Recent prehistory, chart
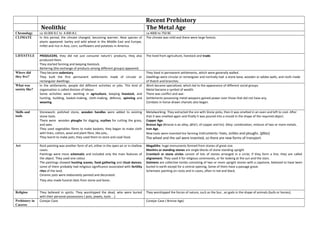
- 1. Recent Prehistory Neolithic The Metal Age Chronology ca 10.000 B.C to 4.000 B.C ca 4000 to 750 BC CLIMATE In this period, the climate changed, becoming warmer. New species of plants appeared: barley and wild wheat in the Middle East and Europe, millet and rice in Asia, corn, sunflowers and potatoes in America. The climate was mild and there were large forests. LIFESTYLE PRODUCERS, they did not just consume nature’s products, they also produced them. They started farming and keeping livestock. Bartering (the exchange of products among different groups) appeared. The lived off agriculture, livestock and trade. Where did they live? They became sedentary. They built the first permanent settlements made of circular or rectangular dwellings. They lived in permanent settlements, which were generally walled. Dwellings were circular or rectangular and normally had a stone base, wooden or adobe walls, and roofs made of thatch and branches. What was society like? In the settlements, people did different activities or jobs. This kind of organisation is called division of labour. Some activities were: working in agriculture, keeping livestock, and hunting, building, basket-making, cloth-making, defence, spinning and weaving. Work became specialized, which led to the appearance of different social groups. Metal became a symbol of wealth. There was conflict and war. Settlements possessing metal weapons gained power over those that did not have any. Combats in horse-drawn chariots also began. Skills and tools Stonework: polished stone, wooden handles were added to existing stone tools. There were wooden ploughs for tilling the land, scythes for cutting the grass, and axes. They used vegetables fibres to weave baskets; they began to make cloth with linen, cotton, wool and plant fibre, like jute,. They learnt to make pots; they used them to store and cook food. Metalworking: They extracted the ore with Stone picks, then it was smelted in an oven and left to cool. After that it was smelted again and finally it was poured into a mould in the shape of the required object. Copper Age. Bronze Age (Bronze is an alloy, (ăl′oi′), of copper and tin). Alloy: combination, mixture of two or more metals. Iron Age. New tools were invented liKe farming instruments: hoes, sickles and ploughs. (plou) The wheel and the sail were invented, so there are new forms of transport. Art Rock painting was another form of art, either in the open air or in shallow caves. Paintings were more schematic and included only the main features of the object. They used one colour The paintings showed hunting scenes, food gathering and ritual dances; some of them probably had religious significance associated with fertility rites of the land. Ceramic pots were elaborately painted and decorated. They also made funeral idols from stone and bone. Megaliths: huge monuments formed with stones of great size. Menhirs or standing stones are single blocks of stone standing upright Cromlech or stone circles consist of lots of stones arranged in a circle; if they form a line, they are called alignement. They used it for religious ceremonies, or for looking at the sun and the stars. Dolmens are collective tombs consisting of two or more upright stones with a capstone, believed to have been buried in earth except for a central opening. Some of them have a passage grave. Schematic painting on rocks and in caves, often in red and black. Religion They believed in spirits. They worshipped the dead, who were buried with their personal possessions ( pots, jewels, tools…) They worshipped the forces of nature, such as the Sun , and gods in the shape of animals (bulls or horses). Prehistory in Caceres Conejar Cave Conejar Cave ( Bronze Age)