Reading Comprehension
- 1. By: Karl Joshua E. Jumoc BEED-I S.Y. â12-â13
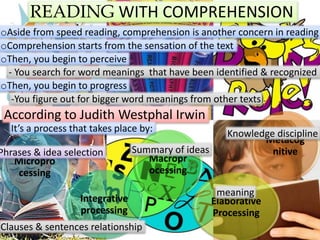
- 2. READING WITH COMPREHENSION oAside from speed reading, comprehension is another concern in reading oComprehension starts from the sensation of the text oThen, you begin to perceive - You search for word meanings that have been identified & recognized oThen, you begin to progress -You figure out for bigger word meanings from other texts According to Judith Westphal Irwin Itâs a process that takes place by: Micropro cessing Integrative processing Macropr ocessing Elaborative Processing Metacog nitivePhrases & idea selection Clauses & sentences relationship Summary of ideas meaning Knowledge discipline
- 3. continuation Comprehension is affected by your; ïžEmotional State ïžExperience ïžPrevious knowledge ïžLanguage competencies Comprehension is also considered as a; Bottom-up view Interactive view Top-Down view Comprehension comes to you & you derive appreciation of the tex Corresponds to microprocessing, integrative & macroprocessing Comes from your previous experience & knowledge Corresponds to elaborative processing Interaction of bottom-up & top-down view Corresponds to all processes
- 4. STEPS TOWARDS COMPREHENSION Suggested for comprehension tasks 1. Scanning unfamiliar words & overcoming problems in meaning about them Encountering strange words & difficulty in comprehending Scan for them & overcome your blocked words Some suggestions are helpful like; ïžConsulting the dictionary ïžTaking a clue from context ïžTaking a clue from word structures ï§ familiarizes denotative or literal word meaning ï§ given in bits & pieces of information ï§ have several meaning levels Example: cause (koz) n. 1. The power or efficient agent producing any thing 2. Any occasion/condition upon occurrence 3. Law An action or suit,also, a ground of action 4.Obs. Behalf; interest 5. Philos. The object for which anything is done
- 5. ïžtaking a clue from context continuation ï§ text surrounding the problem world ï§ text may give definitions, examples, re-statements, synonyms or antonyms that can give meaning Examples: The Philippines is an archipelago, a group of islands surrounding by water An amphibian like a frog, toad, newt or salamander has smooth skin One of the components of a national territory is the fluvial & maritime domain or the external & internal waters While Narcisa is a natural glibber, her young sister Ana is an introvert Definition Context Clue Example Context Clue Re-Statement Context Clue Synonym Context Clue Antonym Context Clue Life is naturally ambivalent. Sometimes it is serene; sometimes itâs turbulent
- 6. ïžtaking a clue from the structure of the word ï§Words are deciphered for their meaning from their structure of root & affix ï§Knowing the meaning of the root or base which may be a prefix/suffix PREFIXES & MEANING Mono â 1 Il â bad Neo â new Di â 2 Mal â bad Para â beside Tri-3 Un â not Extra â outside Tetra â 4 Im â not Inter â within Penta â 5 Sub â secondary Circum â around Hexa â 6 Anti â against Pre â before Hepta â 7 Contra â against Pro â for Octa â 8 Auto â self Con â with Nona â 9 Micro â small Demi â half Deca â10 Macro - big Semi - half c.1
- 7. WORD FORMATIONS Monometer â monogram - monologue - monosyllable Diameter â disect â dialouge - dichotomy Trimeter â triangle â trilogy - triumvirate Tetrameter â tetragram â tetralogy - tetragon Pentameter â pentagram â pentacle - pentad Hexameter â hexagram â hexachord - hexad Heptameter â heptagram â heptachord â heptad Octameter â octagon â octachord â octangle Decameter â decagram - decahedron â decade Illegal â illicit â illogical - illegible Malnourished â malfunction â malpractice â malady Unfair â unfit â uncertain â unconscious Immature â imperfect â immortal â improper Subplot â subway - subsequent - subconscious
- 8. Semifinal â semicircle â semiconductor - semicolon antidote â antifungal â antibiotic - antiseptic Contraband â contradict â contraceptive â contravene Automobile â autograph â autobiography â autobus Microscope â microwave â microeconomics â microcosm Macrograph â macrospecies â macroeconomics â macrocosm Neophyte â neology â neonatal â neoclassic Parasite â parameter â paraphase â paralegal Extralegal â extrapolate â extracurricular â extraneous Interpersonal â interfere â internation â intercommune Circumstance â circumference â circumnavigate â circumlocution Premature â pretest â predestined â prenatal Probate â prolong â provoke â promotion Concur â conspire â constrict â contract Demivolt â demigod â demiwolf - demitasse
- 9. SUFFIXES & MEANING Er, or, ist for action verbs Ment , ance, ence, ion for abstract nouns Able for adjectives Ity for abstract nouns c.2 WORD FORMATIONS Enjoy â enjoyment procure â procurement require â requirement Encourage â encouragement enlarge â enlargement Govern â governance endure â endurance deliver â deliverance Deliver â deliverance persevere â perseverance import - importance Repentance â repentance interfere â interference refer â reference Deter â deterence confer â conference predict â prediction Correlate â correlation infuse â infusion profuse â profusion Direct â direction subtract - subtraction
- 10. Bank â bankable wash â washable plastic -plasticity Perish â perishable manage â manageable work â workable Read â readable mature â maturity pure â purity Secure â security effective â effectivity elastic - elasticity continuation 2. Getting the Literal meaning 3. Getting the Connotative meaning