RDBMS
- 1. ∫›∫›fl£ Title
- 2. GROUP 3 ÔÉò Aqsa Rafique ÔÉòAyesha Qayyum ÔÉòNoor-us-Subah ÔÉòMaria Batool ÔÉòSidra Iftikhar ÔÉòMaham Zahid
- 3. BS(SOFTWARE ENGINEERING) GROUP-2 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE FAISALABAD 1
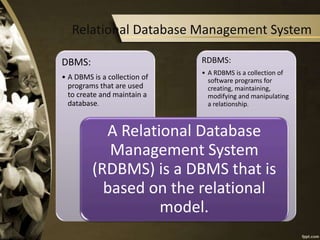
- 5. Relational Database Management System RDBMS: • A RDBMS is a collection of software programs for creating, maintaining, modifying and manipulating a relationship. DBMS: • A DBMS is a collection of programs that are used to create and maintain a database. A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a DBMS that is based on the relational model.
- 6. COMPONENTS  COMPONENTS OF RDBMS 1. File Manager 2. Database Manager 3. Query Processor 4. Data Dictionary 5. DML Pre-compiler 6. DDL Compiler
- 7. Types of Relations 1.Base Tables 2. Query Results 3. Views
- 8. BASE TABLE Reg. No Roll No Name Class 2013-ag-1411 1 Amer Palwasha BS 2013-ag-2301 2 Abdul Rafy BS 2011-ag-7369 3 Ameer Hamza MS
- 9. QUERY RESULTS Name Class Amer Palwasha BS Abdul Rafy BS SELECT Name FROM student WHERE class=‘BS’
- 10. VIEWS Reg. No Name 2013-ag-1411 Amer Palwasha 2013-ag-2301 Abdul Rafy 2011-ag-7369 Ameer Hamza  VIEWS
- 11. Relational Data Integrity Data Integrity means reliability and accuracy of data. DBMS provides several mechanism to enforce integrity of the data in a column. Data integrity falls into following categories: Entity Integrity Domain Integrity Referential Integrity
- 12. CONTIUNE…  Entity Integrity  Entity integrity means it should be easy to identify each entity in the database.  An entity is any thing like an object, subject or event represented in the database.  Domain Integrity  A set of values that can be stored in a column is called a DOMAIN.  Domain Integrity enforces restriction on the values entered in a column.  It specify the validity of a specific data entry in a column.
- 13. CONTINUE…  REFERENTIAL INTEGRITY  referential integrity preserves the defined relationship between tables when records are added or deleted.  It ensures that key values are consistent across the table.
- 14. REFERENTIAL INTEGRITY MASTER TABLE Reg. No. Name class 2013-ag-1411 Amer Palwasha BS 2013-ag-2301 Abdul Rafy BS 2011-ag-6988 Ameer Hamza MS CHILD TABLE Reg. No. Subjects Marks 2013-ag-1411 DBMS 82 2013-ag-1411 OOP 77 2013-ag-2301 DBMS 91 2013-ag-2301 OOP 88 2011-ag-6988 DBMS 78 201-ag-6988 OOP 80
- 15. DATABASE LANGUAGES ÔÉò Data Definition Language (DDL) ÔÉò Data Manipulation Language (DML) These languages are called data sub-languages. Many DBMSs provide the facility to embed the sub-language in a high level programming Language like C++, Java and Visual Basic etc. In this situation, the high level language is called HOST language.
- 16. DDL Data Definition Language (DDL) statements are used to define the database structure or schema. Some examples: • CREATE - to create objects in the database • ALTER - alters the structure of the database • DROP - delete objects from the database • TRUNCATE - remove all records from a table including all spaces allocated for the records are removed • COMMENT - add comments to the data dictionary • RENAME - rename an object
- 17. DML Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements are used for managing data within schema objects. Some examples: • SELECT - retrieve data from the a database • INSERT - insert data into a table • UPDATE - updates existing data within a table • DELETE - deletes all records from a table, the space for the records remain • MERGE - UPSERT operation (insert or update) • CALL - call a PL/SQL or Java subprogram • EXPLAIN PLAN - explain access path to data • LOCK TABLE - control concurrency
- 18. PROPERTIES ÔÉò Atomic Values in Fields ÔÉò Entries From Same Domain ÔÉò Unique Tuples ÔÉò Unique Attribute Name ÔÉò Insignificant Attribute Sequence ÔÉò Insignificant Tuple Sequence
- 19. ADVANTAGES OF RDBMS ÔÉò Increases the sharing of data and faster development of new applications ÔÉò Support a simple data structure, namely tables or relations ÔÉò Limit redundancy or replication of data ÔÉò Provide physical data independence so users do not have to be aware of underlying objects ÔÉò Expandability is relatively easy to achieve by adding new views of the data as they are required. ÔÉò Better backup and recovery procedures ÔÉò Solves many problems created by other data models ÔÉò The ability to handle efficiently simple data types ÔÉò Multiple users can access which is not possible
- 20. DISADVANTAGES OF RDBMS ÔÉòSoftware is complex ÔÉòComplex software means expensive hardware ÔÉòRequires skilled knowledge to implement ÔÉòCertain applications are slower processing ÔÉòMore difficult to recover if data is lost ÔÉòDifficult to represent complex data types
- 21. .
- 22. Edgar Frank Ted Codd E.F.Codd was an English Computer scientist who while working for IBM, Invented the relational model for DBMS.
- 23. Codd’s Rule  Rule 1: The Information Rule  Rule 2: the Guaranteed Access Rule  Rule 3: Systematic Treatment of NULL values  Rule 4: Active online catalog Base don the Relational Model  Rule 5: Comprehensive Data Sub-language Rule Rule 6: View Updating Rule
- 24. CONTINUE…  Rule 7: High Level Insert, Update and Delete  Rule 8: Physical Data Independence Rule  RULE 9:Logical Data Independence Rule  Rule 10: Integrity Independence Rule  Rule 11: Distribution Independence Rule  Non-Subversion Rule