you like?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-12-320.jpg)
![8. Distinctive Words of Each Chapter
14
(2) Click ¡°Heading 1.¡±
Top 10 distinctive words of each chapter
are tabulated. The ¡°distinctiveness¡± is
calculated using Jaccard index.
Basically, if a word shows larger
probability of appearance in a specific
chapter, It¡¯s considered distinctive.
(1) Go to [Tools] [Variables & Headings] [List] in the menubar.
(3) Select ¡°Sentences.¡±
(4) Select ¡°catalogue: Excel.¡±](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-14-320.jpg)
![9. Correspondence Analysis of Words and Chapters
15
(2) Click ¡°OK¡±
Using correspondence analysis,
you can visually interpret
characteristics of each chapter.
(1) Go to [Tools] [Words] [Correspondence Analysis] in the menubar.
(3) Click ¡°Config¡±, then reduce words
to ¡°Top 30,¡± check ¡°Bubble plot,¡±
uncheck ¡°Size of variables...,¡± and
click ¡°OK.¡± (This step is optional.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-15-320.jpg)

![10. Search Documents with Coding Rules
17
(1) Go to [Tools] [Documents] [Search Documents] in the menubar.
(2) Click ¡°Browse¡± and select
¡°tutorial_en/themes.txt¡±
(3) Select ¡°Paragraphs¡±
(4) Double click a code
(5) Double click a result to
view the whole paragraph. When you compose a coding
rule, it is important to search and
check the actual documents
which are acceptable under the
rule.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-17-320.jpg)
![11. Cross Tabulation of Codes
18
(1) Go to [Tools] [Coding] [Crosstab] in the menubar.
(2) Click ¡°Browse¡± and select
¡°tutorial_en/themes.txt¡±
(3) Select ¡°Sentences¡±
(5) Click ¡°all¡± to
make a graph.
In the latter half of the novel,
it looks like ¡°aggression¡±
overwhelms ¡°positive affect¡±
and forms the climax of the
story at chapter X.
(4) Click ¡°Run¡±](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readmeengmain-120227061748-phpapp02/85/Quick-Start-Tutorial-of-KH-Coder-2-Quantitative-Content-Analysis-or-Text-Mining-of-English-Language-Data-18-320.jpg)