Ratesofreaction (1)
- 1. 1 of 39 ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 2007
- 2. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 20072 of 39
- 3. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 20073 of 39 What does rate of reaction mean? The speed of different chemical reactions varies hugely. Some reactions are very fast and others are very slow. What is the rate of these reactions? The speed of a reaction is called the rate of the reaction. rusting baking explosion slow fast very fast
- 4. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 20074 of 39 Rates of reaction Why are some reactions faster than others?
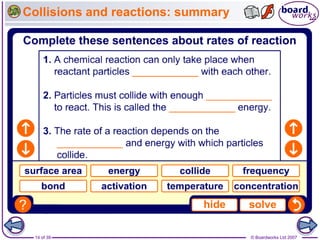
- 5. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 20075 of 39 Reactions, particles and collisions Reactions take place when particles collide with a certain amount of energy. The minimum amount of energy needed for the particles to react is called the activation energy, and is different for each reaction. The rate of a reaction depends on two things: ïŽ the frequency of collisions between particles ïŽ the energy with which particles collide. If particles collide with less energy than the activation energy, they will not react. The particles will just bounce off each other.
- 6. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 20076 of 39 Changing the rate of reactions ïŽ increased temperature ïŽ increased concentration of dissolved reactants, and increased pressure of gaseous reactants ïŽ increased surface area of solid reactants ïŽ use of a catalyst. Anything that increases the number of successful collisions between reactant particles will speed up a reaction. What factors affect the rate of reactions?
- 7. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 20077 of 39 Slower and slower! Reactions do not proceed at a steady rate. They start off at a certain speed, then get slower and slower until they stop. As the reaction progresses, the concentration of reactants decreases. This reduces the frequency of collisions between particles and so the reaction slows down. percentage completion of reaction 100%0% 25% 50% 75% reactants product
- 8. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 20078 of 39 Graphing rates of reaction
- 9. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 20079 of 39 Reactantâproduct mix
- 10. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200710 of 39 How can rate of reaction be measured? Measuring the rate of a reaction means measuring the change in the amount of a reactant or the amount of a product. What can be measured to calculate the rate of reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid? ïŽ The amount of hydrochloric acid used up (cm3/min). ïŽ The amount of magnesium chloride produced (g/min). ïŽ The amount of hydrogen product (cm3/min). +magnesium hydrochloric acid +ïĻ magnesium chloride hydrogen
- 11. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200711 of 39 Setting up rate experiments What equipment is needed to investigate the rate of hydrogen production? gas syringe rubber bung rubber connecterglass tube conical flask magnesium hydrochloric acid
- 12. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200712 of 39 hydrogenproduced(cm3) time (seconds) 10 20 30 40 50 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 0 0 x y Calculating rate of reaction from graphs rate of reaction = x y rate of reaction = 20s 45cm3 rate of reaction = 2.25cm3/s The gradient of the graph is equal to the initial rate of reaction at that time How can the rate of reaction be calculated from a graph?
- 13. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200713 of 39 The reactant/product mix
- 14. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200714 of 39 Collisions and reactions: summary
- 15. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200715 of 39
- 16. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200716 of 39 Temperature and collisions How does temperature affect the rate of particle collision?
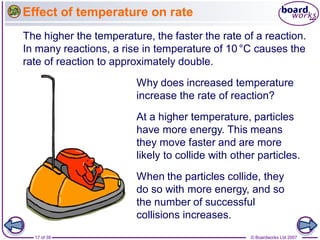
- 17. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200717 of 39 Effect of temperature on rate The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of a reaction. In many reactions, a rise in temperature of 10°C causes the rate of reaction to approximately double. Why does increased temperature increase the rate of reaction? At a higher temperature, particles have more energy. This means they move faster and are more likely to collide with other particles. When the particles collide, they do so with more energy, and so the number of successful collisions increases.
- 18. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200718 of 39 Temperature and particle collisions
- 19. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200719 of 39 Temperature and batteries Why are batteries more likely to rundown more quickly in cold weather? At low temperatures the reaction that generates the electric current proceeds more slowly than at higher temperatures. This means batteries are less likely to deliver enough current to meet demand.
- 20. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200720 of 39 How does temperature affect rate? The reaction between sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid produces sulfur. Sulfur is solid and so it turns the solution cloudy. How can this fact be used to measure the effect of temperature on rate of reaction? hydrochloric acid sodium chloride sulfur sodium thiosulfate + +ïĻ water sulfur dioxide ++ Na2S2O3 (aq) 2HCl (aq) 2NaCl (aq) S (s)++ ïĻ SO2 (g) H2O (l)+ +
- 21. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200721 of 39 The effect of temperature on rate
- 22. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200722 of 39
- 23. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200723 of 39 Effect of concentration on rate of reaction The higher the concentration of a dissolved reactant, the faster the rate of a reaction. Why does increased concentration increase the rate of reaction? At a higher concentration, there are more particles in the same amount of space. This means that the particles are more likely to collide and therefore more likely to react. higher concentrationlower concentration
- 24. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200724 of 39 Concentration and particle collisions
- 25. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200725 of 39 The effect of concentration on rate
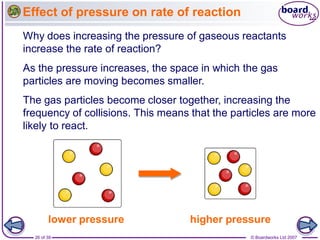
- 26. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200726 of 39 Effect of pressure on rate of reaction The gas particles become closer together, increasing the frequency of collisions. This means that the particles are more likely to react. Why does increasing the pressure of gaseous reactants increase the rate of reaction? As the pressure increases, the space in which the gas particles are moving becomes smaller. lower pressure higher pressure
- 27. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200727 of 39
- 28. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200728 of 39 Effect of surface area on rate of reaction Any reaction involving a solid can only take place at the surface of the solid. If the solid is split into several pieces, the surface area increases. What effect will this have on rate of reaction? The smaller the pieces, the larger the surface area. This means more collisions and a greater chance of reaction. This means that there is an increased area for the reactant particles to collide with. low surface area high surface area
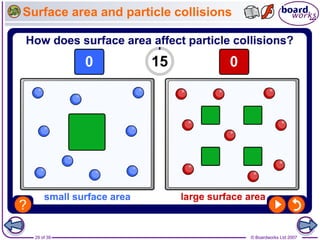
- 29. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200729 of 39 Surface area and particle collisions
- 30. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200730 of 39 Reaction between a carbonate and acid Marble chips are made of calcium carbonate. They react with hydrochloric acid to produce carbon dioxide. The effect of increasing surface area on the rate of reaction can be measured by comparing how quickly the mass of the reactants decreases using marble chips of different sizes. hydrochloric acid calcium chloride calcium carbonate + +ïĻ water + carbon dioxide CaCO3 (aq) 2HCl (aq) CaCl2 (aq) ++ ïĻ H2O (aq) + CO2 (g)
- 31. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200731 of 39 The effect of surface area on rate
- 32. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200732 of 39 reaction (time) energy(kJ) What are catalysts? Catalysts are substances that change the rate of a reaction without being used up in the reaction. Catalysts never produce more product â they just produce the same amount more quickly. Different catalysts work in different ways, but most lower the reactionâs activation energy (Ea). Ea with catalyst Ea without catalyst
- 33. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200733 of 39 Everyday catalysts ïŽ Nickel is a catalyst in the production of margarine (hydrogenation of vegetable oils). Many catalysts are transition metals or their compounds. For example: ïŽ Platinum is a catalyst in the catalytic converters of car exhausts. It catalyzes the conversion of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide into the less polluting carbon dioxide and nitrogen. ïŽ Iron is a catalyst in the production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen (the Haber process).
- 34. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200734 of 39 Catalysts in industry Catalysts are also essential for living cells. Biological catalysts are special types of protein called enzymes. Why are catalysts so important for industry? ïŽ Products can be made more quickly, saving time and money. ïŽ Catalysts reduce the need for high temperatures, saving fuel and reducing pollution.
- 35. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200735 of 39
- 36. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200736 of 39 Glossary ïŽ activation energy â The amount of energy needed to start a reaction. ïŽ catalyst â A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up. ïŽ concentration â The number of molecules of a substance in a given volume. ïŽ enzyme â A biological catalyst. ïŽ rate of reaction â The change in the concentration over a certain period of time.
- 37. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200737 of 39 Anagrams
- 38. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200738 of 39 Rates of reaction: summary
- 39. ÂĐ Boardworks Ltd 200739 of 39 Multiple-choice quiz