R&D Progression Bias and Rational Optimism
- 1. RATIONAL OPTIMISM IN RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT Dennis Lendrem
- 2. RATIONAL OPTIMISM IN RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT Dennis Lendrem
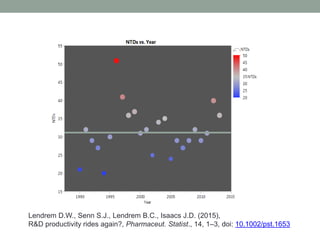
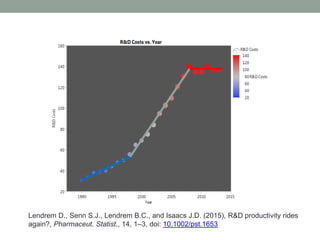
- 3. Lendrem D.W., Senn S.J., Lendrem B.C., Isaacs J.D. (2015), R&D productivity rides again?, Pharmaceut. Statist., 14, 1â3, doi: 10.1002/pst.1653
- 4. Lendrem D., Senn S.J., Lendrem B.C., and Isaacs J.D. (2015), R&D productivity rides again?, Pharmaceut. Statist., 14, 1â3, doi: 10.1002/pst.1653
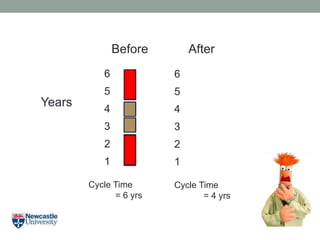
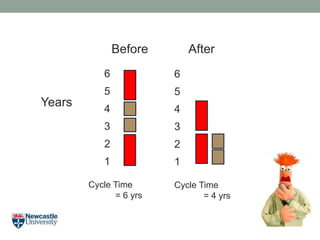
- 5. Years Cycle Time = 4 yrs 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cycle Time = 6 yrs 1 2 3 4 5 6 Before After
- 6. Years Cycle Time = 4 yrs 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cycle Time = 6 yrs 1 2 3 4 5 6 Before After
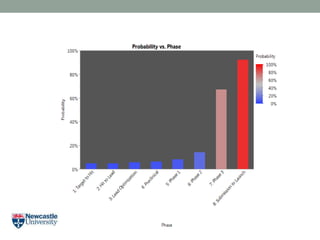
- 7. Rational Optimism âĒ By placing tasks in parallel to reduce cycle time we inadvertently: âĒ Increased R&D costs âĒ Increased late-stage attrition rates âĒ Increased expected time to market
- 8. Rational Optimism âĒ By placing tasks in parallel to reduce cycle time we inadvertently: âĒ Increased R&D costs âĒ Increased late-stage attrition rates âĒ Increased expected time to market Lendrem DW, Lendrem BC Torching the Haystack: Modelling fast-fail strategies in drug development. Drug Discov Today. 2013 Apr;18(7-8):331-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2012.11.011 Lendrem DW, Lendrem BC The Development Speed Paradox: Can increasing development speed reduce R&D productivity? Drug Discov Today. 2014 Mar;9(3):209-214 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2013.09.002
- 9. Rational Optimism Looking for a needle in a haystack? Torch the haystack.
- 10. Rational Optimism âĒ It is more important to do the right science than to do the wrong science quickly. âĒ Build opportunities to kill projects earlier in the development cycle. âĒ Focus on tests that prevent projects from entering the development process. âĒ Focus on tests that allow elimination of projects early in the development process.
- 12. Rational Optimism âĒ Progression Bias âĒ terminations are viewed as âlossesâ and project teams are loss- averse âĒ sunk-costs fallacy â terminating a project risks losing investment that has already been lost âĒ marginal cost associated with a decision to continue development may seem trivial compared to the losses associated with terminating a potential NTD âĒ organizational and market incentives to load the pipeline with âpromisingâ candidates âĒ Progression bias leads to continued development even in the light of strong evidence supporting termination.
- 13. Rational Optimism âĒ Rational Optimism âĒ Continued pursuit of a line of research in the knowledge that it is likely to be successful.
- 14. Rational Optimism âĒ Rational Optimism âĒ Continued pursuit of a line of research in the knowledge that it is likely to be successful. âĒ Mindless Optimism âĒ Continued pursuit of a line of research in the hope that it will be successful.
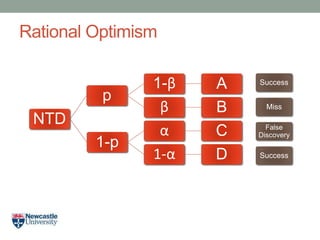
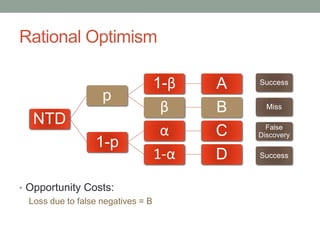
- 16. Rational Optimism NTD p 1-Îē A Îē B 1-p Îą C 1-Îą D Success Miss False Discovery Success
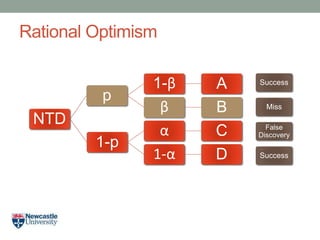
- 17. Rational Optimism NTD p 1-Îē A Îē B 1-p Îą C 1-Îą D Success Miss False Discovery Success
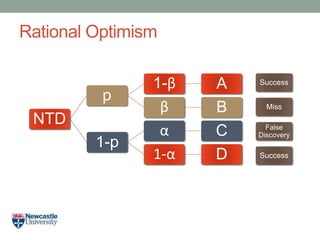
- 18. Rational Optimism NTD p 1-Îē A Îē B 1-p Îą C 1-Îą D Success Miss False Discovery Success
- 19. Rational Optimism âĒ Opportunity Costs: Loss due to false negatives = B NTD p 1-Îē A Îē B 1-p Îą C 1-Îą D Success Miss False Discovery Success
- 20. Rational Optimism âĒ Opportunity Costs: Loss due to false negatives = B Loss due to false positives = C NTD p 1-Îē A Îē B 1-p Îą C 1-Îą D Success Miss False Discovery Success
- 21. Rational Optimism âĒ Opportunity Costs: Loss due to false negatives = B Loss due to false positives = CxA NTD p 1-Îē A Îē B 1-p Îą C 1-Îą D Success Miss False Discovery Success
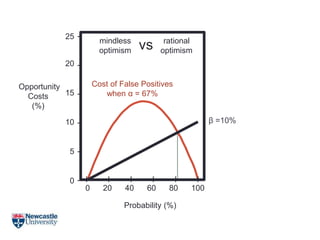
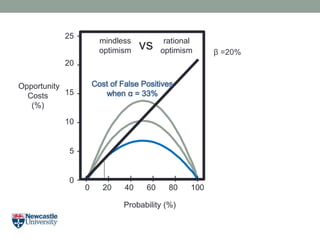
- 22. Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I Cost of False Positives when Îą = 67% Îē =10% mindless optimism rational optimismvs
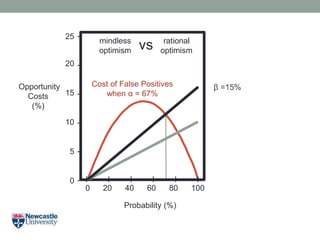
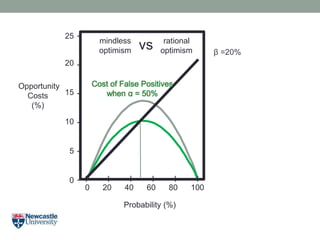
- 23. Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I Îē =15%Cost of False Positives when Îą = 67% mindless optimism rational optimismvs
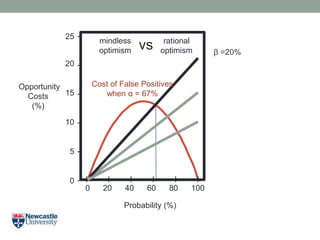
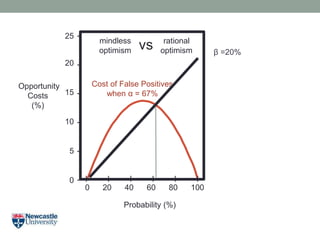
- 24. Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I mindless optimism rational optimism Îē =20% Cost of False Positives when Îą = 67% vs
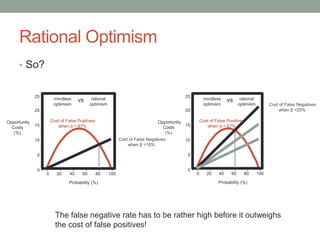
- 25. Rational Optimism âĒ So? Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I Cost of False Positives when Îą = 67% Cost of False Negatives when Îē =10% mindless optimism rational optimism vs Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I mindless optimism rational optimism Cost of False Negatives when Îē =20% Cost of False Positives when Îą = 67% vs The false negative rate has to be rather high before it outweighs the cost of false positives!
- 26. Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I Îē =20% Cost of False Positives when Îą = 67% mindless optimism rational optimismvs
- 27. Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I Îē =20% mindless optimism rational optimismvs
- 28. Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I Îē =20% mindless optimism rational optimismvs
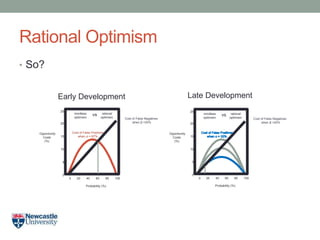
- 29. Rational Optimism âĒ So? Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I Cost of False Negatives when Îē =20% Cost of False Positives when Îą = 67% mindless optimism rational optimism vs Opportunity Costs (%) Probability (%) 20 15 10 5 0 25 - - - - - - 0 20 40 60 80 100 I I I I I I Cost of False Negatives when Îē =20% mindless optimism rational optimism vs Early Development Late Development
- 30. Rational Optimism âĒ So? âĒ We fear false negatives, but the opportunity costs of false positives are huge. âĒ Terminating projects frees up R&D resources to pursue other prospects. âĒ Thinking about opportunity costs allows project teams to reframe termination decisions as prospective future gains.
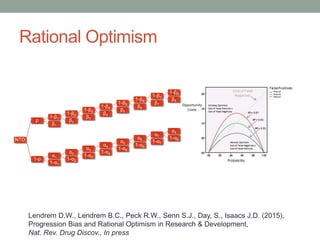
- 31. Rational Optimism Lendrem D.W., Lendrem B.C., Peck R.W., Senn S.J., Day, S., Isaacs J.D. (2015), Progression Bias and Rational Optimism in Research & Development, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., In press NTD p 1-Îē1 1-Îē2 1-Îē3 1-Îē4 1-Îē5 1-Îē6 1-Îē7 1-Îē8 Îē8 Îē7 Îē6 Îē5 Îē4 Îē3 Îē2 Îē1 1-p Îą1 Îą2 Îą3 Îą4 Îą5 Îą6 Îą7 Îą8 1-Îą8 1-Îą7 1-Îą6 1-Îą5 1-Îą4 1-Îą3 1-Îą2 1-Îą1
- 32. Rational Optimism âĒ Richard Peck (Roche) âĒ Stephen Senn (CRP SantÃĐ) âĒ Simon Day (MHRA) âĒ John Isaacs (MRG) âĒ John Loughlin (MRG) NIHR Newcastle BRC
- 33. Rational Optimism âĒ Richard Peck (Roche) âĒ Stephen Senn (CRP SantÃĐ) âĒ Simon Day (MHRA) âĒ John Isaacs (MRG) âĒ John Loughlin (MRG) âĒ Clare Lendrem (AHG) NIHR Newcastle BRC
- 34. fin
Editor's Notes
- #8: As a result, the industry became really slick at delivering late-stage failures to the market place, precipitating the current R&D productivity crisis.
- #9: As a result, the industry became really slick at delivering late-stage failures to the market place, precipitating the current R&D productivity crisis.
- #11: 10