Railway loco ppt
- 1. RISHIRAJ INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY TECHNICAL TRAINING REPORT ON ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE WORKSHOP PRESENTED BY:ANAND DWIVEDI (0817EC101020) EC 4TH YEAR 1
- 2. CONTENT âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ INTRODUCTION HISTORY OVERVIEW OF E. L. PARTS OF E. L. INTERNAL PARTS OF CAB FRONT VIEW OF THE LOCO LOWER FRONT VIEW ADVANTAGES OF 3-Éļ ADVANTAGES OF E.L. CONCLUSION 2
- 3. INTRODUCTION âĒ Locomotives in india consist of electric and diesel locomotives. Locomotives are also called locos or engines. âĒ An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, an on-board energy storage device such as a chemical battery or fuel cell. âĒ Electricity is used to eliminate smoke and take advantage of the high efficiency of electric motors. 3
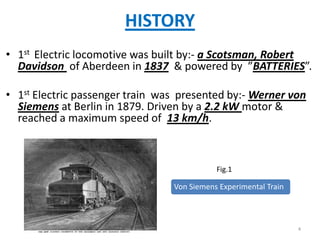
- 4. HISTORY âĒ 1st Electric locomotive was built by:- a Scotsman, Robert Davidson of Aberdeen in 1837 & powered by âBATTERIESâ. âĒ 1st Electric passenger train was presented by:- Werner von Siemens at Berlin in 1879. Driven by a 2.2 kW motor & reached a maximum speed of 13 km/h. Fig.1 Von Siemens Experimental Train 4
- 5. HISTORY âĒ Railways first introduced to India in 1853 & journeyed of 22 miles Between Bombay to Thane. Fig.2 5
- 6. OVERVIEW OF ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE âĒ Now a days all locos are running through Electricity with the help of OHE line. âĒ Pentagraph is used to connect the loco with OHE line. âĒ Loco contains 2 Bogies, each Bogie consist of 6 wheels. So totally loco consists of 12 wheels. âĒ Pantagraph draws 25 KV of electricity from OHE line, which is very high AC voltage. Fig.3 Pentagraph 6
- 7. Parts Of Electric Locomotive âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ Transformer Rectifier Arno Convertor Traction Motors Air Compressors Motor-Alternator 7
- 8. âĒ Electrical equipments generate a lot of heat during their normal operation. âĒ Hence the different auxiliaries provided for cooling and other purposes. These locos is described below:- 8
- 9. TRANSFORMER âĒ Transformer Oil Circulating Pump. âĒ Transformer Oil Cooling Radiator Blower. Fig.4 9
- 15. INTERNAL PARTS OF CAB âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ Buzzers RHS Loco Control Desk Central Portion Ammeters & Voltmeters LHS Corner Of The Cab Brake Air Pressure Gauges Transformer Smoothening Reactors DJ Main Contactor 15
- 17. A view of the RHS corner of the loco control desk âĒ "A" - Horn valves âĒ "B" - Emergency brake flap âĒ "C" - Flasher light control unit âĒ "D" - Marker lamps control unit Fig.11 17
- 18. A view of the central portion of the control desk âĒ âĒ âĒ âĒ NR2 ZPT2 ZLC1 & ZLC2 BPISX Fig.12 18
- 19. Ammeters & Voltmeters âĒ AM4 TM4 âĒ U-5 TM-5 âĒ U-6 TM-6 âĒ UA-2 Fig.13 19
- 20. A view of the LHS corner of the cab Fig.14 20
- 21. A Close View Of The Brake Air Pressure Gauges Fig.15 21
- 22. TRANSFORMER âĒ The transformer that steps down 110 volts from the batteries to 32 volts. Fig.16 22
- 25. Front view of the loco Fig.19 25
- 26. Lower front view of the loco Fig.20 26
- 28. ADVANTAGES OF THREE PHASE TECHNOLOGY âĒ It Require little maintenance. âĒ 3-Éļ drive allows regeneration and unity power factor operation. âĒ It improves operational efficiency besides reduction in maintenance efforts. The energy saving due to regeneration and improved power factor sizable. 28
- 29. ADVANTAGES OF ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE âĒ Electric engines do not produce much heat and noise. âĒ Electric engines are therefore easier to maintain whereas the moving parts of a diesel engine require constant maintenance. âĒ The simple nature of the electric engine makes them efficient and powerful. 29
- 30. ADVANTAGES OF ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE âĒ Electric engines are light weight, constituting only motors and wheel axles, and have almost no moving parts. âĒ Do Not Produce Smock. Fig.23 DIESEL LOCOMOTIVE 30
- 31. CONCLUSION âĒ Main Objective was to learn electric locomotive In Railways. âĒ I am thankful to the supporting people of the POH Bhusawal. âĒ Electricity is used to eliminate smoke and take advantage of the high efficiency of electric motors. 31
- 32. 32
- 33. ? 33